Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Methodol. Sep 20, 2023; 13(4): 359-365
Published online Sep 20, 2023. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v13.i4.359
Published online Sep 20, 2023. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v13.i4.359
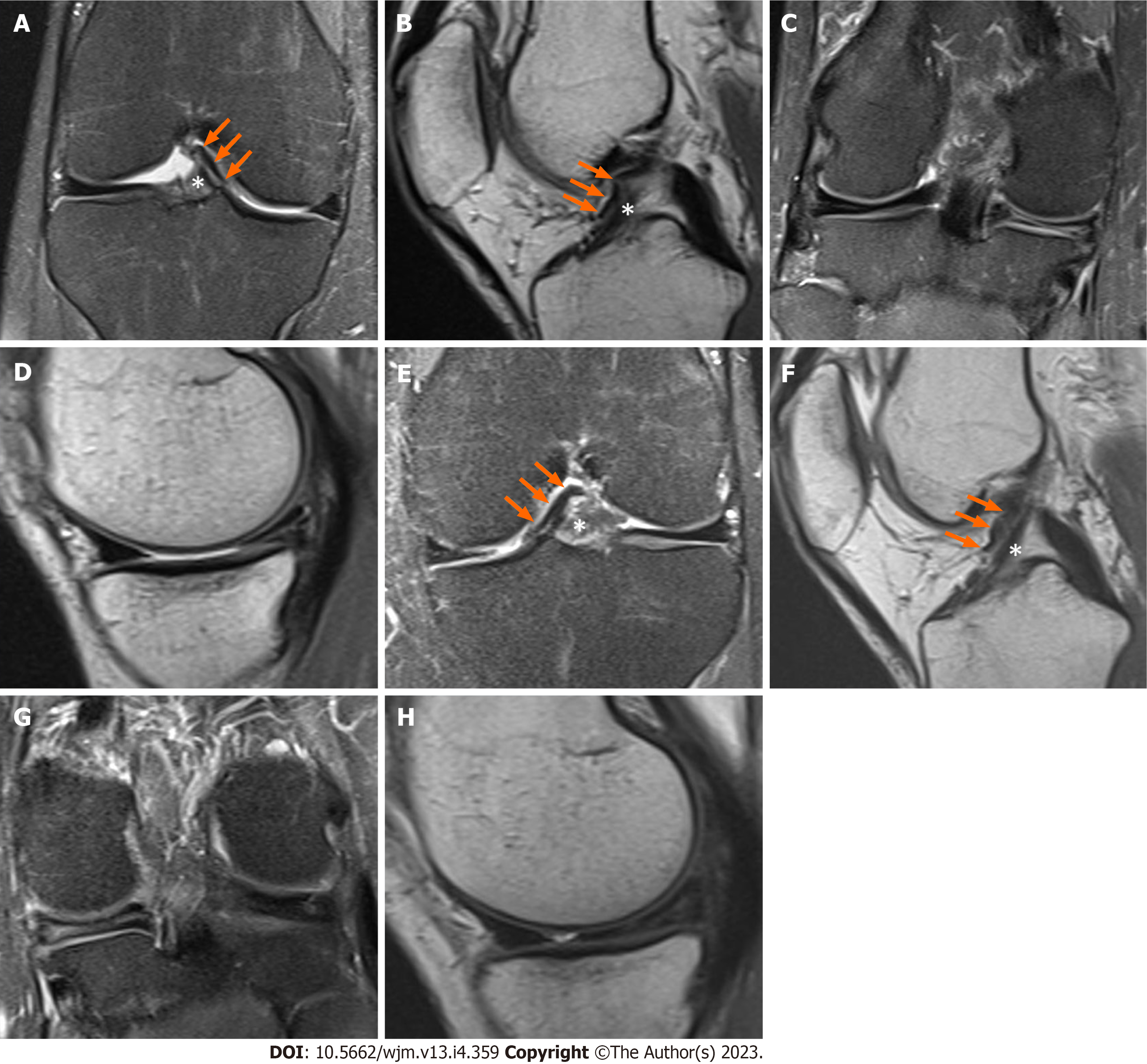
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging images of the knee.
A-D: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) images of the right knee. Coronal T2-weighted fat-saturated image demonstrating the anteromedial meniscofemoral ligament (AMMFL) (green arrow) and the distal aspect of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) (white asterisk) (A); sagittal T1-weighted image showing the AMMFL (green arrow) running anteriorly to the ACL (white asterisk) (B); coronal T2-weighted fat-saturated and sagittal images showing the medial meniscus with a previous partial meniscectomy and tear of the posterior horn (C and D); E-H: MRI images of the left knee. Coronal T2-weighted fat-saturated image demonstrating the AMMFL (green arrow) and the distal aspect of the ACL (white asterisk) (E); sagittal T1-weighted image showing the AMMFL (green arrow) running anteriorly to the ACL (white asterisk) (F); coronal T2-weighted fat-saturated and sagittal images showing a tear of the posterior horn of the medial meniscus (G and H).
