Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Methodol. Sep 20, 2023; 13(4): 323-336
Published online Sep 20, 2023. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v13.i4.323
Published online Sep 20, 2023. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v13.i4.323
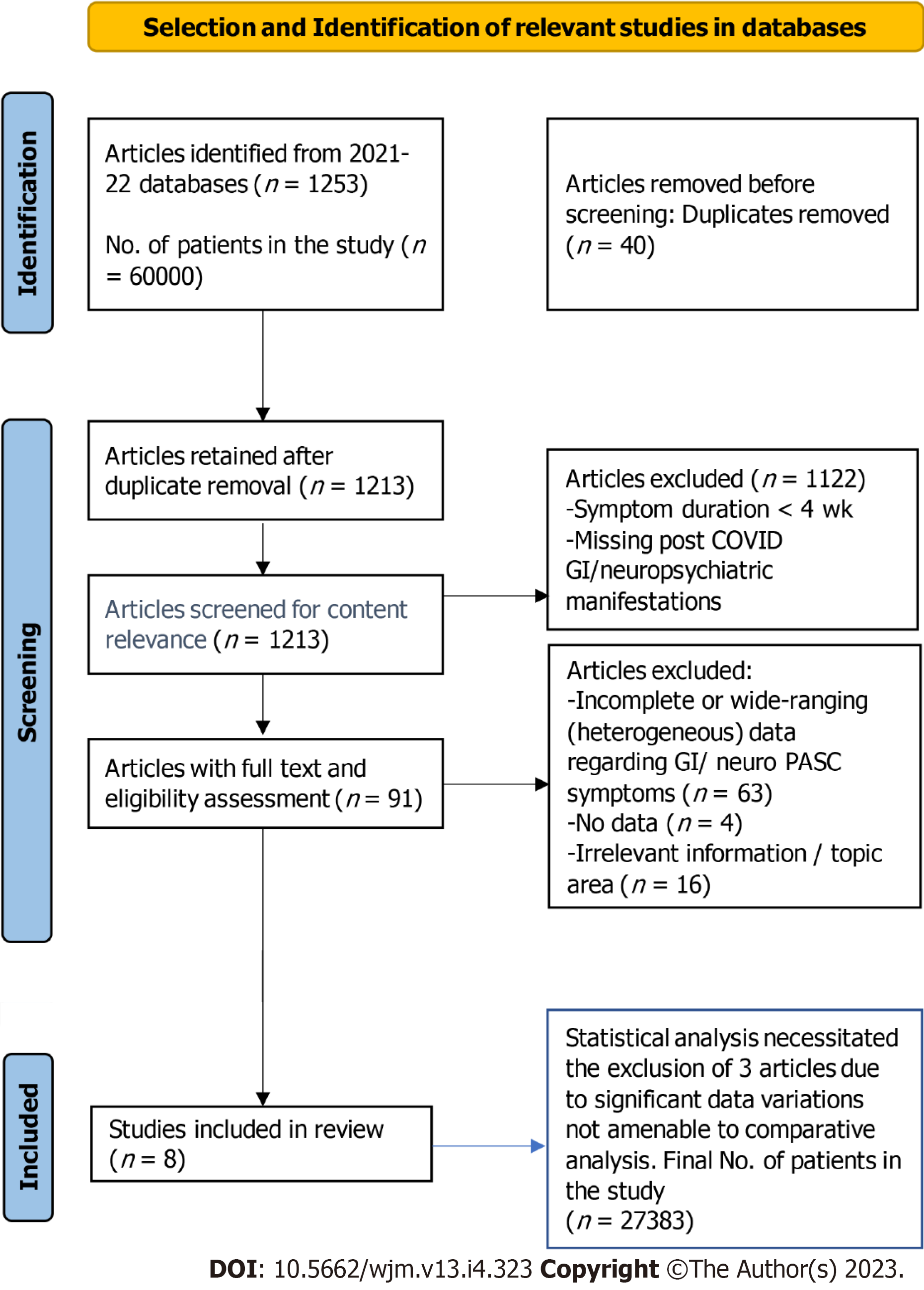
Figure 1 Selection and identification of relevant studies in databases.
