Published online Jul 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.319
Peer-review started: February 4, 2022
First decision: April 11, 2022
Revised: April 26, 2022
Accepted: July 11, 2022
Article in press: July 11, 2022
Published online: July 20, 2022
Processing time: 165 Days and 12.9 Hours
Metoclopramide may be used to treat people suffering from acute migraine. However, no comprehensive investigation on this issue has been recorded. This review will provide more solid evidence for the use of metoclopramide in treating acute migraine.
To compare the efficacy of intravenous metoclopramide with other therapies in migraine attack treatment in an emergency department (ED).
We included randomized controlled trials of participants older than 18 years with acute migraine headaches, which included at least one arm that received intravenous (IV) metoclopramide at the ED. A literature search of PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Collaboration, and Reference Citation Analysis on December 31, 2021 retrieved other drugs or placebo-controlled studies without language limitation. The risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane risk of bias tool. The primary endpoint was pain reduction at 60 min or closest to 1 h after treatment, as measured by the pain scale. Secondary endpoints included adverse effects or reactions resulting from metoclopramide or comparisons.
Fourteen trials with a total of 1661 individuals were eligible for review. The risk of bias ranged from low to intermediate. IV metoclopramide administration was not associated with higher pain reduction at 1 h (Standard mean difference [SMD] = -0.03, 95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.33-0.28, P = 0.87). However, metoclopramide was associated with better pain reduction than placebo (SMD = 1.04, 95%CI: 0.50-1.58, P = 0.0002). In addition, side effects were not significantly different between IV metoclopramide and other drugs or placebo (odds ratio [OR] = 0.76, 95%CI: 0.48-1.19, P = 0.09 and OR = 0.92, 95%CI: 0.31-2.74, P = 0.54, respectively).
Metoclopramide is more effective than placebo in treating migraine in the ED. Despite the observed tendency of decreased side effects, its effectiveness compared to other regimens is poorly understood. More research on this area is needed to treat migraine in acute care settings effectively.
Core Tip: Metoclopramide may be used to treat people suffering from acute migraine. However, no comprehensive investigation on this issue has been recorded. We conducted an up-to-date systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical efficacy of metoclopramide during an acute migraine attack. This study comprised 14 studies and found that metoclopramide was more effective than placebo in treating migraine at the emergency department. When compared to other medications, however, no substantial advantage was detected. More study is needed to enhance migraine therapy in acute care settings effectively.
- Citation: Ungrungseesopon N, Wongtanasarasin W. Pain reduction and adverse effects of intravenous metoclopramide for acute migraine attack: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials. World J Methodol 2022; 12(4): 319-330
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v12/i4/319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.319
Migraine, a chronic neurological disease, is one of the most common causes that lead patients to seek medical attention[1]. Apart from regular follow-up at the outpatient department, many patients with migraine suffer from acute migraine attacks requiring an emergency department (ED) visit. There were approximately 1.2 million annual ED visits for acute migraine headaches in the United States[2]. At the same time, persons who suffer from this illness frequently encounter several other accompanying symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and sensitivity to light, sound, touch, or scent[3,4]. Unfortunately, its pathogenesis remains complicated and little understood. As a result, if such a problem cannot be effectively treated, it significantly impacts the health-related quality of life of individuals suffering from acute migraine[5,6].
According to the American Headache Society recommendations, several acute migraine treatments include triptans, ergotamine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, combination analgesic, and anti-emetics[7]. Metoclopramide, an anti-emetic drug acting as a dopamine/serotonin antagonist, was initially used in migraine patients who experienced nauseating symptoms[8]. Later, it was shown to be effective in pain control of acute migraine attacks[9,10]. In the recent recommendation, metoclopramide was considered the “probably effective drug,” even though several studies showed the efficacy of metoclopramide monotherapy. It has been investigated that the efficacy of metoclopramide was neither inferior to sumatriptan nor opioids[11,12].
Moreover, apart from the efficacy aspect, metoclopramide showed superiority in other aspects, such as lower adverse severe effects and lower addiction rates which are considered an essential issue in the ED as patients with migraine tend to revisit. It is undeniable that metoclopramide might not be the first choice for clinicians to use in acute migraine as its efficacy might not be outstanding compared to other drugs. As prior mentioned, the severe side effects of metoclopramide, which are extrapyramidal symptoms, such as tardive dyskinesia and akathisia, though rarely reported in short term use and less worrisome than those of triptans and opioids, should also be concerned as they might result in an irreversible and sufferable experience for the patient[11].
To comprehend the big picture of using metoclopramide in acute care for migraine, this study aimed to compare metoclopramide use with other therapy in migraine attack treatment in an acute care setting. Our study hypothesized that metoclopramide monotherapy should effectively treat acute migraine attacks in an ED.
We conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses statement guidelines[13]. We prospectively registered our protocol with the International prospective register of systematic reviews (ID: CRD42022322609).
We (N.U. and W.W.) independently searched four standard databases, PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane Collaboration, and Reference Citation Analysis, from their inception until December 31, 2021, without language restriction. The search words “metoclopramide,” “Meclopran,” “Plasil,” “Reglan,” “methoxyprocainamide,” “migraine,” and “headache” were the Medical Subject Headings used, in combination and with different spellings and endings. We also searched websites, organizations, relevant reviews, grey literature, and references to identify additional eligible studies. Additionally, we searched for any unpublished trials registered on the “clinicaltrials.gov” Internet site.
