Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
Artif Intell Med Imaging. Sep 8, 2025; 6(2): 108032
Published online Sep 8, 2025. doi: 10.35711/aimi.v6.i2.108032
Published online Sep 8, 2025. doi: 10.35711/aimi.v6.i2.108032
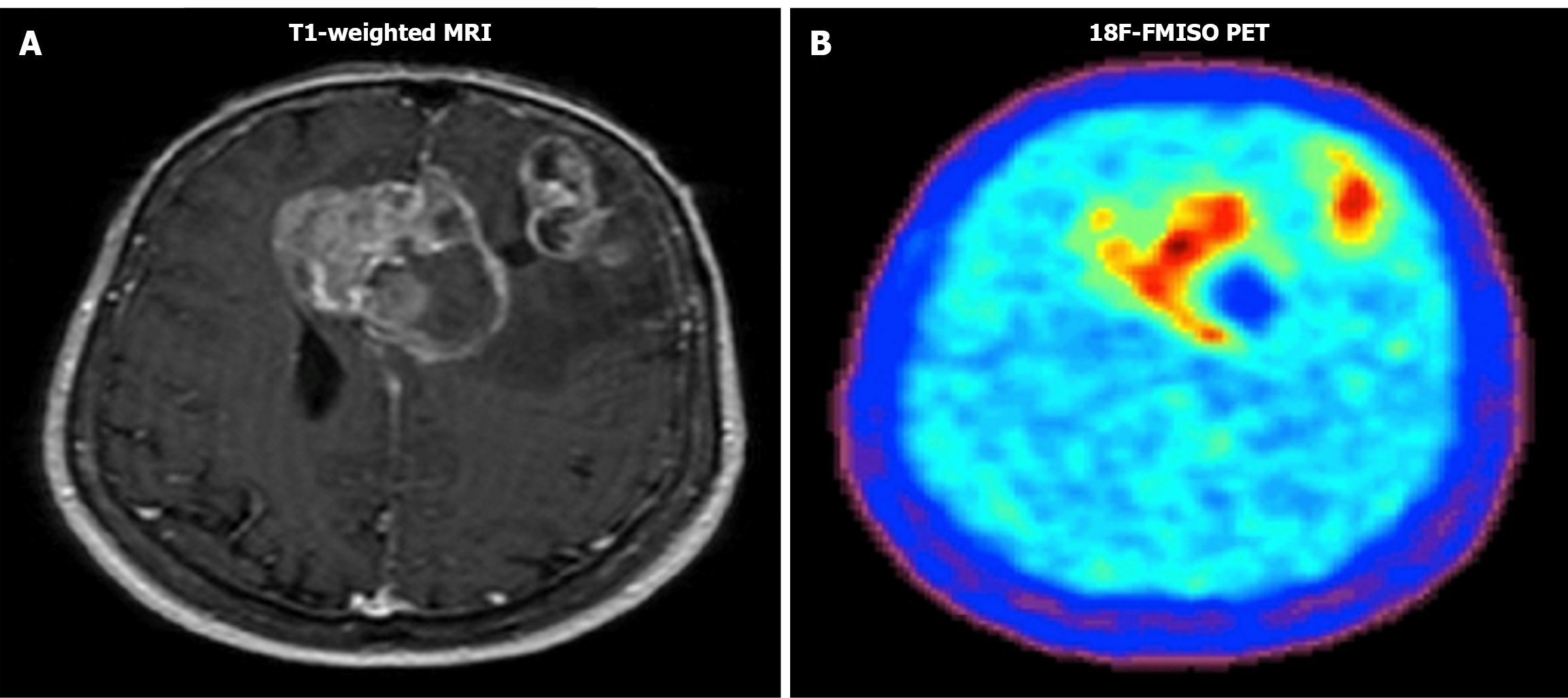
Figure 1 Example of Tl-weighted magnetic resonance imaging image and 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography image.
Both images show the tumor and the necrosis. A: Magnetic resonance imaging image; B: 18F-fluoromisonidazole positron emission tomography image.