COVID: Coronavirus disease; PASC: Post-acute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection; GI: Gastrointestinal.
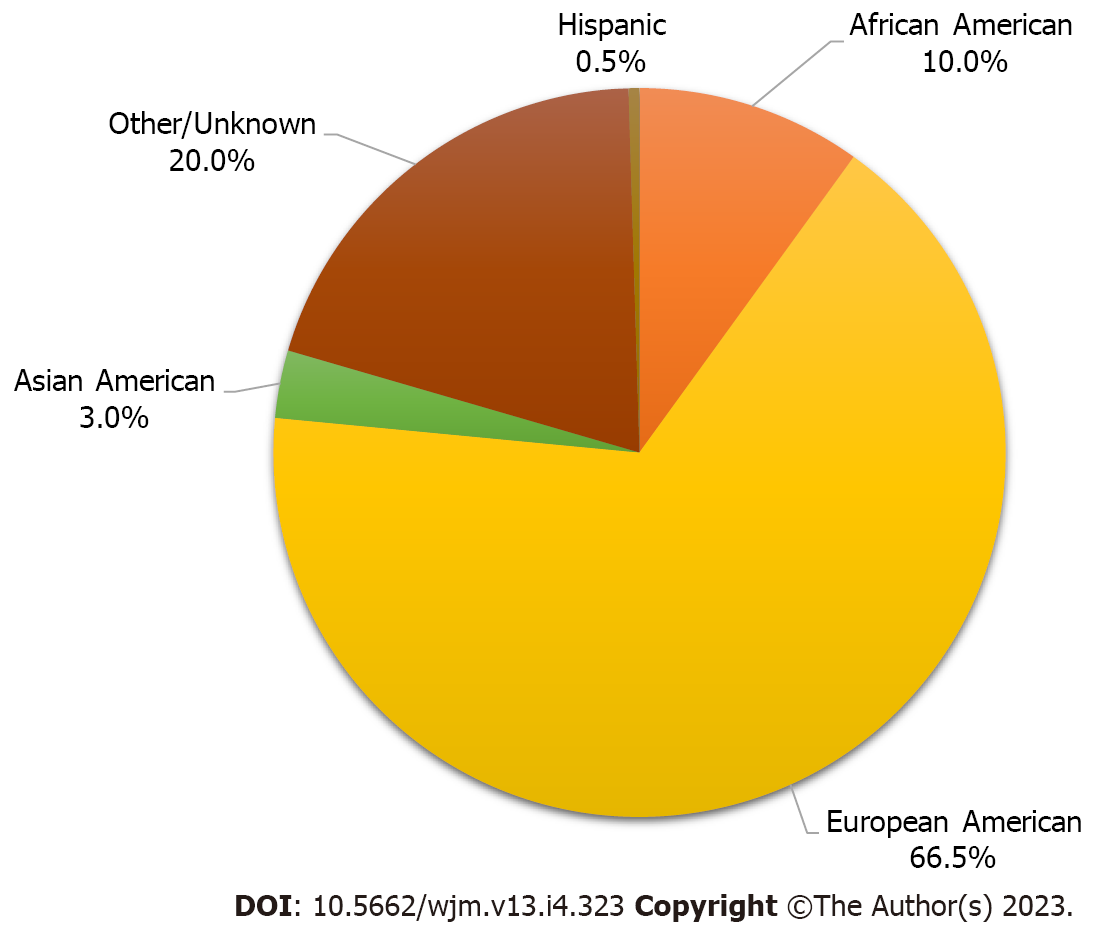
Figure 2 Aggregate racial identities of the study cohorts.