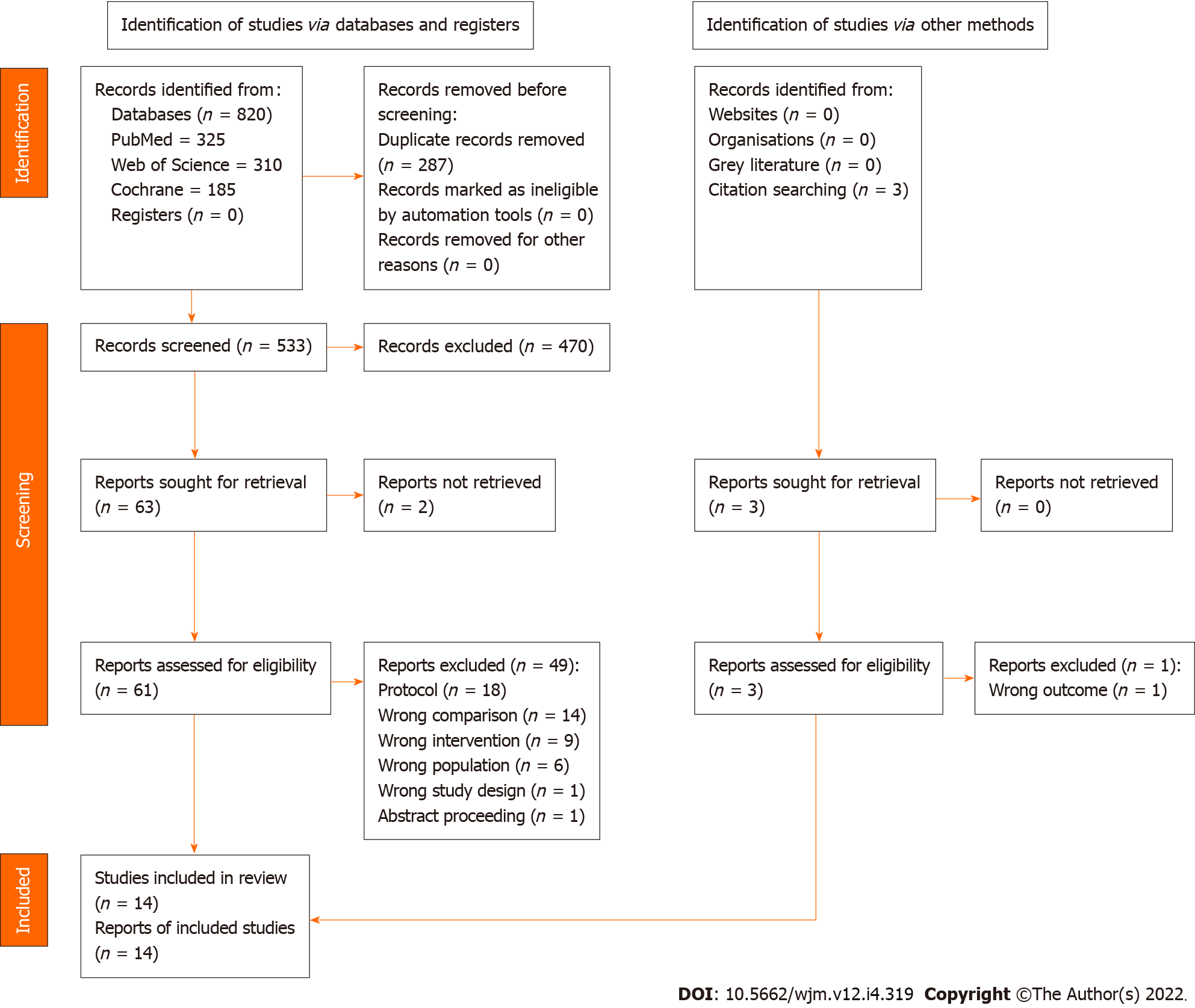
The selection criteria were as follows: (1) Randomized controlled trials including adults more than 18 years of age with acute migraine headaches, regardless of their types (i.e., with or without aura); (2) at least one arm having received an intravenous (IV) metoclopramide during ED stay; (3) comparing of at least one agent or placebo; (4) reporting of average pain scale before the administration of each agent; and (5) reporting of at least one of the following: Pain scale at 60 or other minutes, any adverse effects, and rescue medications needed at the ED. We excluded pre-clinical studies, review articles, and studies without a control group (e.g., case reports and case series). The two authors (N.U. and W.W.) independently screened the search results to identify eligible studies. Full-text articles of the retrieved studies were retrieved and independently assessed by the two authors against the pre-specified criteria (Figure 1). Any discrepancies were discussed with a third party and concluded by consensus.
The primary endpoint was pain reduction at 60 min or closest to 1 h after treatment administration, as measured by the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) or others. Secondary endpoints included adverse effects or reactions resulting from metoclopramide or interventions. Adverse effects in this study were defined by any of the following symptoms: Upper gastrointestinal complaints (dyspepsia, heartburn, and bloating), allergic reaction, dizziness, drowsiness, nasal congestion, dry mouth, dystonic reaction, akathisia, and significant blood pressure drop.
We separately extracted the data from the included articles using a prepared data extraction form. Specifically, we extracted basic characteristics (first author, publication year, study location and setting, and number and age of participants), treatment details and interventions in the study groups, and the outcomes of interest. We sought to contact the associated author by email for incomplete or missing data or clarification. The two authors (N.U. and W.W.) independently assessed the risk of study bias using the latest version of the Cochrane Collaboration tool for assessing the trial risk of bias[14]. Any disagreements were handled through discussion with the assistance of a third independent expert.
The data was imported into pre-formatted record forms. We calculated individuals and pooled estimates as standard mean differences (SMDs) for continuous endpoints, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We calculated individuals and pooled estimates using odds ratios (ORs) with CIs for dichotomous endpoints. We estimated heterogeneity among the included studies using the I2 statistic (the percentage of total variation across studies due to heterogeneity). We applied a fixed-effect model if the heterogeneity was minor (I2 ≤ 50%). However, if there was evidence of strong heterogeneity (I2 > 50%), a random-effect model was employed instead. Visual assessment of funnel plots and Egger’s test were used to assess publication bias caused by small-study effects. For statistical analyses, we applied RevMan version 5.3 (Nordic Cochrane Center, Cochrane Collaboration, 2014, Copenhagen, Denmark)[15]. All tests were two-tailed, and P values < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Figure 1 demonstrates how the 820 retrieved articles were screened for inclusion in the review and analysis. After excluding duplicated studies, 533 remained. Of those, 470 were excluded following title and abstract screening according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The remaining 63 articles were retrieved and reviewed for full-text copies before including 12 studies in the data analysis. In addition, three articles were also searched by citation searching, and two articles met the pre-specified criteria. Finally, 14 articles[10,16-28] with 1661 participants were included in the meta-analysis.