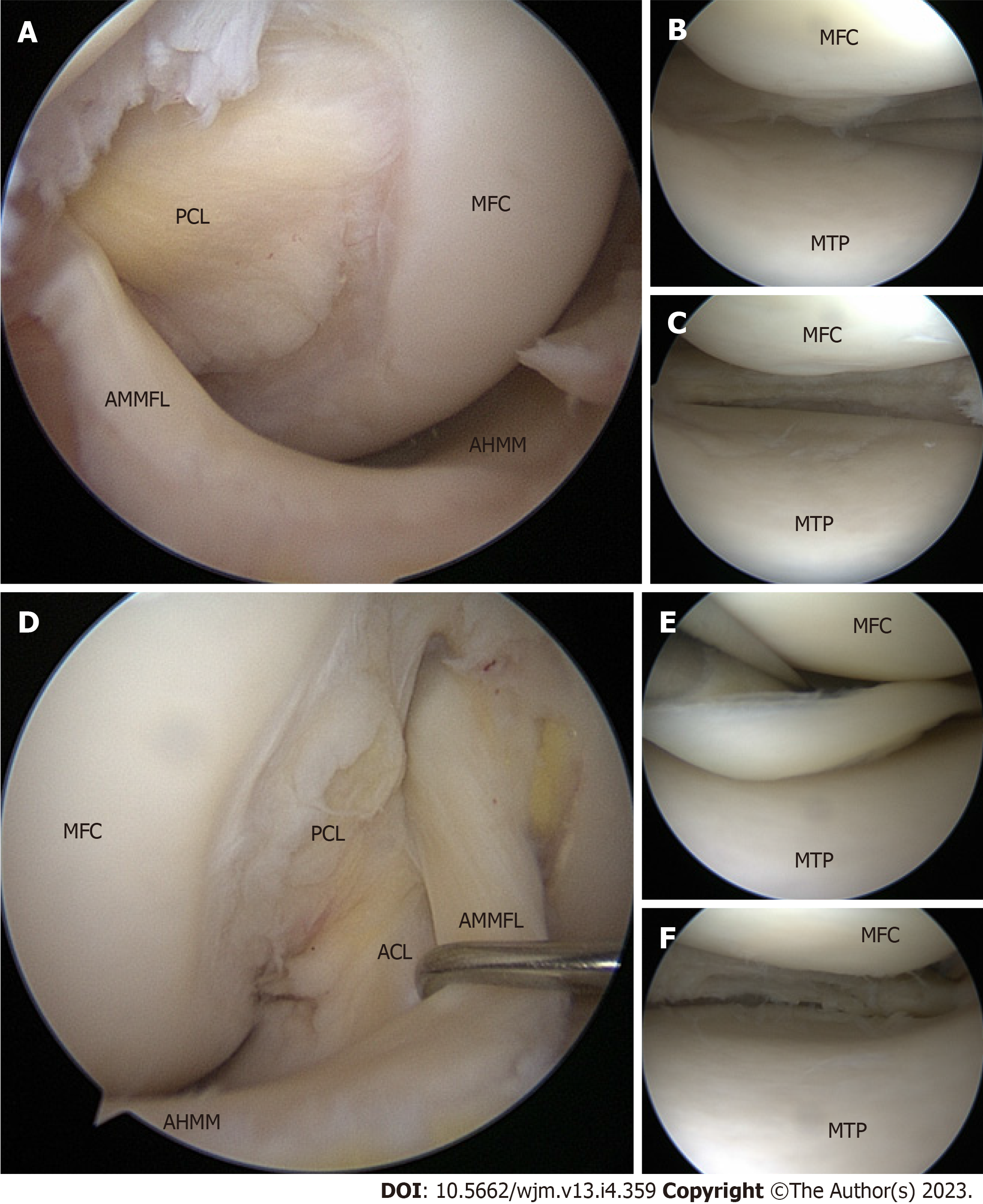
Figure 2 Arthroscopic images of the knee obtained through the anterolateral portal.
A-C: Arthroscopic images of the right knee obtained through the anterolateral portal. The anteromedial meniscofemoral ligament (AMMFL) can be seen coursing anteriorly to the anterior aspect of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and connecting the anterior horn medial meniscus (AHMM) to the posterolateral intercondylar notch (A); tear of the medial meniscus (B); image of the medial meniscus after partial meniscectomy (C); D-F: Arthroscopic images of the left knee obtained through the anterolateral portal. The AMMFL can be seen coursing anteriorly to the anterior aspect of the ACL and connecting the AHMM to the posterolateral intercondylar notch (D); tear of the medial meniscus (E); image of the medial meniscus after partial meniscectomy (F). PCL: Posterior cruciate ligament; MFC: Medial femoral condyle; AMMFL: Anteromedial meniscofemoral ligament; AHMM: Anterior horn medial meniscus; MTP: Medial tibial plateau; ACL: Anterior cruciate ligament.