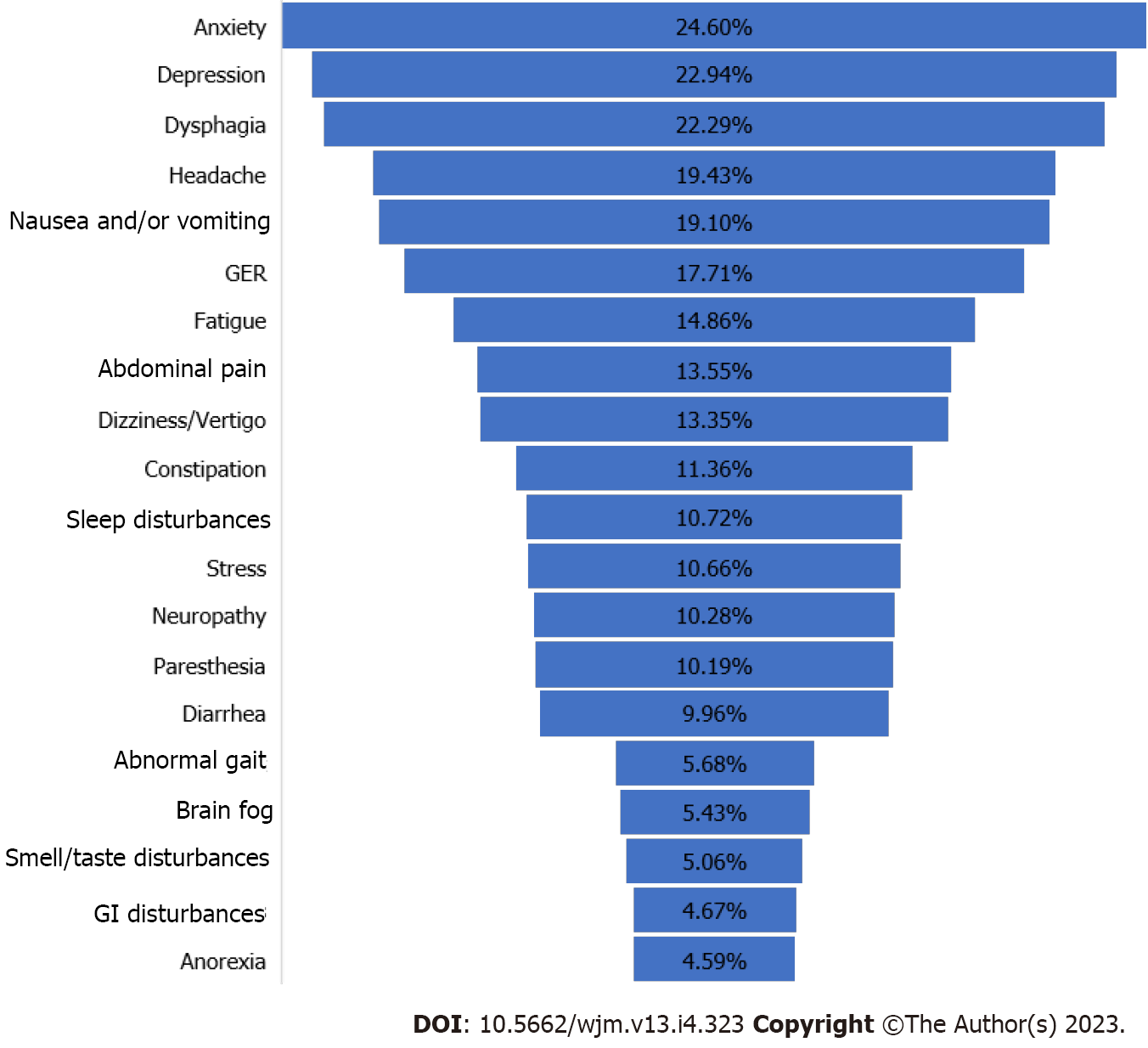
Figure 3 Percentages of post-acute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-gastrointestinal/neurological symptoms in all patients of the five studies reviewed.
Patients with neurological or gastrointestinal symptoms may or may not harbor both symptoms. GI: Gastrointestinal; GER: Gastroesophageal reflux.
