Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Methodol. Sep 26, 2017; 7(3): 101-107
Published online Sep 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i3.101
Published online Sep 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i3.101
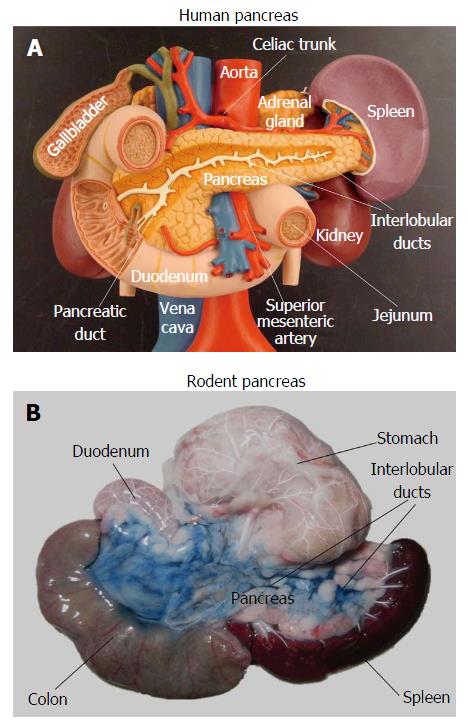
Figure 1 Anatomical difference between human and rodent pancreas.
Unlike the human pancreas which is a well-defined solid organ (A), the rat pancreas appears as a soft, diffuse and irregularly lobulated organ (B), which is very difficult to discern from surrounding tissues even at open abdominal surgery. To better visualize it, the pancreatic ductal system was infused with Evans blue dye while the arterial system was injected with a barium sulphate suspension.
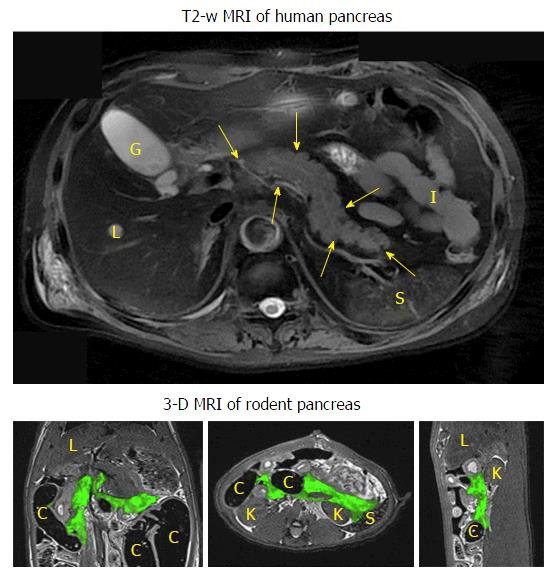
Figure 2 Typical human pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging vs rodent pancreatic magnetic resonance imaging.
The upper transverse image shows the human pancreas (contoured by arrowheads) as a solid organ adjacent to the liver (L), gallbladder (G), spleen (S), kidney (K) and small intestines (I). The lower 3-D images display the coronal (left), transverse (mid) and sagittal (right) views of the contrast-infused rat pancreas with green color coding, adjacent to the liver (L), spleen (S), kidney (K) and colon (C). MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Yin T, Liu Y, Peeters R, Feng Y, Ni Y. Pancreatic imaging: Current status of clinical practices and small animal studies. World J Methodol 2017; 7(3): 101-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v7/i3/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v7.i3.101