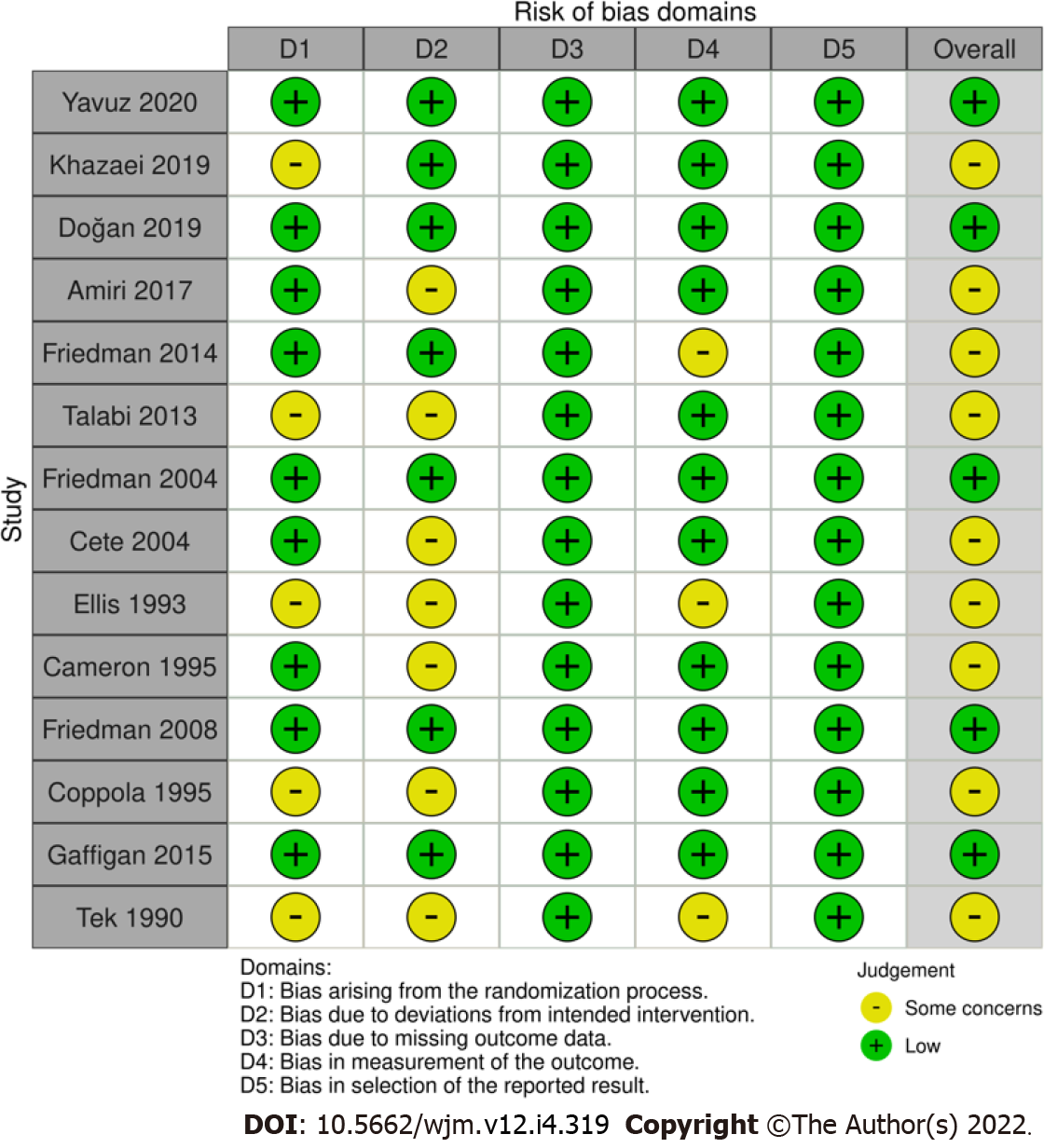
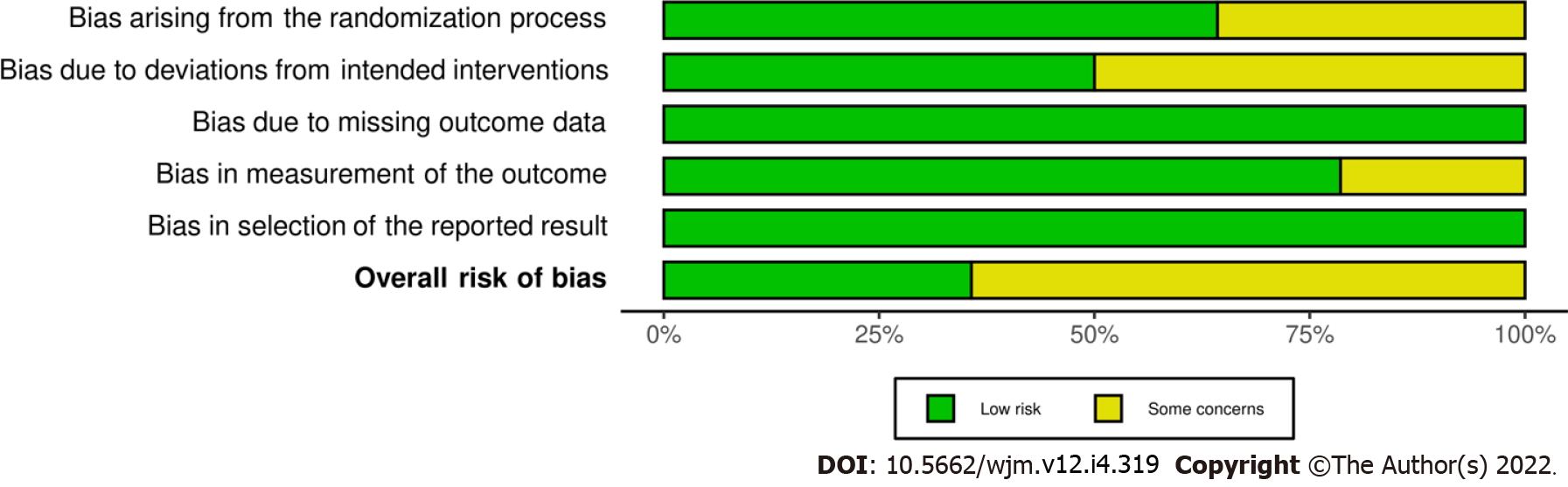
Data extraction and meta-analysis were performed on 14 papers published between 1990 and 2020. The research was carried out in the United States of America (n = 7), Turkey (n = 3), and Iran (n = 4). The mean ages were around 34-40 years. Most studies applied 10 mg of IV metoclopramide, while three administered 20 mg of metoclopramide as interventions. Five trials investigated the efficacy of IV metoclopramide against placebo. Most studies compared more than one arm. All trials reported pain intensity at 0 and other minutes after drug administration, as VAS or other appropriate methods. Table 1 summarizes the baseline demographics and clinical characteristics of the included studies. Deviation from the intended interventions and randomization contributed to a high proportion of concerns over risk of bias. Five out of fourteen had an overall low risk of bias. The risk of bias assessment by Cochrane risk of bias assessment is illustrated in Figures 2 and 3.
