Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Transl Med. Dec 12, 2015; 4(3): 88-100
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.88
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.88
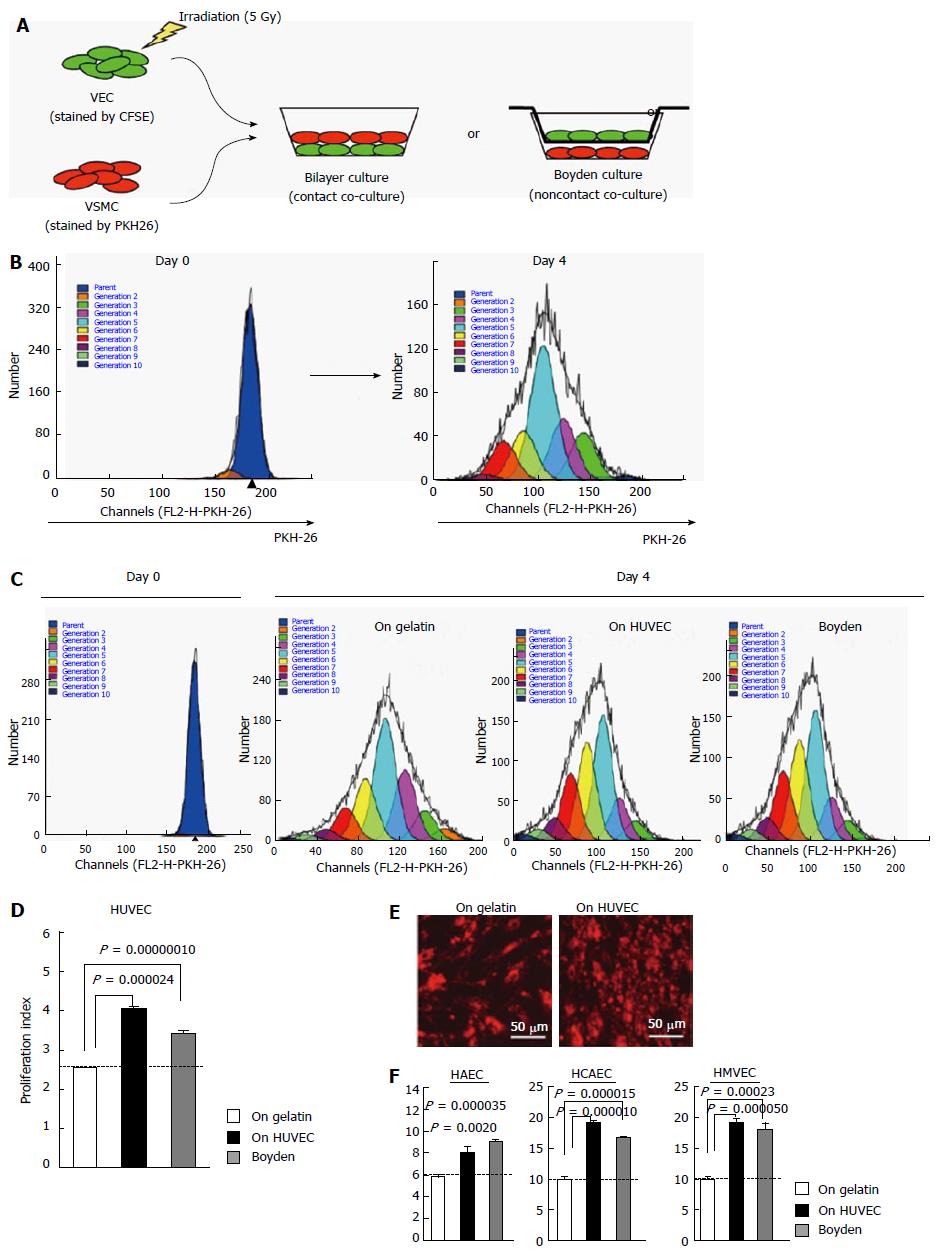
Figure 1 Phenotype determination of primary cultured human vascular endothelial cells.
A and B: Illustrations of the method to calculate proliferation indexes of VEC-co-cultured VSMC via ModFit LT™ software-based analyses; C: Results of flow cytometric analyses of HUVEC-co-cultured VSMC with ModFit LT™ analyses; D: Results in C were statistically evaluated (n = 3); E: Fluorescent microscopy of PKH-26-stained VSMC subjected to contact co-culture with HUVEC; F: Results of VSMC-co-culture experiments using HAEC, HCAEC and HMVEC (n = 3). VEC: Vascular endothelial cells; HAEC: Human umbilical artery endothelial cells; HCAEC: Human coronary artery endothelial cells; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; HMVEC: Human microvascular endothelial cell; VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cell.
