Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Methodol. Mar 20, 2024; 14(1): 88518
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.88518
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.88518
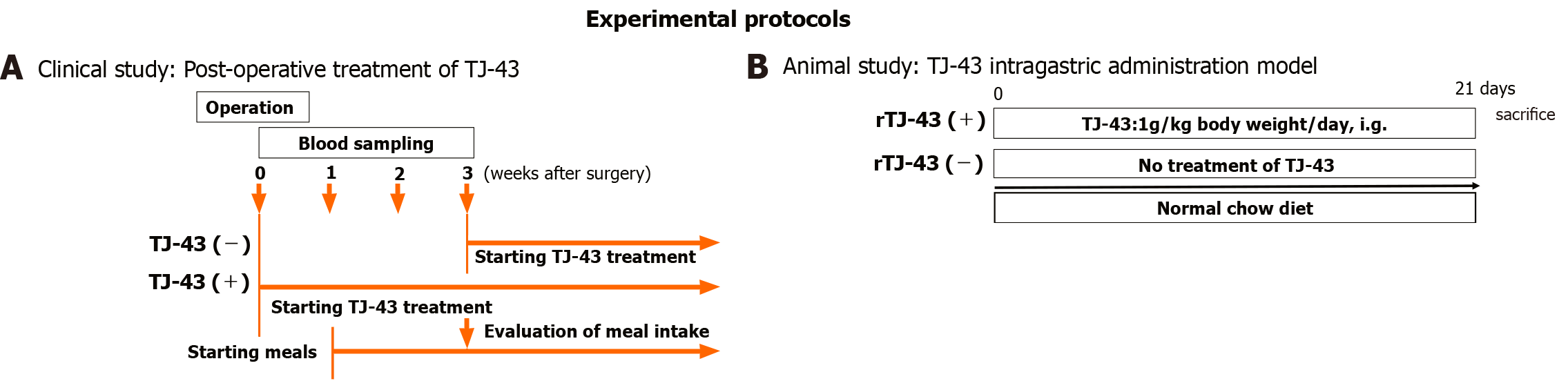
Figure 1 Experimental protocols.
A: Clinical study; B: Animal study. Rikkunshito (TJ-43); TJ-43(-), patients without TJ-43 treatment; and TJ43(+), patients with TJ-43 treatment; rTJ-43(-), and rats without TJ-43 treatment; rTJ43(+), rats with TJ-43 treatment; and i.g.; intragastric administration. TJ-43: Rikkunshito.
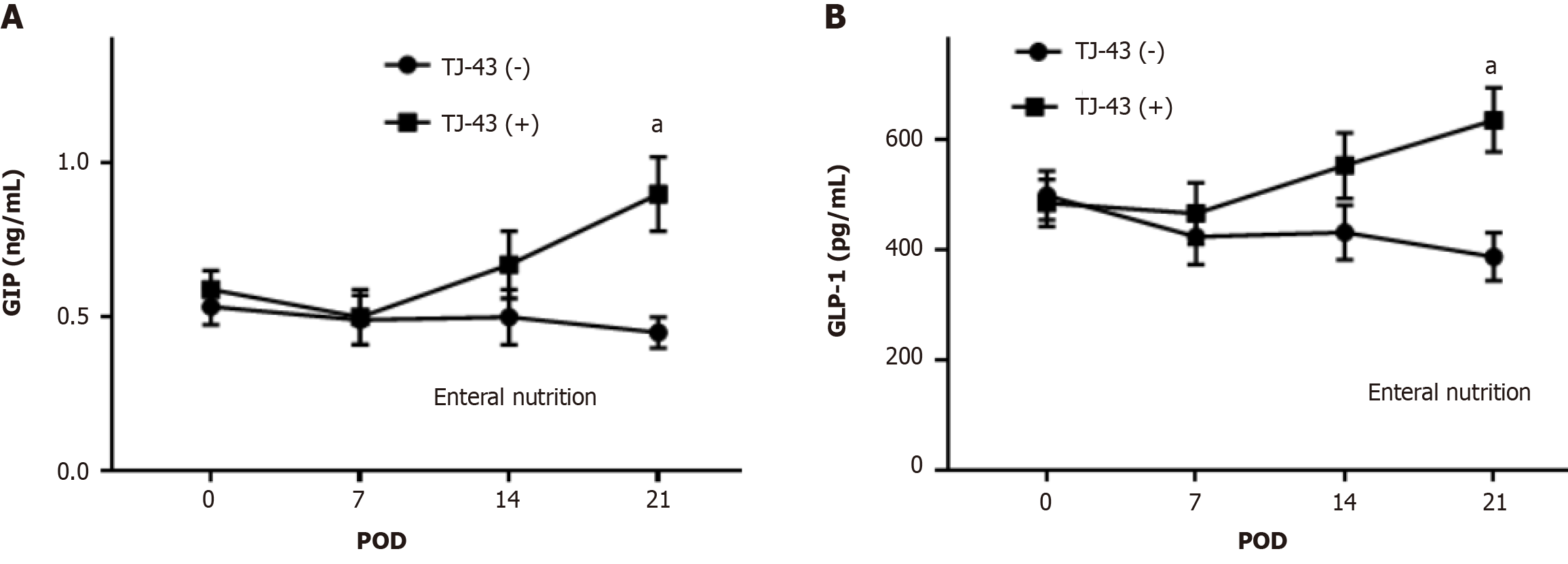
Figure 2 Effects of rikkunshito on plasma incretin levels.