| Ref. | Age, year | Intervention | Comparisons | Sample size (intervention/comparisons) | Outcomes of interest |
| Yavuz et al[16], 2020, Turkey | 36.8 ± 11.4 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV dexketoprofen trometamol 50 mg; 2 IV dexketoprofen trometamol 50 mg plus IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 150 (50/50/50) | VAS at 0, 15, and 30 min, adverse effects, and requirement of rescue medicine |
| Khazaei et al[17], 2019, Iran | 36.8 ± 9.9 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV dexamethasone 8 mg; 2 IV ketorolac 30 mg; 3 IV chlorpromazine 25 mg | 128 (32/32/32/32) | VAS at 0 min, 60 min, and 24 h, adverse effects |
| Doğan et al[18], 2019, Turkey | 34 ± 13.3 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 Placebo | 148 (74/74) | Pain intensity at 30 min, adverse effects, and requirement of rescue analgesicChange in pain intensity, additional ED visit in 24-72 h after discharge |
| Amiri et al[19], 2017, Iran | 33.5 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV granisetron 2 mg | 148 (73/75) | VAS before and at 1, 2, and 4 h after drug administration, emesis episode |
| Friedman et al[20], 2014, USA | 33.7 ± 13.1 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV sodium valproate 1000 mg; 2 IV ketorolac 30 mg | 330 (110/110/110) | Verbal NRS and ordinal pain scale every 30 min, adverse effects, and requirement of rescue medication |
| Talabi et al[21], 2013, Iran | 30.9 ± 8.0 | IV metoclopramide 20 mg | 1 SC sumatriptan 6 mg | 124 (62/62) | VAS at 0 and 60 min |
| Friedman et al[22], 2004, Turkey | 34 ± 4.4 | IV metoclopramide 20 mg | 1 SC sumatriptan 6 mg | 78 (40/38) | NRS at 0, 2, and 24 h, and rate of pain free headache response at 2 and 24 h, rate of modified headache response, associated symptoms, satisfaction, disability score, and requirement for rescue drug |