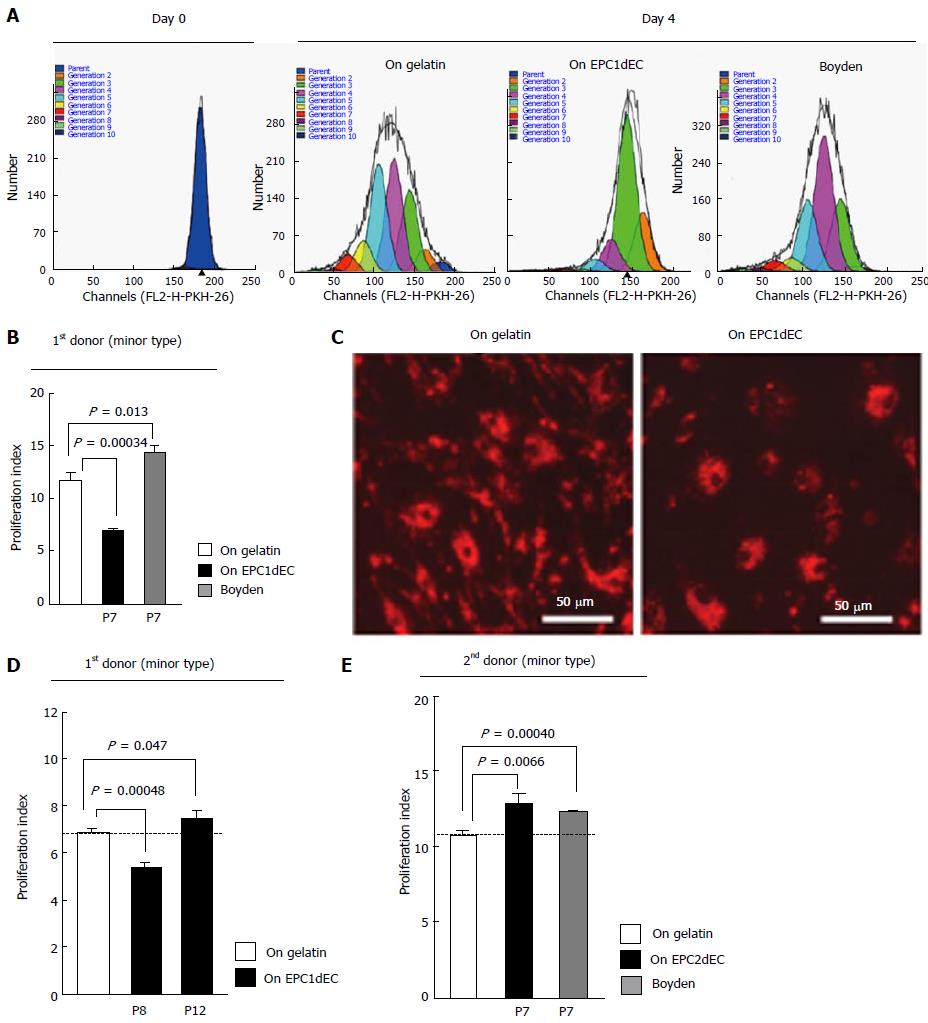
Figure 2 Phenotype determination of human embryonic stem cell-derived vascular endothelial cells.
A: Results of flow cytometric analyses of hEPC1dEC[P7]-co-cultured VSMC with ModFit LT™ analyses; B: Results in (A) were statistically evaluated (n = 3); C: Fluorescent microscopy of PKH-26-stained VSMC subjected to contact co-culture with hEPC1dEC[P7]; D: Results of VSMC-co-culture experiments on the layer of hEPC1dEC at passage 8 and on that of hEPC1dEC passage 12; E: Results of VSMC-co-culture experiments using hEPC2dEC[P7] (n = 3). VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell.
