Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Methodol. Dec 26, 2015; 5(4): 216-222
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v5.i4.216
Published online Dec 26, 2015. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v5.i4.216
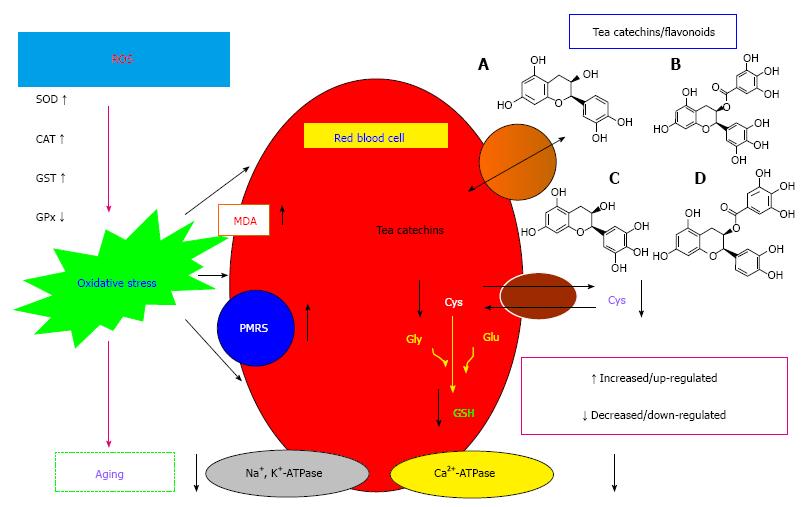
Figure 1 Aerobic cell produce reactive oxygen species as a byproduct of cellular respiration.
Erythrocytes are equipped with antioxidant defense system for overcome excess production of ROS. The activity of SOD, CAT, GST and PMRS is upregulated while GPx activity is down regulated during human aging. Increased oxidative stress during aging results in elevated MDA levels and decreased GSH levels. Cysteine influx and efflux decreases during aging, which is an important amino acid for GSH biosynthesis. Red blood cell membrane bound enzymes (Na+, K+-ATPase; Ca2+-ATPase) activity decreases as a function of human age. Dietary flavonoids like tea catechins modulate various biomarkers of oxidative stress and are protective in nature. Chemical structures of epicatechin (A), epigallocatechin gallate (B), epigallocatechin (C), and epicatechin gallate (D). Cys: Cysteine; Glu: Glutamic acid; Gly: Glycine; GSH: Reduced gluathione; GSSG: Oxidised glutathione; MDA: Malonaldehyde; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CAT: Catalase; GST: Glutathione-S-transferase; GPx: Glutathione peroxidase; PMRS: Plasma membrane redox system; ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
- Citation: Maurya PK, Kumar P, Chandra P. Biomarkers of oxidative stress in erythrocytes as a function of human age. World J Methodol 2015; 5(4): 216-222
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v5/i4/216.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v5.i4.216