| Cete et al[10], 2004, Iran | 40 ± 12 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV magnesium sulphate 2 g; 2 Placebo | 113 (37/36/40) | VAS at 0, 15, and 30 min, additional analgesic, rescue medication, adverse events in ED, and recurrence rate at 24 h |
| Ellis et al[23], 1993, USA | N/A | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 Oral ibuprofen 600 mg; 2 IV metoclopramide 10 mg + PO ibuprofen 600 mg; 3 Placebo | 40 (10/10/10/10) | VAS and nausea scores at 0, 30, and 60 min, requirement of rescue medication |
| Cameron et al[24], 1995, USA | 32.1 ± 27.0 | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV chlorpromazine 0.1 mg/kg | 91 (44/47) | VAS at 0 and every 15 min, requirement of rescue drug |
| Friedman et al[25], 2008, USA | 36.0 ± 11.1 | IV diphenhydramine 25 mg + IV metoclopramide 20 mg | 1 IV diphenhydramine 25 mg + IV prochlorperazine 10 mg | 77 (38/39) | NRS and pain intensity categorical scale at 0 and every 30 min |
| Coppola et al[26], 1995, USA | N/A | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV chlorpromazine 10 mg; 2 Placebo | 70 (24/22/24) | VAS, nausea, and sedation at 0 and 30 min. Early relapse rate in 48 h |
| Gaffigan et al[27], 2015, USA | 29 ± 7.9 | IV diphenhydramine 25 mg + IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 IV diphenhydramine 25 mg + IV haloperidol 5 mg | 64 (33/31) | Pain, nausea, restlessness, and sedation at 0, 20, 40, 60, and 80 min, requirement of rescue medication, patient satisfaction, adverse events, early discharge, ED revisit, and QT interval |
| Tek et al[28], 1990, USA | N/A | IV metoclopramide 10 mg | 1 Placebo | 50 (24/26) | Degree of pain relief at 1 h after treatment |
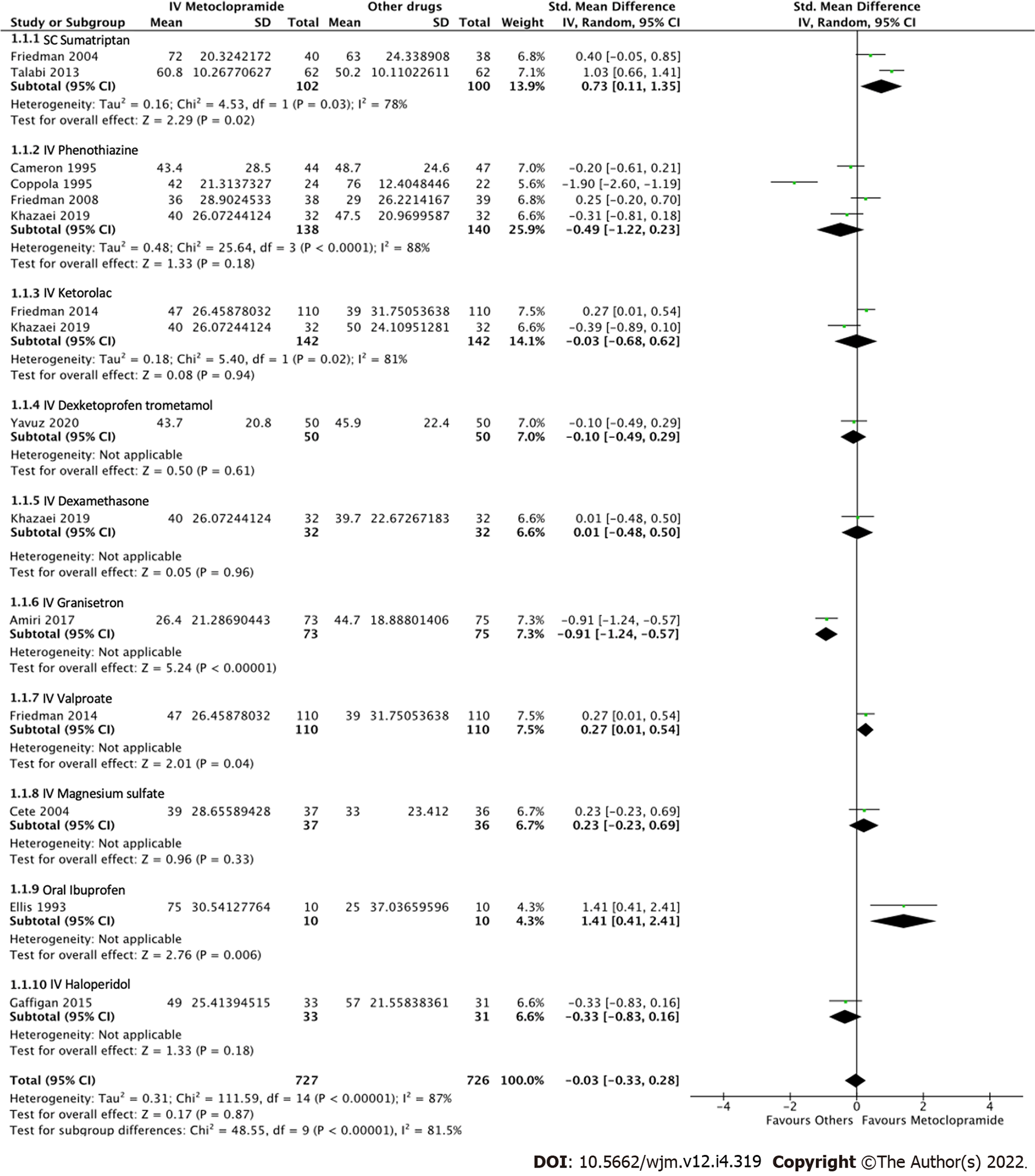
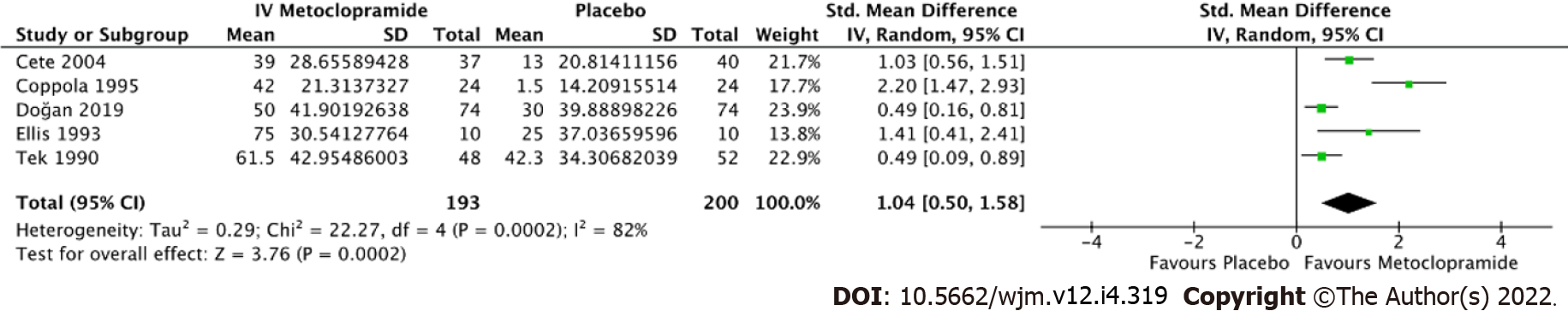