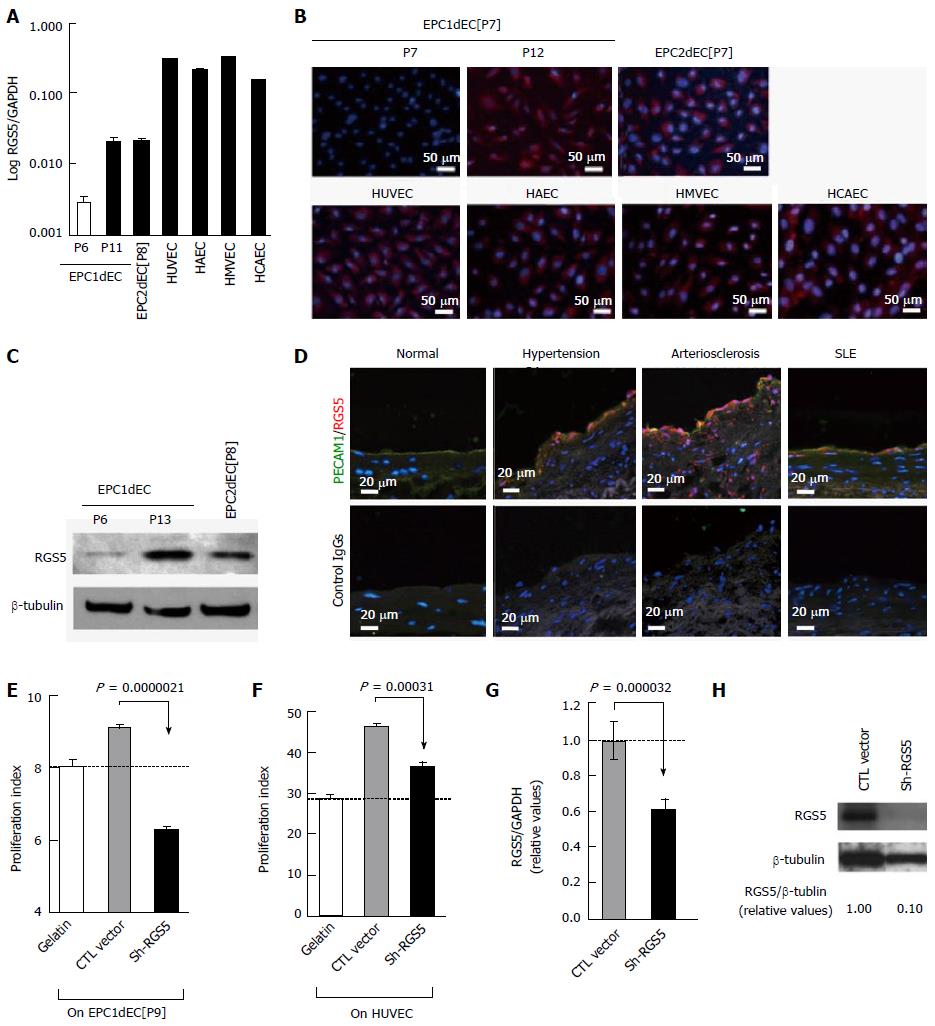
Figure 3 Regulator of G-protein signaling 5 is involved in the phenotype conversion of vascular endothelial cells.
A: qRT-PCR results of RGS5 message expression were shown with normalization by GAPDH. The horizontal axis was demonstrated as logarithm; B: Immunostaining of indicated cells by using an anti-RGS5 antibody (red) with DAPI counterstaining (blue); C: Western blotting of RGS5 protein; D: Clinical specimens of the artery were subjected to immunostaining studies by using an anti-RGS5 antibody (red) and an anti-human PECAM1 antibody (green) with nuclear counterstaining with DAPI (blue); E-G: RGS5 knockdown experiments. An expression vector for shRNA against RGS5 (Sh-RGS5) or control RNA (CTL RNA) were transfected into EPC1dEC[P9] (E) or HUVEC (F). The results of VSMC co-cultured experiments (E and F) along with qRT-PCR (RGS5/GAPDH) (G) and Western blotting (H) regarding HUVEC were shown. GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-phosphate dehydrogenase; VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cell; HAEC: Human adult aortic endothelial cells; HMVEC: Human neonatal dermal microvascular endothelial cells.