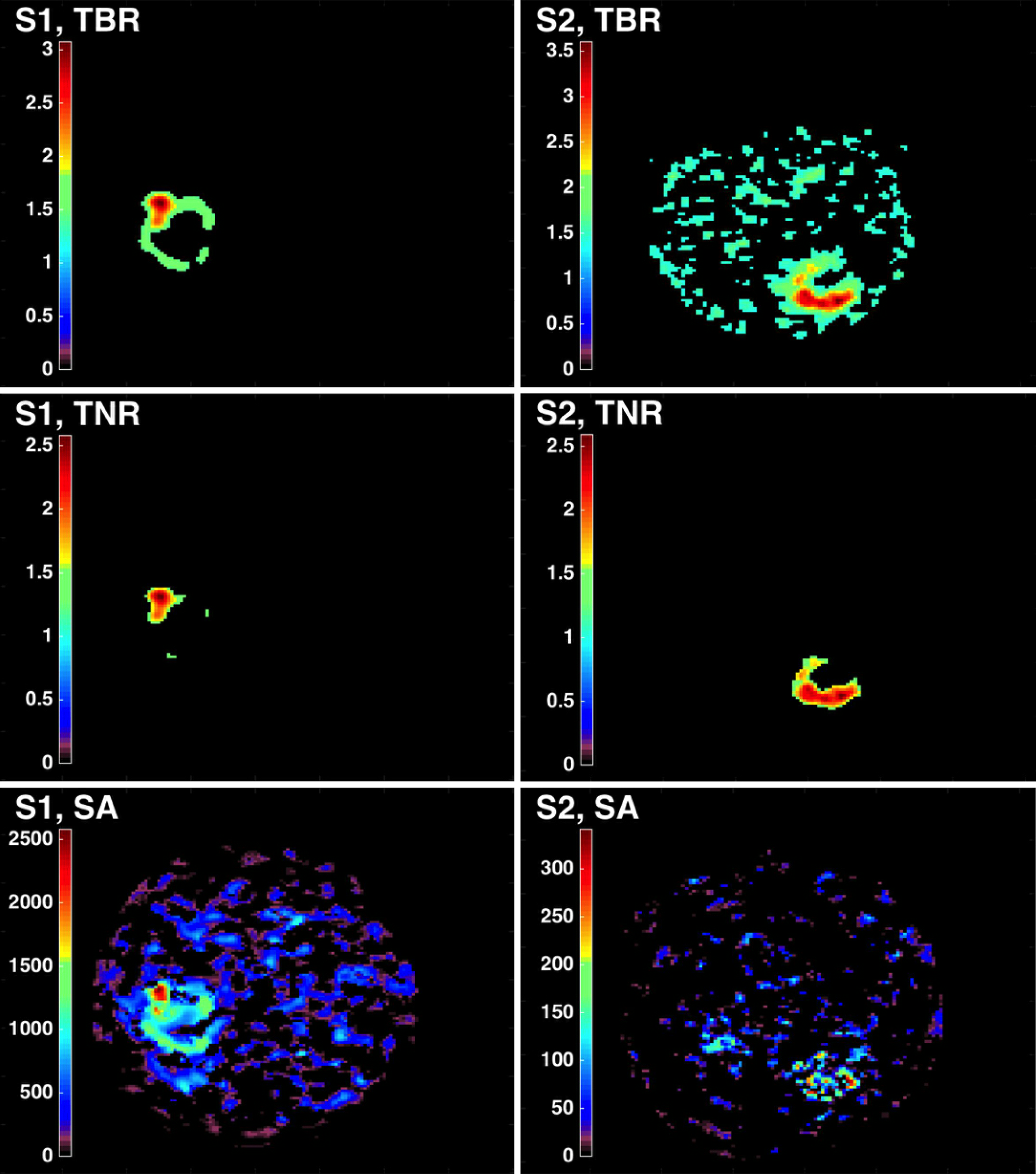
Figure 2 Tumor-to-blood ratio, tumor-to-reference tissue ratio and spectral analysis images for two subjects S1 and S2 scanned with and 18F-fluoromisonidazole at 3 hours post-injection.
Since tumor-to-blood ratio depends on the precision of the blood function, hypoxia delimitation was not always clearly defined in comparison to tumor-to-reference tissue ratio which was able to isolate the high intensity tumor pixels from the background. Spectral analysis still depends on the selected exponentials forming the tumor including noisy pixels[87]. TBR: Tumor-to-blood ratio; TNR: Tumor-to-reference tissue ratio; SA: Spectral analysis.
- Citation: Bentourkia M, Abdo RA. Updates on glioblastoma multiforme: From epidemiology to imaging and artificial intelligence. Artif Intell Med Imaging 2025; 6(2): 108032
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2644-3260/full/v6/i2/108032.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.35711/aimi.v6.i2.108032