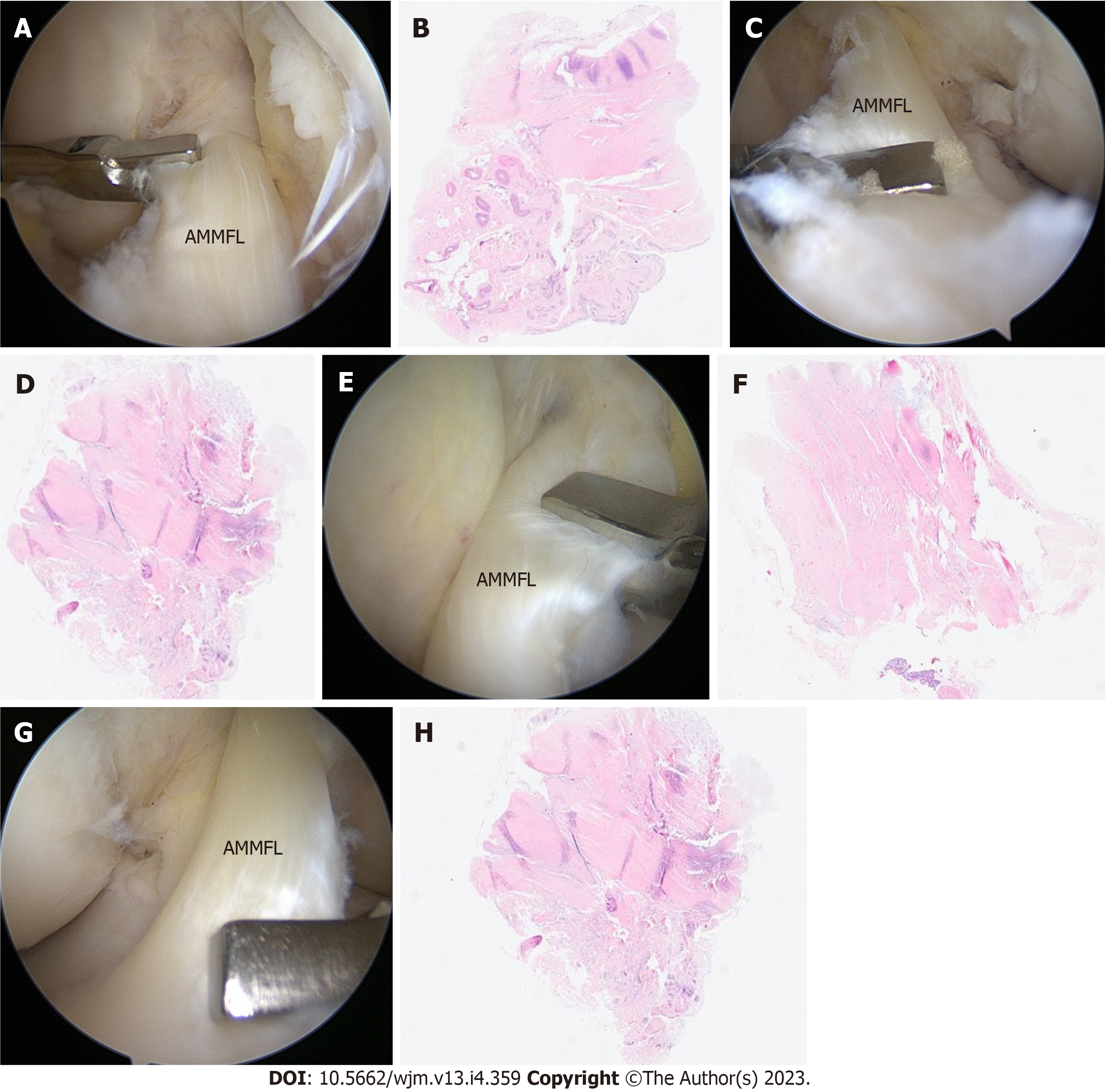
Figure 3 Intraoperative images and histologic examination of the knee.
A-D: Intraoperative images and histologic examination of the right knee. Arthroscopic images obtained through the anteromedial portal showing the biopsies performed through the anterolateral portal (A and B); hematoxylin and eosin staining of the meniscofemoral band reveals fibrocartilaginous tissue compatible with meniscus in both cases (C and D); E-H: Intraoperative images and histologic examination of the left knee. Arthroscopic images obtained through the anteromedial portal showing the biopsies performed through the anterolateral portal (E and F); hematoxylin and eosin staining of the meniscofemoral band reveals fibrocartilaginous tissue compatible with meniscus in both cases (G and H). AMMFL: Anteromedial meniscofemoral ligament.
- Citation: Luco JB, Di Memmo D, Gomez Sicre V, Nicolino TI, Costa-Paz M, Astoul J, Garcia-Mansilla I. Clinical, imaging, arthroscopic, and histologic features of bilateral anteromedial meniscofemoral ligament: A case report. World J Methodol 2023; 13(4): 359-365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v13/i4/359.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v13.i4.359