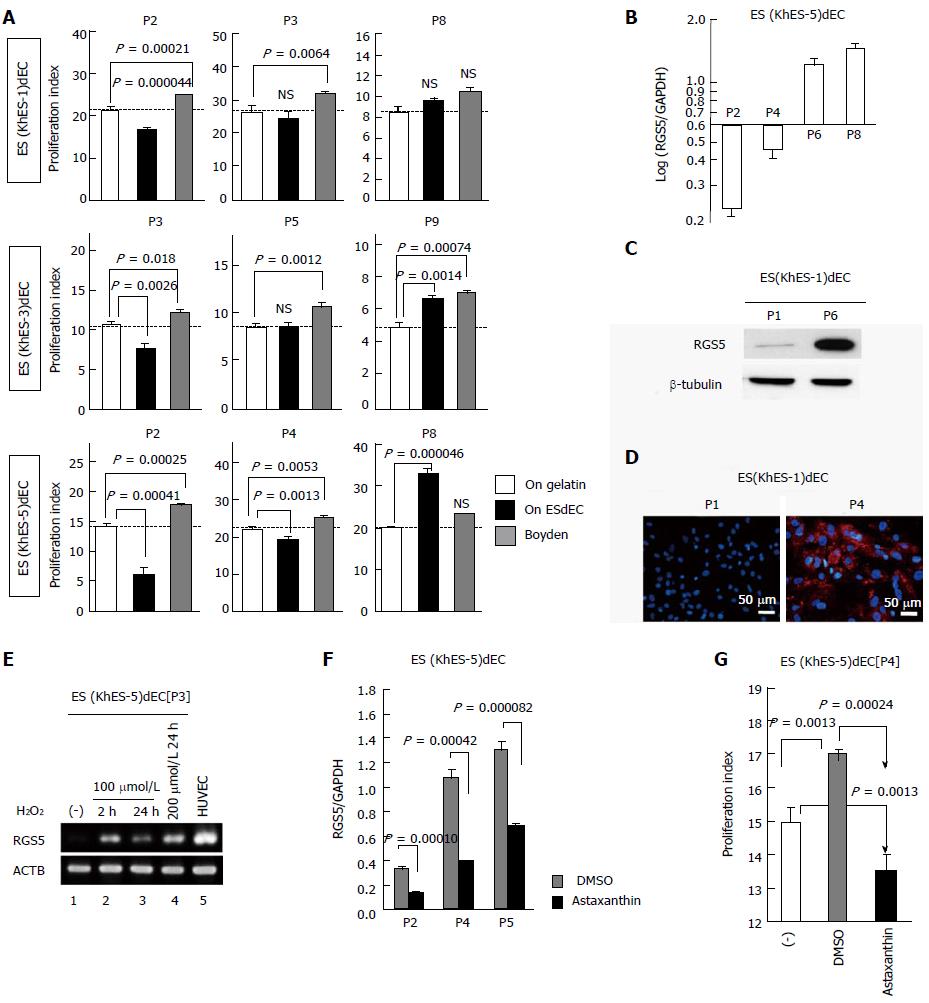
Figure 4 Phenotype evaluation of human embryonic stem cell-derived vascular endothelial cells.
A: VSMC-co-culture experiments of VECs generated from three lines of hESCs (KhES-1, khES-3, khES-5) at indicated passage number (n = 3); B: qRT-PCR of RGS5 message of khES-5-derived VECs [ES (KhES-5) dEC] at indicated passage numbers; C: Western blotting of RGS5 protein in KhES-1-derived VECs [ES (KhES-1) dEC] at passage 1 and passage 6; D: Immunostaining of RGS5 protein in ES (KhES-1) dEC at passage 1 (upper) and passage 4 (lower); E: ES (KhES-5) dECs were treated with hydrogen peroxide and RGS5 message expressions were examined by RT-PCR. Lane 1: no treatment; lane 2: 100 mol/L H2O2 treatment for 2 h; lane 3: 100 μmol/L H2O2 treatment for 24 h; lane 4: 200 mol/L H2O2 treatment for 24 h; lane 5: HUVEC; F: qRT-PCR of RGS5 message of ES (KhES-5) dECs subcultured in the presence of DMSO (gray column) or 10 mol/L astaxanthin (closed columns); G: VSMC-co-culture experiments of ES (KhES-5) dECs maintained with culture medium (open column), in the presence of DMSO (gray column) or 10 mol/L astaxanthin (closed column). VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; DMSO: Dimethylsulfoxide; RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cell.