A and B: Plasma levels of (A): Gastric inhibitory peptide; and (B): Glucagon-like polypeptide-1 were measured by ELISA. Rikkunshito (TJ-43); TJ-43(−), patients without TJ-43 treatment; and TJ43(+), patients with TJ-43 treatment. aP < 0.05 compared with the TJ-43(−) group by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. TJ-43: Rikkunshito; GIP: Gastric inhibitory peptide; GLP-1: Glucagon-like polypeptide-1; POD: Postoperative day.
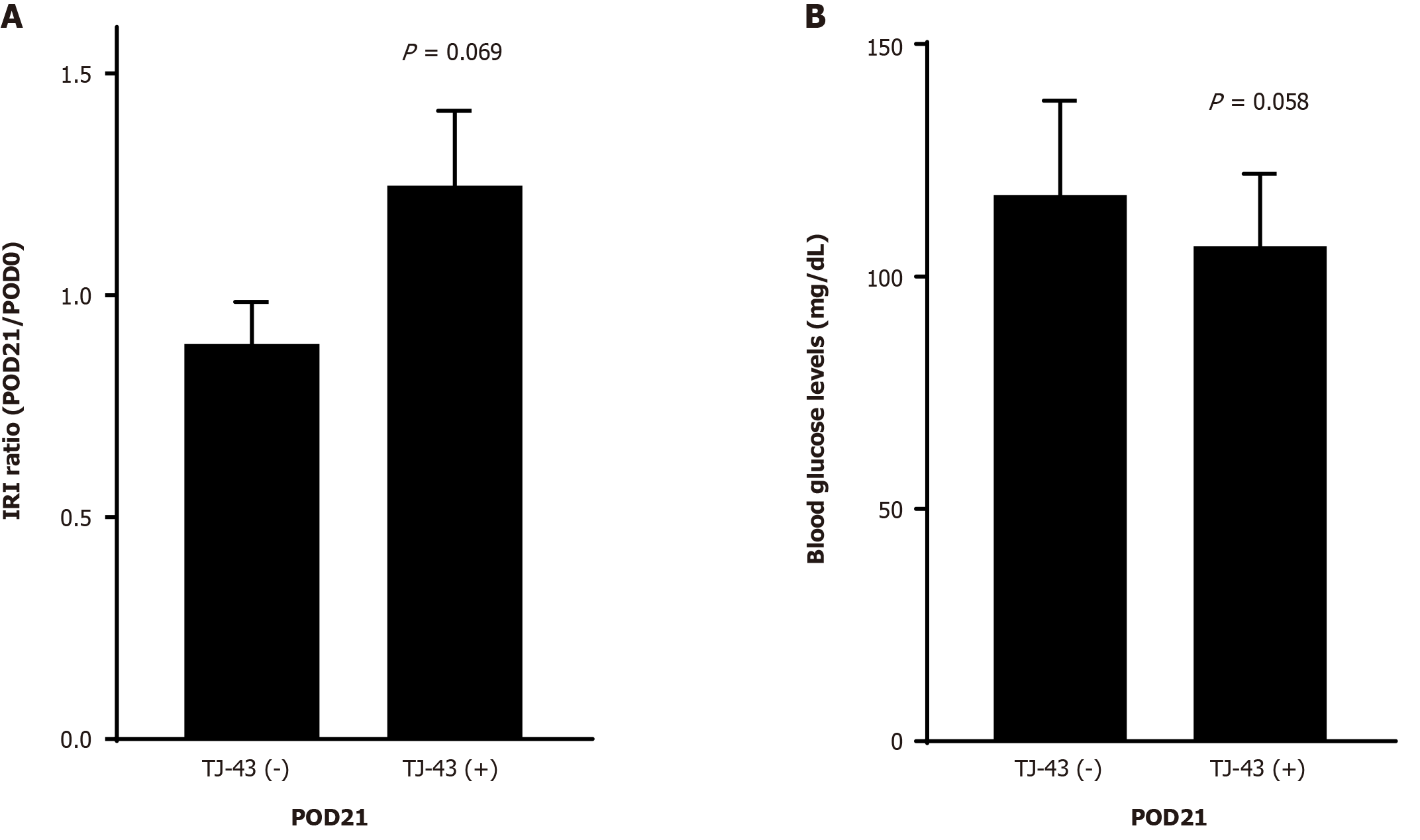
Figure 3 Effect of rikkunshito on insulin secretion and blood glucose levels.
A and B: Immunoreactive insulin levels (A) and blood glucose levels (B) are shown. Rikkunshito (TJ-43); TJ-43(−), patients