All 14 studies reported average pain reduction at 60 min or at the time closest to 1 h. The overall effect size showed no statistical significance with regard to the efficacy between IV metoclopramide and other drugs (SMD = -0.03, 95%CI: -0.33-0.28, P = 0.87). However, IV metoclopramide demonstrated a significant pain reduction compared with placebo (SMD = 1.04, 95%CI: 0.50-1.58, P = 0.0002). Subgroup analyses found that IV metoclopramide had a significant advantage in pain reduction compared with subcutaneous sumatriptan (SMD = 0.73, 95%CI: 0.11-1.35, P = 0.03), IV valproate (SMD = 0.27, 95%CI: 0.01-0.54, P = 0.04), and oral ibuprofen (SMD = 1.41, 95%CI: 0.41-2.41, P = 0.006). Heterogeneity was observed among the subgroups comparing IV metoclopramide and other drugs (I2 = 81.5%, P < 0.0001; Figure 4). Figures 4 and 5 demonstrate the forest plot comparing pain reduction at 60 min between IV metoclopramide and other drugs and placebo, respectively.
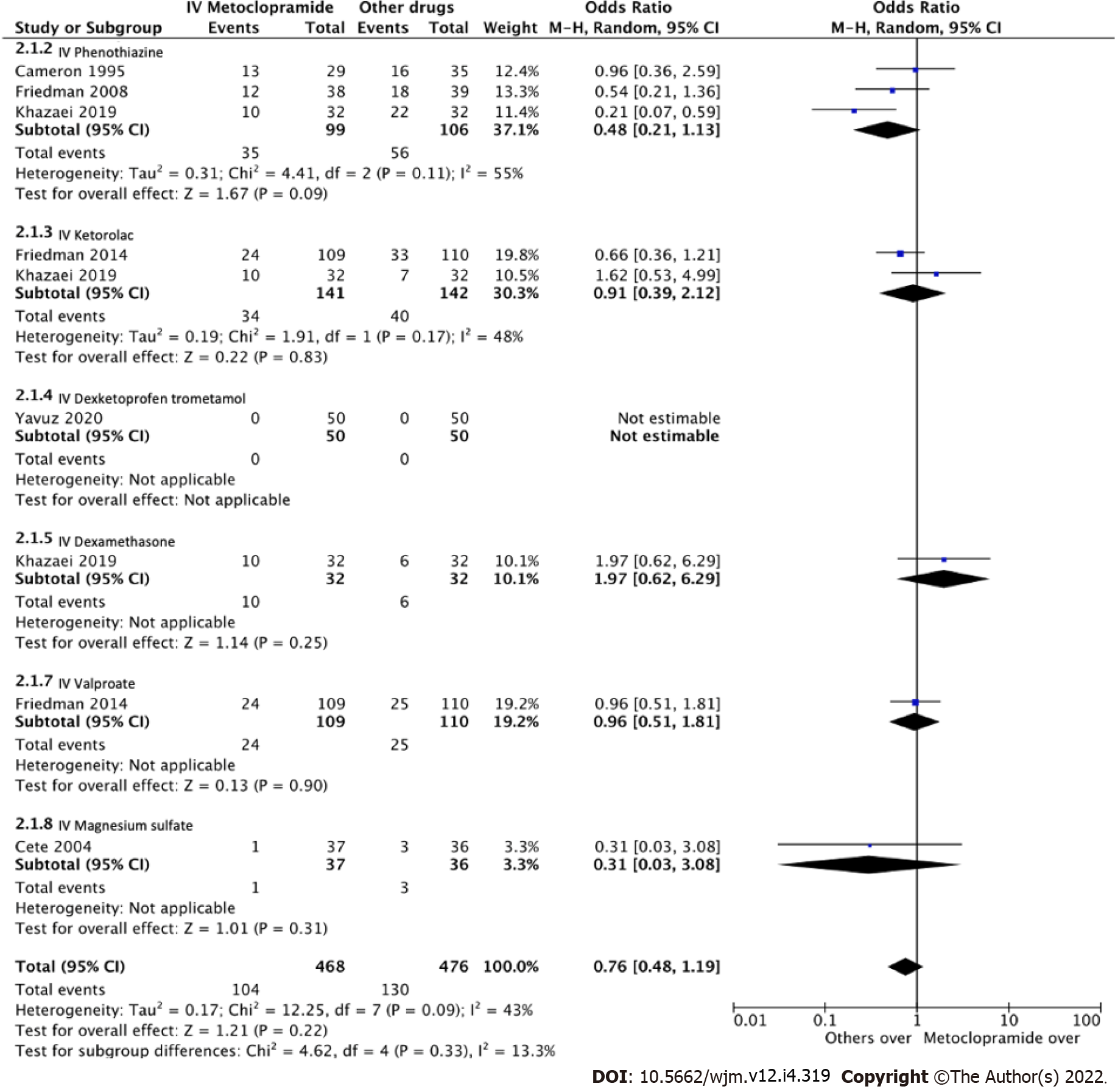
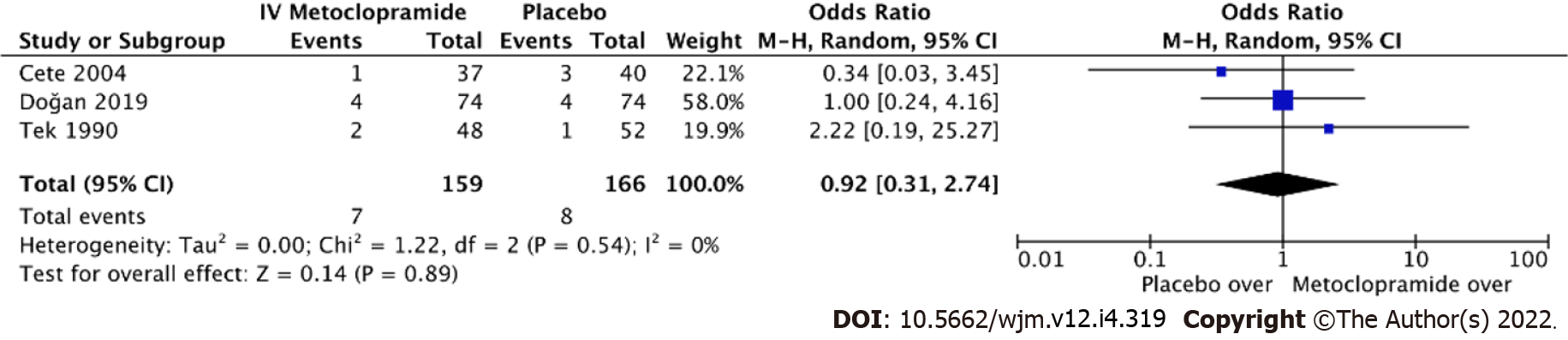
Eight studies measured adverse effects across IV metoclopramide and comparisons. The pooled effect size was homogenous both compared with others (I2 = 13.3%, P = 0.33; Figure 6) and with placebo (I2 = 0%, P = 0.89; Figure 7). Adverse effects were not different across IV metoclopramide and other comparisons (OR = 0.76, 95%CI: 0.48-1.19, P = 0.09) or placebo (OR = 0.92, 95%CI: 0.31-2.74, P = 0.54). Subgroup analyses yielded similar results for all comparisons (Figure 6).
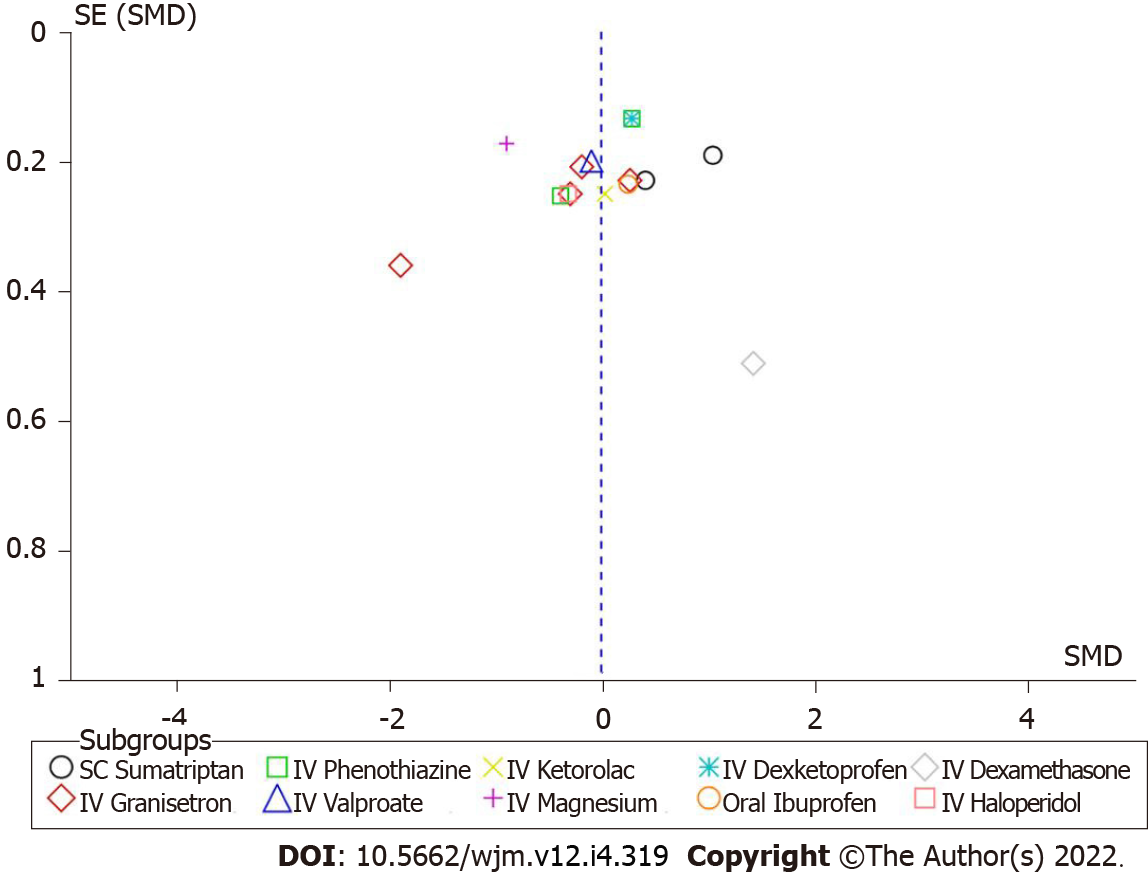
There was no substantial publication bias in the funnel plot for the meta-analysis of the average pain reduction between IV metoclopramide and comparisons (Figure 8). The regression-based Egger’s test was performed using a random-effect model with restricted maximum-likelihood method and found that P value was 0.0814.