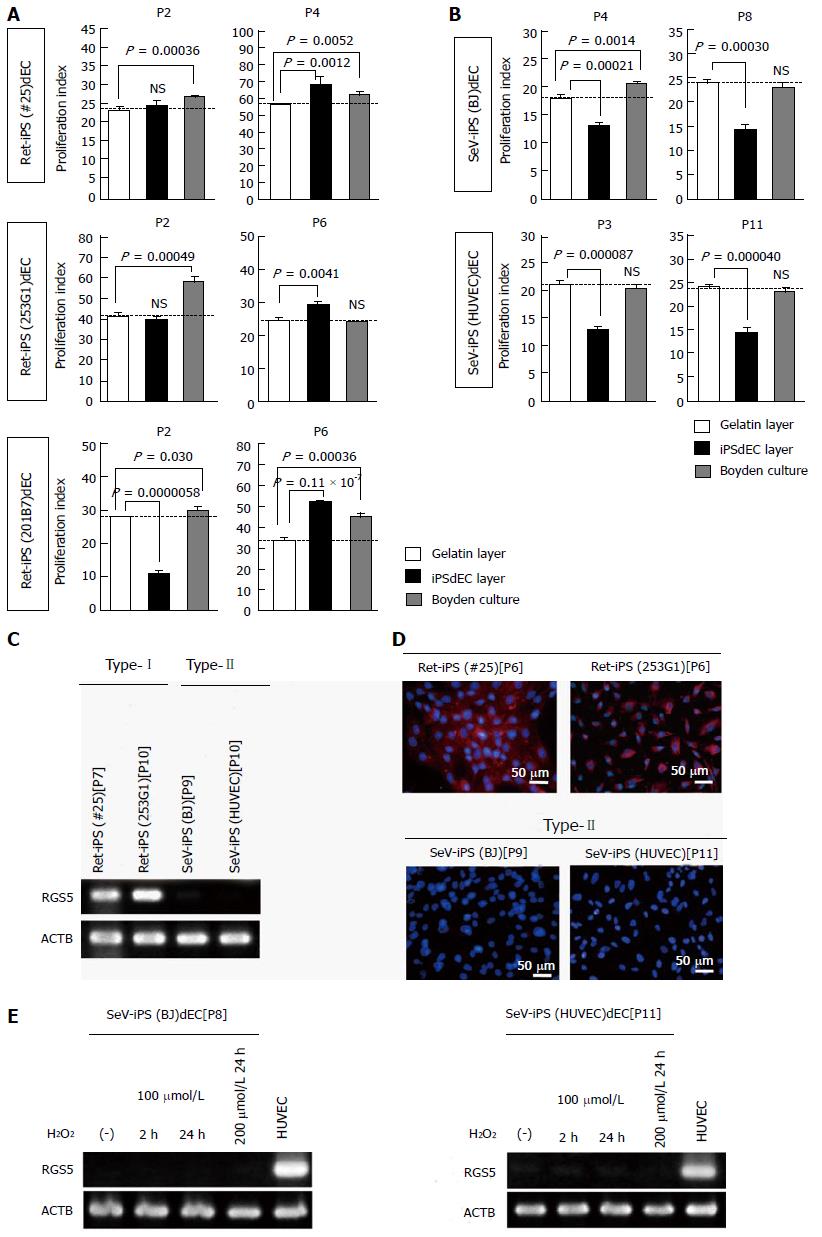
Figure 5 Phenotype evaluation of human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived vascular endothelial cells.
A and B: VSMC-co-culture experiments of VECs generated from three lines of Ret-iPSCs (#25, 253G1 and 201B7); A and those from two lines of SeV-iPSCs(SeV-iPS(BJ) and [SeV-iPS(HUVEC)]; B: At indicated passage number (n = 3); C: RT-PCR of RGS5 message of Ret-iPSdECs (type-I) and SeV-iPSdECs (type-II); D: RGS5 immunostaining studies of Ret-iPSdECs (upper) and SeV-iPSdECs (lower); E: H2O2-treating experiments were performed in type-II SeV-iPSdECs as in Figure 4E. VSMC: Vascular smooth muscle cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cell.
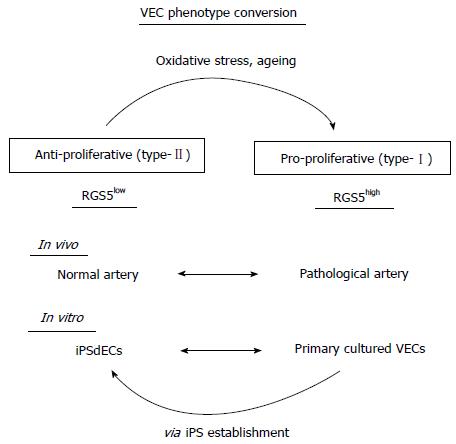
Figure 6 A model for the type-I vs type-II phenotype regulation of human vascular endothelial cells.
RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell.
- Citation: Nishio M, Nakahara M, Sato C, Saeki K, Akutsu H, Umezawa A, Tobe K, Yasuda K, Yuo A, Saeki K. New categorization of human vascular endothelial cells by pro- vs anti-proliferative phenotypes. World J Transl Med 2015; 4(3): 88-100
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6132/full/v4/i3/88.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.88