without TJ-43 treatment; TJ43(+), patients with TJ-43 treatment. TJ-43: Rikkunshito; POD: Postoperative day; IRI: Immunoreactive insulin.
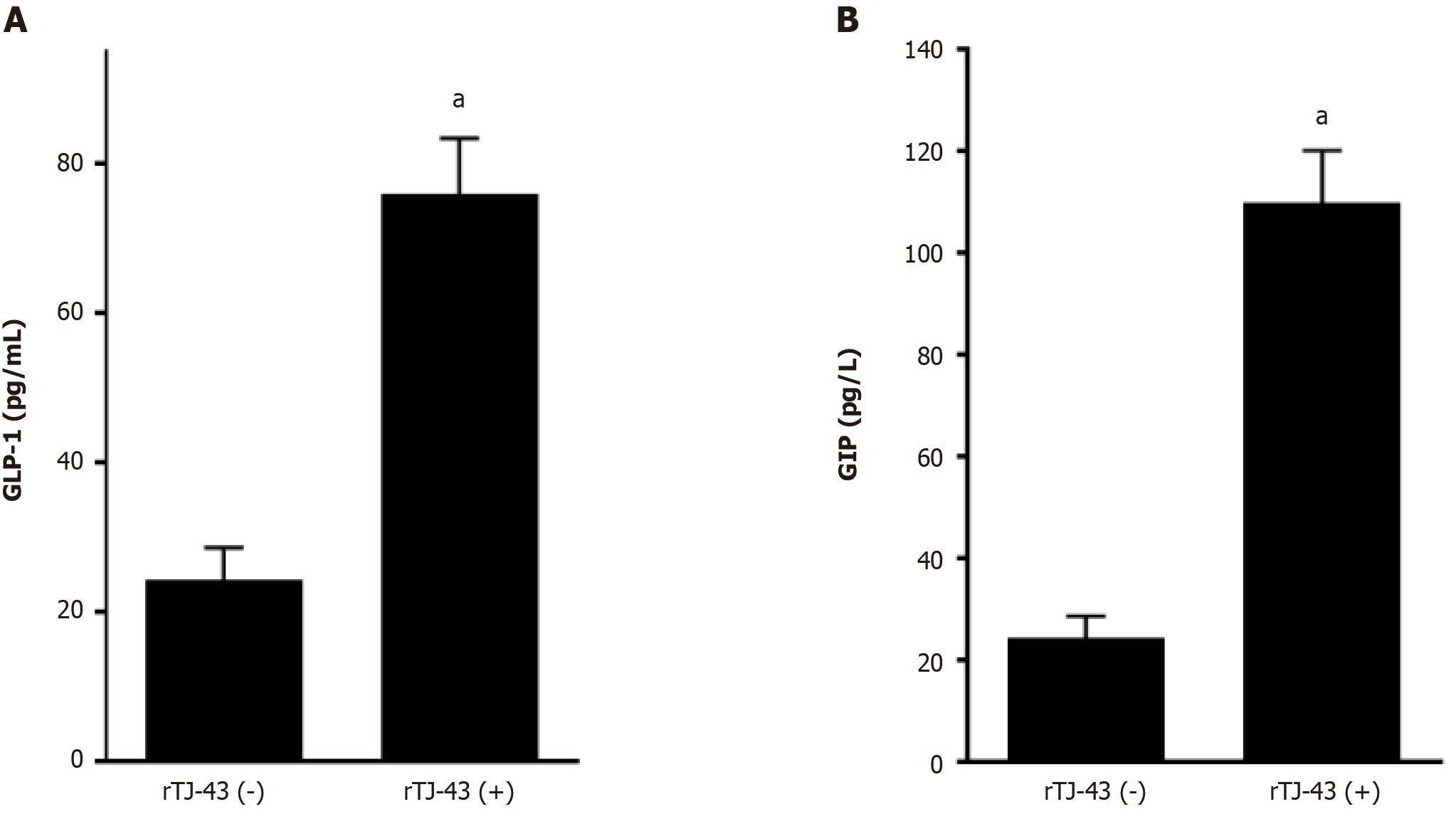
Figure 4 Effects of rikkunshito on plasma incretin hormone levels.
A and B: Plasma levels of gastric inhibitory peptide; and glucagon-like polypeptide-1 were measured by ELISA. Rikkunshito (TJ-43); rTJ-43(−), rats without TJ-43 treatment; and TJ43(+), rats with TJ-43 treatment. aP < 0.05 compared with the TJ-43(−) group by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. TJ-43: Rikkunshito; GLP: Glucagon-like polypeptide-1; GIP: Gastric inhibitory peptide.
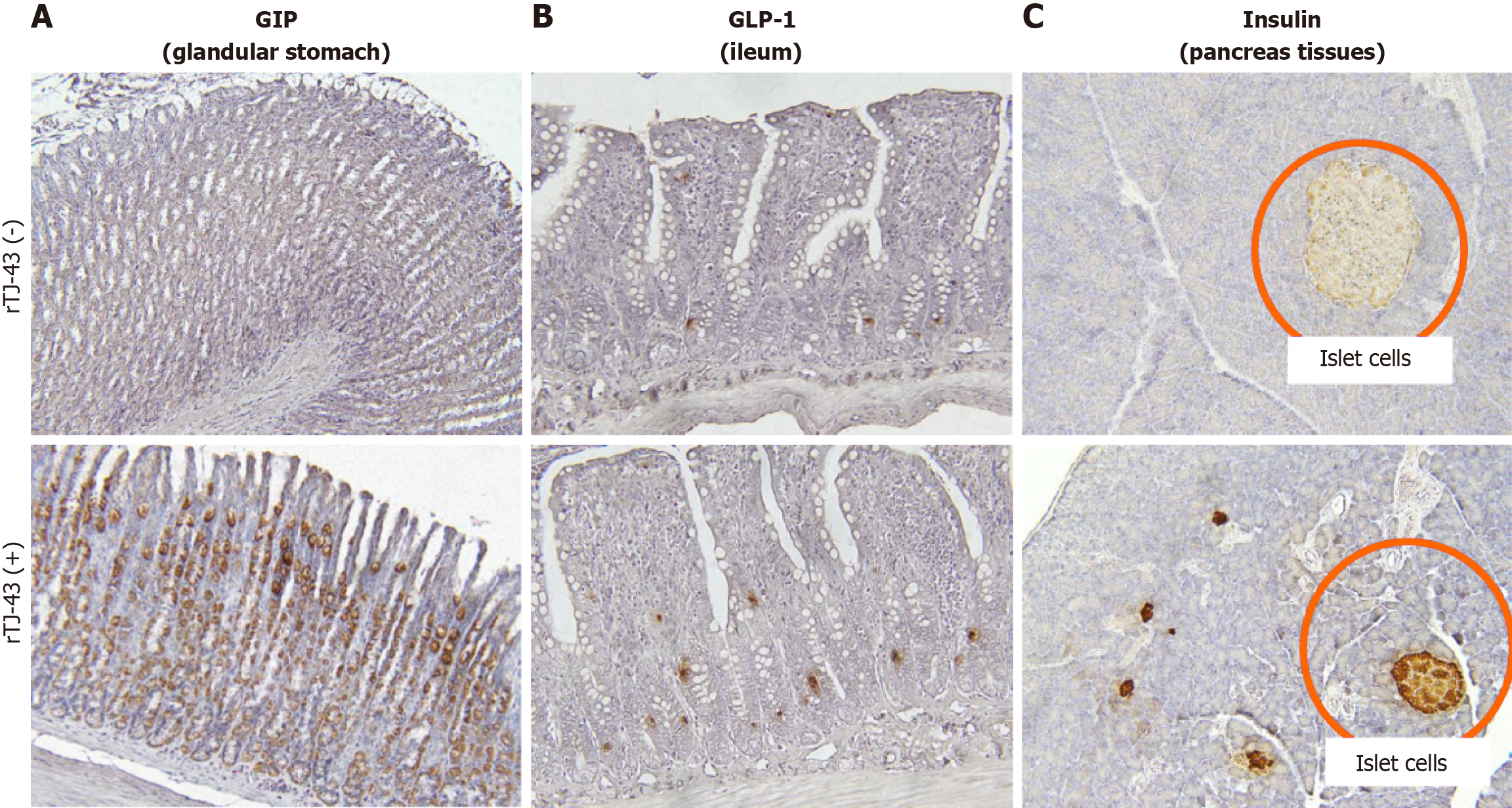