This meta-analysis investigated the clinical efficacy of IV metoclopramide for treating acute migraine attacks in the ED. This study showed that administration of IV metoclopramide was an effective treatment for migraine headache in adults, compared with placebo. However, the benefit of metoclopramide was not superior to other drugs. Our systematic review also demonstrated that IV metoclopramide tended to have fewer side effects than other interventions. The overall study risk of bias ranged from low to some concerns.
Acute migraine is a common neurovascular disorder. It is described as a moderate to severe, predominantly unilateral, and recurrent headache that lasts for several hours to a few days[3,29]. Metoclopramide is initially used to treat acute migraine for decades[11]. A few studies over the years have highlighted that metoclopramide has substantial therapeutic effectiveness in treating acute migraine episodes[26,30]. The reason behind the use of metoclopramide could be that it antagonizes the dopamine D2 receptor, which is proposed to be one of the pathogeneses of pain in migraine[11]. A meta-analysis of pooled data illustrated that metoclopramide significantly reduced headache pain, and those patients were less likely to rescue medicines than the placebo groups[3]. However, the authors chose various inclusion and exclusion criteria for this study, which may contain data on non-migraine headaches, confounding any conclusions to be derived[3]. Furthermore, metoclopramide also had an anti-emetic effect that ameliorates migraine patients’ symptoms[11]. Therefore, metoclopramide could be a first-line treatment for acute migraine episodes. Our findings are consistent with the prior research finding that metoclopramide was more effective than placebo in pain reduction[9]. In addition, metoclopramide had a higher benefit than some drugs in our analysis (subcutaneous sumatriptan, intravenous valproate, and oral ibuprofen). These findings fit with the pattern described previously by Colman et al[9]. However, that study selected both ED and headache clinic settings, which differed from ours. Besides, Colman and colleagues analyzed the pain using a complete relief of headache or significant reduction in headache pain. As a result, discrepancies were likely to occur across that definition. Our study provided the difference aiming to close this gap. We compared all studies based on the pre- and post-intervention mean pain intensity in each study, which is more feasible to apply and compare.
However, the side effects of metoclopramide might be serious and irreversible, for example, tardive dyskinesia. It is characterized by the uncontrollable movement of the tongue, face, and extremities. Nonetheless, our findings reveal that the adverse effects resulting from metoclopramide were not different across the other drugs. Results obtained by Orr and colleagues[31] are consistent with our findings. Moreover, compared to other suggested therapies, metoclopramide’s adverse effect profile is less concerning than triptans, which are commonly utilized in ED situations[32,33].
This review contains some limitations. First, all included studies were conducted in only three countries, including Iran, United States, and Turkey, which possibly resulted in the generalizability bias. Secondly, most trials did not report exclusion criteria in sufficient detail; therefore, the definitions for migraine might be varied among studies. In addition, several studies did not report the confirmation of migraine diagnosis, duration of headache, and prior therapies. As a result, we probably combined studies with varying patient characteristics, making it difficult to determine if our findings are generalizable to other contexts. Finally, this meta-analysis included studies done at different dates (between 1990 and 2020), resulting in the observed heterogeneity.
To conclude, metoclopramide was proven to be beneficial to treating migraine in the acute care setting, such as in the ED, compared to placebo. Despite the demonstrated trend of a lower adverse effect, its efficacy compared to other regimens is little comprehended. More studies on this topic should be further conducted to improve migraine treatment in acute care settings effectively.
Metoclopramide may be used to treat people suffering from acute migraine. However, no comprehensive investigation on this issue has been recorded. This review will provide more solid evidence for the use of metoclopramide in treating acute migraine.
Metoclopramide was considered the “probably effective drug”, even though several studies showed the efficacy of metoclopramide monotherapy. It has been investigated that the efficacy of metoclopramide was neither inferior to sumatriptan nor opioid. Moreover, apart from the efficacy aspect, metoclopramide showed superiority in other aspects, such as lower adverse severe effects and lower addiction rates.
The objective of this review was to investigate the efficacy of intravenous metoclopramide with other therapies in migraine attack treatment in an emergency department (ED).
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.
The administration of received intravenous metoclopramide was an effective treatment for migraine headache in adults, compared with placebo. However, the benefit of metoclopramide was not superior to other drugs.
Metoclopramide is more effective than placebo in treating migraine in the ED. Although its effectiveness was not observed on other medications, clinicians may select metoclopramide as one of the first line treatments for acute migraine.
Despite the observed tendency of decreased side effects, the effectiveness of metoclopramide compared to other regimens is poorly understood. More research on this area is needed to treat migraine in acute care settings effectively.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Emergency medicine
Country/Territory of origin: Thailand
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Patoulias D, Greece; Shibata Y, Japan A-Editor: Yao QG, China S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Friedman BW, Hochberg ML, Esses D, Grosberg B, Corbo J, Toosi B, Meyer RH, Bijur PE, Lipton RB, Gallagher EJ. Applying the International Classification of Headache Disorders to the emergency department: an assessment of reproducibility and the frequency with which a unique diagnosis can be assigned to every acute headache presentation. Ann Emerg Med. 2007;49:409-419, 419.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 76] [Cited by in RCA: 77] [Article Influence: 4.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Friedman BW, West J, Vinson DR, Minen MT, Restivo A, Gallagher EJ. Current management of migraine in US emergency departments: an analysis of the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey. Cephalalgia. 2015;35:301-309. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Charles A. Migraine. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:553-561. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 4. | Valade D. Early treatment of acute migraine: new evidence of benefits. Cephalalgia. 2009;29 Suppl 3:15-21. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Steiner TJ, Stovner LJ, Jensen R, Uluduz D, Katsarava Z; Lifting The Burden: the Global Campaign against Headache. Migraine remains second among the world's causes of disability, and first among young women: findings from GBD2019. J Headache Pain. 2020;21:137. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 122] [Cited by in RCA: 511] [Article Influence: 102.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Saylor D, Steiner TJ. The Global Burden of Headache. Semin Neurol. 2018;38:182-190. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 98] [Cited by in RCA: 184] [Article Influence: 26.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Ailani J, Burch RC, Robbins MS; Board of Directors of the American Headache Society. The American Headache Society Consensus Statement: Update on integrating new migraine treatments into clinical practice. Headache. 