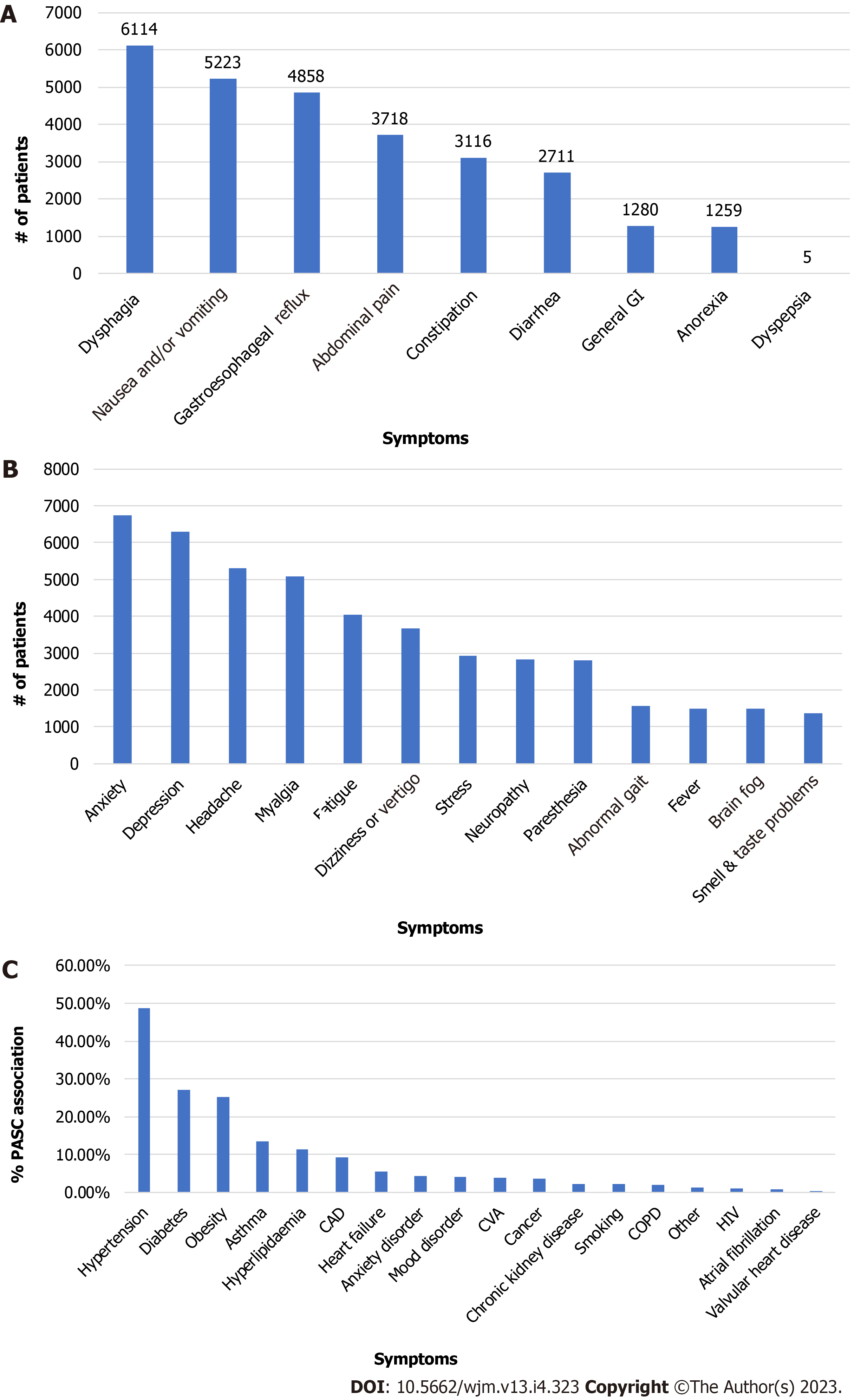
Figure 4 Gastrointestinal, neurologic, and comorbidities post-acute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 symptoms.
A: Gastrointestinal post-acute sequelae of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection (PASC); B: Neurologic PASC; C: Comorbidities in PASC patients. GI: Gastrointestinal; CAD: Coronary artery disease; CVA: Cerebral vascular accident; COPD: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; HIV: Human immunodeficiency virus infection.
- Citation: Sherif ZA, Deverapalli M, Challa SR, Martirosyan Z, Whitesell P, Pizuorno AM, Naqvi Z, Tulloch IK, Oskrochi G, Brim H, Ashktorab H. Potential long-term neurological and gastrointestinal effects of COVID-19: A review of adult cohorts. World J Methodol 2023; 13(4): 323-336
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v13/i4/323.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v13.i4.323