Figure 5 Effects of rikkunshito on expressions of incretin hormones in gastrointestinal and insulin in pancreatic tissues.
A: Gastric inhibitory peptide in the glandular stomach; B: Glucagon-like polypeptide-1 in the ileum; C: Insulin in the pancreas. The expression of incretin hormones in the gastrointestinal tracts and insulin in the pancreas was investigated by immunohistochemistry. TJ-43: Rikkunshito; rTJ-43(−): Rats treated without TJ-43; rTJ43(+): Rats treated with TJ-43; GIP: Gastric inhibitory peptide; GLP-1: Glucagon-like polypeptide-1.
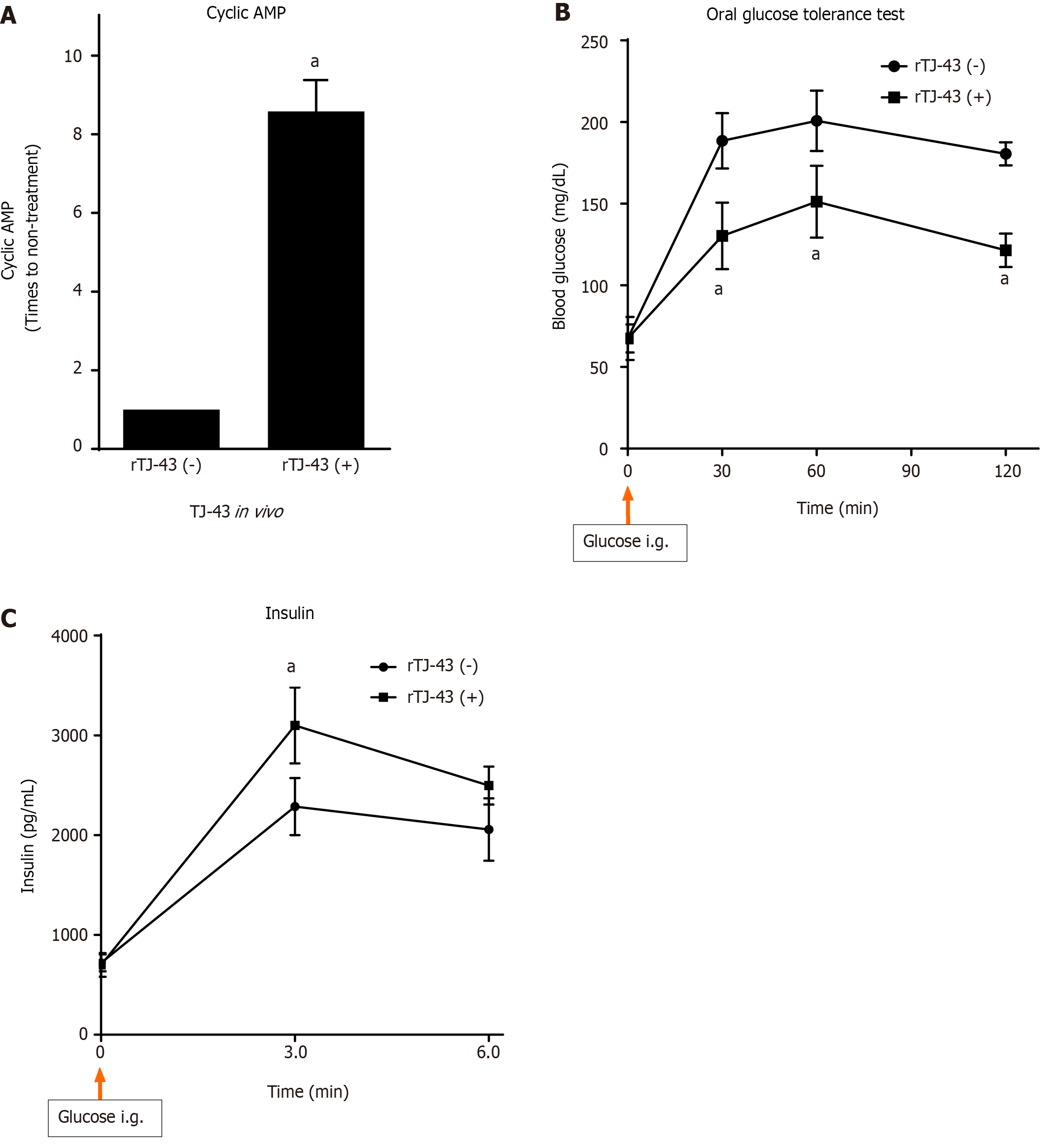
Figure 6 Effects of rikkunshito on cyclic adenosine monophosphate activities in pancreatic tissues, oral glucose tolerance test, and plasma insulin levels.
A: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate activities in the pancreatic tissues; B: Oral glucose tolerance test; C: Plasma insulin levels. The cyclic adenosine monophosphate activities were investigated in the pancreatic tissues of rats treated with rikkunshito (TJ-43) for 3 wk or without treatment. Blood glucose levels are measured after intragastric glucose administration (2.0 g/kg) in rats treated with TJ-43 (1 g/kg) for 3 wk or without treatment at designated time points (n = 6 in each group). In the oral glucose tolerance test, plasma insulin levels are measured in rats treated with TJ-43(+) or without TJ-43(−) (n = 6 in each group) after glucose administration at designated time points. TJ-43, rikkunshito; rTJ-43(−), rats treated without TJ-43; and rTJ43(+), rats treated with TJ-43. aP < 0.05 compared with the TJ-43(−) group by ANOVA with Bonferroni’s post-hoc test. TJ-43: Rikkunshito; AMP: Adenosine monophosphate.
- Citation: Kono H, Furuya S, Akaike H, Shoda K, Kawaguchi Y, Amemiya H, Kawaida H, Ichikawa D. Rikkunshito increases peripheral incretin-hormone levels in humans and rats. World J Methodol 2024; 14(1): 88518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v14/i1/88518.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.88518