2021;61:1021-1039. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 356] [Cited by in RCA: 404] [Article Influence: 101.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Eken C. Critical reappraisal of intravenous metoclopramide in migraine attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33:331-337. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 27] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Colman I, Brown MD, Innes GD, Grafstein E, Roberts TE, Rowe BH. Parenteral metoclopramide for acute migraine: meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ. 2004;329:1369-1373. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 134] [Cited by in RCA: 123] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Cete Y, Dora B, Ertan C, Ozdemir C, Oktay C. A randomized prospective placebo-controlled study of intravenous magnesium sulphate vs. metoclopramide in the management of acute migraine attacks in the Emergency Department. Cephalalgia. 2005;25:199-204. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 72] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 8.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Najjar M, Hall T, Estupinan B. Metoclopramide for Acute Migraine Treatment in the Emergency Department: An Effective Alternative to Opioids. Cureus. 2017;9:e1181. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Funato Y, Kimura A, Matsuda W, Uemura T, Fukano K, Kobayashi K, Sasaki R. Metoclopramide versus sumatriptan in the treatment of migraine in the emergency department: a single-center, open-label, cluster-randomized controlled non-inferiority trial. Glob Health Med. 2020;2:259-262. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan SE, Chou R, Glanville J, Grimshaw JM, Hróbjartsson A, Lalu MM, Li T, Loder EW, Mayo-Wilson E, McDonald S, McGuinness LA, Stewart LA, Thomas J, Tricco AC, Welch VA, Whiting P, Moher D. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;134:178-189. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 312] [Cited by in RCA: 1308] [Article Influence: 327.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 14. | Higgins JP, Savović J, Page MJ, Sterne JAC. Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2) Full Guidance Document. Br Med J 2019; 1–72. Available from: https://methods.cochrane.org/bias/resources/rob-2-revised-cochrane-risk-bias-tool-randomized-trials. |
| 15. | Review Manager (RevMan) [Computer program]. 2014. |
| 16. | Yavuz E, Gulacti U, Lok U, Turgut K. Intravenous metoclopramide versus dexketoprofen trometamol versus metoclopramide+ dexketoprofen trometamol in acute migraine attack in the emergency department: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:2254-2258. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Khazaei M, Hosseini Nejad Mir N, Yadranji Aghdam F, Taheri M, Ghafouri-Fard S. Effectiveness of intravenous dexamethasone, metoclopramide, ketorolac, and chlorpromazine for pain relief and prevention of recurrence in the migraine headache: a prospective double-blind randomized clinical trial. Neurol Sci. 2019;40:1029-1033. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Doğan NÖ, Pekdemir M, Yılmaz S, Yaka E, Karadaş A, Durmuş U, Avcu N, Koçkan E. Intravenous metoclopramide in the treatment of acute migraines: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Acta Neurol Scand. 2019;139:334-339. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Amiri H, Ghodrati N, Nikuyeh M, Shams-Vahdati S, Jalilzadeh-Binazar M. Comparison of granisetron and metoclopramide in the treatment of pain and emesis in migraine patients: A randomized controlled trial study. Turk J Emerg Med. 2017;17:61-64. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Friedman BW, Garber L, Yoon A, Solorzano C, Wollowitz A, Esses D, Bijur PE, Gallagher EJ. Randomized trial of IV valproate vs metoclopramide vs ketorolac for acute migraine. Neurology. 2014;82:976-983. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 57] [Cited by in RCA: 60] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Talabi S, Masoumi B, Azizkhani R, Esmailian M. Metoclopramide versus sumatriptan for treatment of migraine headache: A randomized clinical trial. J Res Med Sci. 2013;18:695-698. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Friedman BW, Corbo J, Lipton RB, Bijur PE, Esses D, Solorzano C, Gallagher EJ. A trial of metoclopramide vs sumatriptan for the emergency department treatment of migraines. Neurology. 2005;64:463-468. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 99] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Ellis GL, Delaney J, DeHart DA, Owens A. The efficacy of metoclopramide in the treatment of migraine headache. Ann Emerg Med. 1993;22:191-195. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 83] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Cameron JD, Lane PL, Speechley M. Intravenous chlorpromazine vs intravenous metoclopramide in acute migraine headache. Acad Emerg Med. 1995;2:597-602. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 69] [Cited by in RCA: 69] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Friedman BW, Esses D, Solorzano C, Dua N, Greenwald P, Radulescu R, Chang E, Hochberg M, Campbell C, Aghera A, Valentin T, Paternoster J, Bijur P, Lipton RB, Gallagher EJ. A randomized controlled trial of prochlorperazine versus metoclopramide for treatment of acute migraine. Ann Emerg Med. 2008;52:399-406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 68] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Coppola M, Yealy DM, Leibold RA. Randomized, placebo-controlled evaluation of prochlorperazine versus metoclopramide for emergency department treatment of migraine headache. Ann Emerg Med. 1995;26:541-546. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 158] [Cited by in RCA: 151] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Gaffigan ME, Bruner DI, Wason C, Pritchard A, Frumkin K. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Intravenous Haloperidol vs. Intravenous Metoclopramide for Acute Migraine Therapy in the Emergency Department. J Emerg Med. 2015;49:326-334. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Tek DS, McClellan DS, Olshaker JS, Allen CL, Arthur DC. A prospective, double-blind study of metoclopramide hydrochloride for the control of migraine in the emergency department. Ann Emerg Med. 1990;19:1083-1087. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 95] [Cited by in RCA: 90] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Lipton RB, Nicholson RA, Reed ML, Araujo AB, Jaffe DH, Faries DE, Buse DC, Shapiro RE, Ashina S, Cambron-Mellott MJ, Rowland JC, Pearlman EM. Diagnosis, consultation, treatment, and impact of migraine in the US: Results of the OVERCOME (US) study. Headache. 2022;62:122-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 76] [Article Influence: 25.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Friedman BW, Mulvey L, Esses D, Solorzano C, Paternoster J, Lipton RB, Gallagher EJ. Metoclopramide for acute migraine: a dose-finding randomized clinical trial. Ann Emerg Med. 2011;57:475-82.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 48] [Article Influence: 3.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Orr SL, Friedman BW, Christie S, Minen MT, Bamford C, Kelley NE, Tepper D. Management of Adults With Acute Migraine in the Emergency Department: The American Headache Society Evidence Assessment of Parenteral Pharmacotherapies. Headache. 2016;56:911-940. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 155] [Cited by in RCA: 147] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Chalaupka FD. Acute myocardial infarction with sumatriptan: a case report and review of the literature. Headache. 2009;49:762-764. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Jensen C, Riddle M. ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction After Sumitriptan Ingestion in Patient with Normal Coronary Arteries. West J Emerg Med. 2015;16:781-783. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |