Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Methodol. Dec 26, 2017; 7(4): 139-147
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.139
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.139
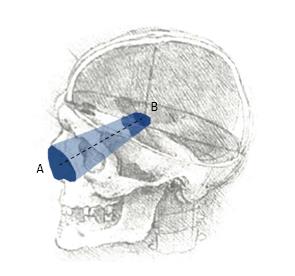
Figure 1 Schematic description of a surgical approach, as a “truncated pyramid”[4,5]: (1) Superficial surface (A), more commonly defined “surgical window” or “access area”; it represents the area through which instruments are introduced to work at the level of the deep area; (2) deep surface (B), usually defined “area of exposure”, as it is the surface exposed by the approach; and (3) height of the truncated pyramid (dotted line).
Volume and trajectory of this pyramid complete the essential anatomical definition of a neurosurgical approach. Background head image is from: Studies of human skull, Leonardo Da Vinci, supplied by Royal Collection Trust ©Her Majesty Queen Elizabeth II 2016.
- Citation: Doglietto F, Qiu J, Ravichandiran M, Radovanovic I, Belotti F, Agur A, Zadeh G, Fontanella MM, Kucharczyk W, Gentili F. Quantitative comparison of cranial approaches in the anatomy laboratory: A neuronavigation based research method. World J Methodol 2017; 7(4): 139-147
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v7/i4/139.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.139