Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Transl Med. Dec 12, 2015; 4(3): 113-122
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.113
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.113
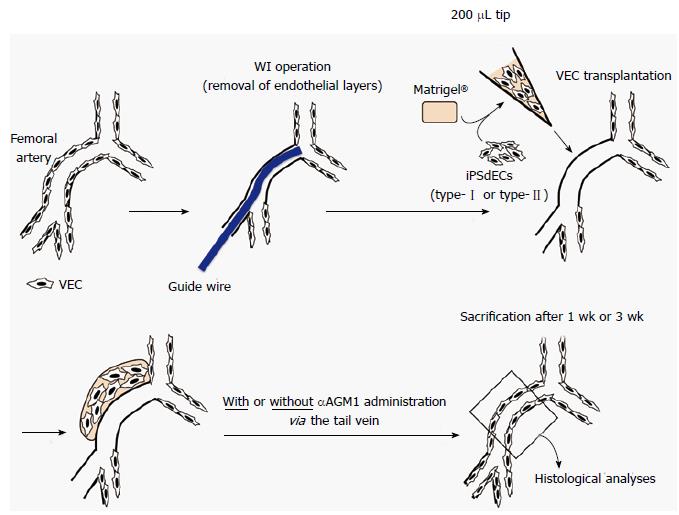
Figure 1 The procedure of pervasa vasorum transplantation.
Human iPSCdECs were mixed with Matrigel® Matrix and the mixtures were put into the subcutaneous regions around the WI-injured femoral arteries. WI: Wire injury; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSdECs: iPSC-derived VECs; αAGM1: Anti-asialo GM1 monoclonal antibody.
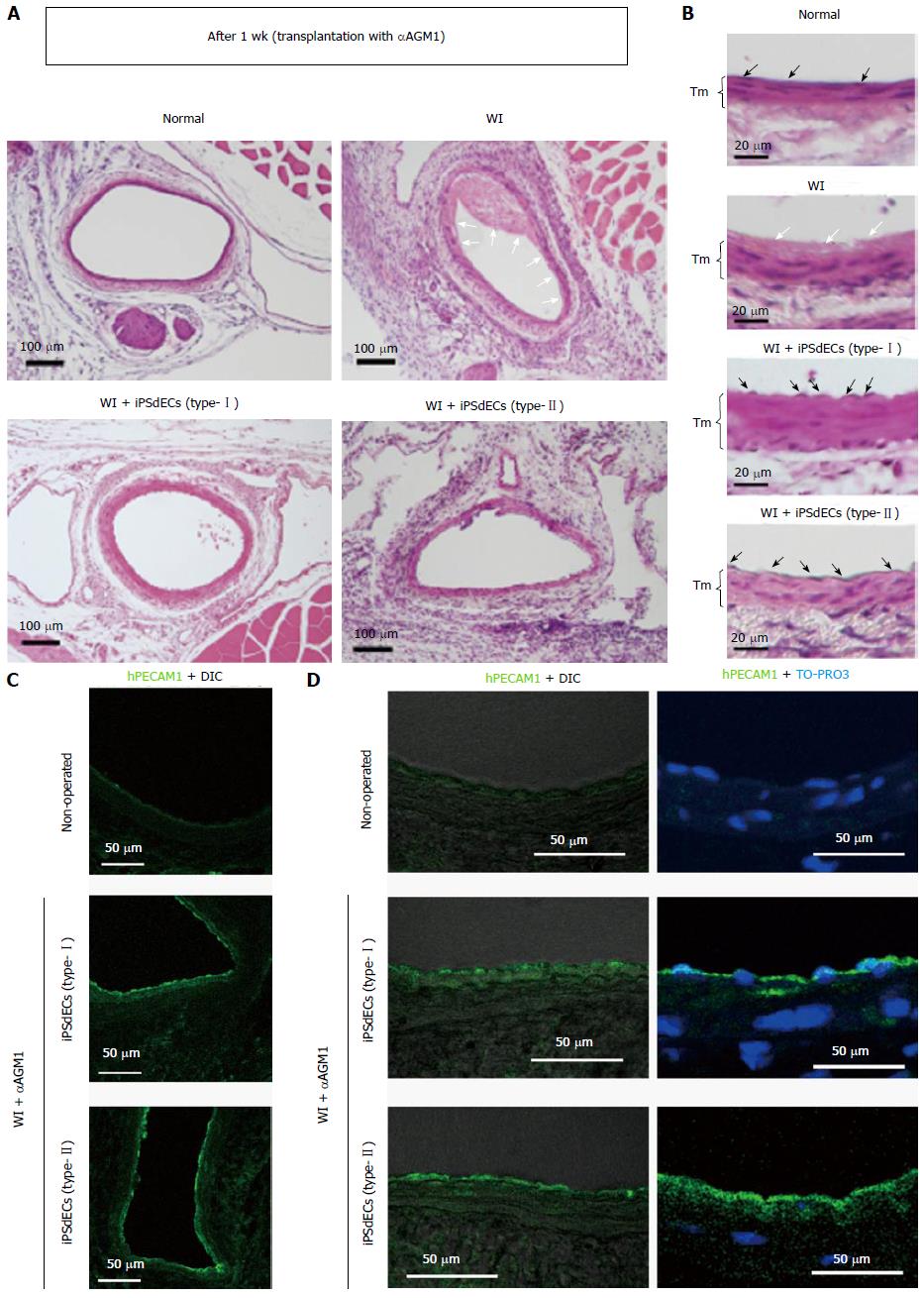
Figure 2 Histological analyses after one week.
A and B: WI-operated femoral arteries that were transplanted with type-I or type-II iPSdECs were examined after one week from PVVT in mice regularly administrated with asialo GM1 antibody αAGM1). Open arrows indicate fibrin deposits, closed arrows indicate nuclei of endothelial cells and Tm indicate tunica media; C and D: Con-focal microscopies of immunostained samples using anti-human PECAM1 antibody with differential interference contrast (DIC) (C) or nuclear counterstaining by TO-PRO3 (D). WI: Wire injury; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSdECs: iPSC-derived VECs; αAGM1: Anti-asialo GM1 monoclonal antibody.
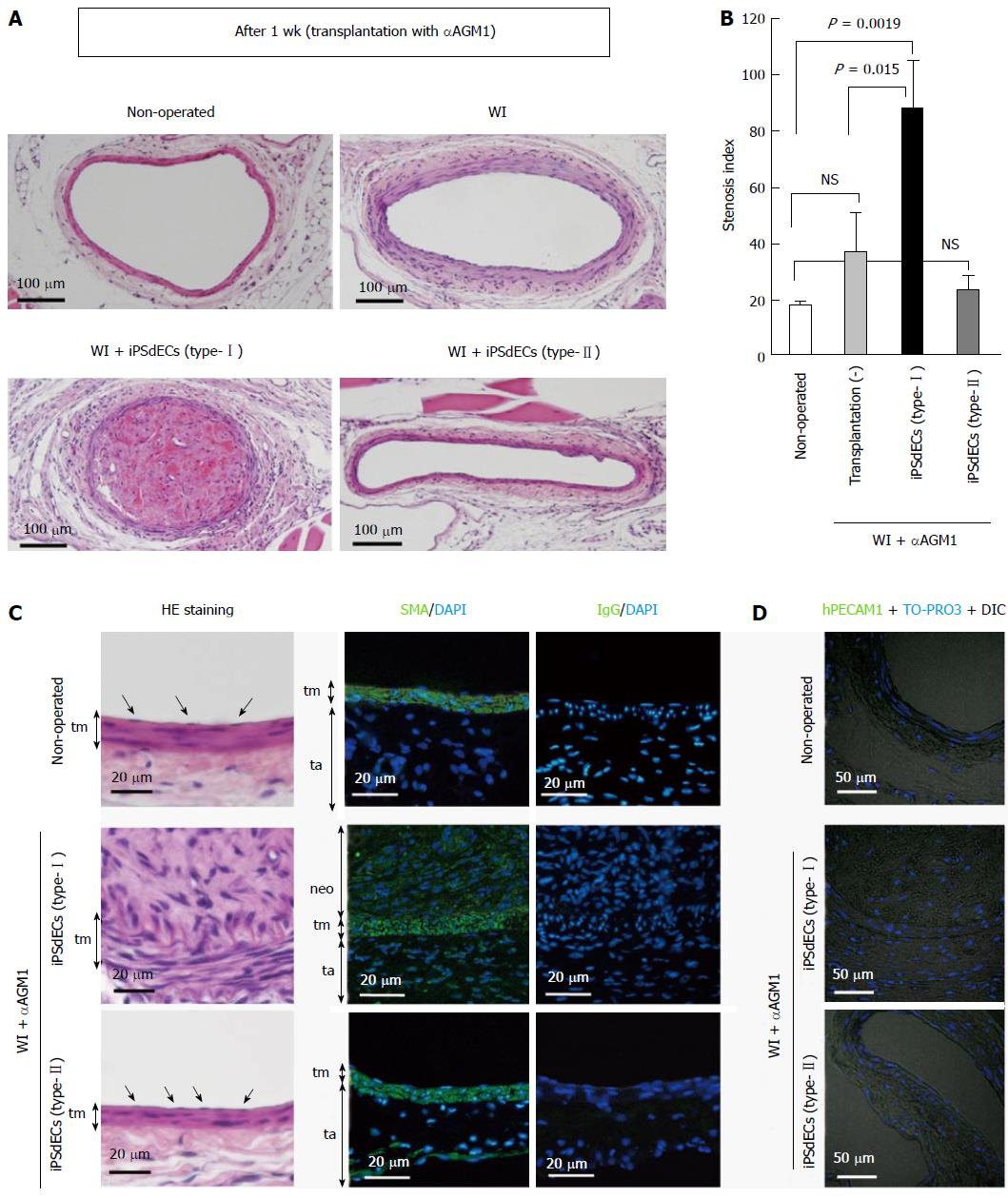
Figure 3 Histological analyses after three weeks.
Histologies of WI-operated femoral arteries after three weeks from PVVT in mice regularly administrated with aAGM1 were examined. A: Photographs of HE-stained samples at low magnification; B: Stenosis indexes were calculated and statistically analyzed by student-t test. Data were presented as average (Av) ± standard deviation (SD). Experiments were performed using three mice for each condition (n = 3); C and D: High magnification photographs of the samples with HE staining (C, left), immunostaining using anti-smooth muscle actin (SMA) antibody with nuclear counterstaining by DAPI (C, right) and immunostaining using anti-hPECAM1antibody with DIC and nuclear counterstaining by DAPI (D). WI: Wire injury; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSdECs: iPSC-derived VECs; αAGM1: Anti-asialo GM1 monoclonal antibody.
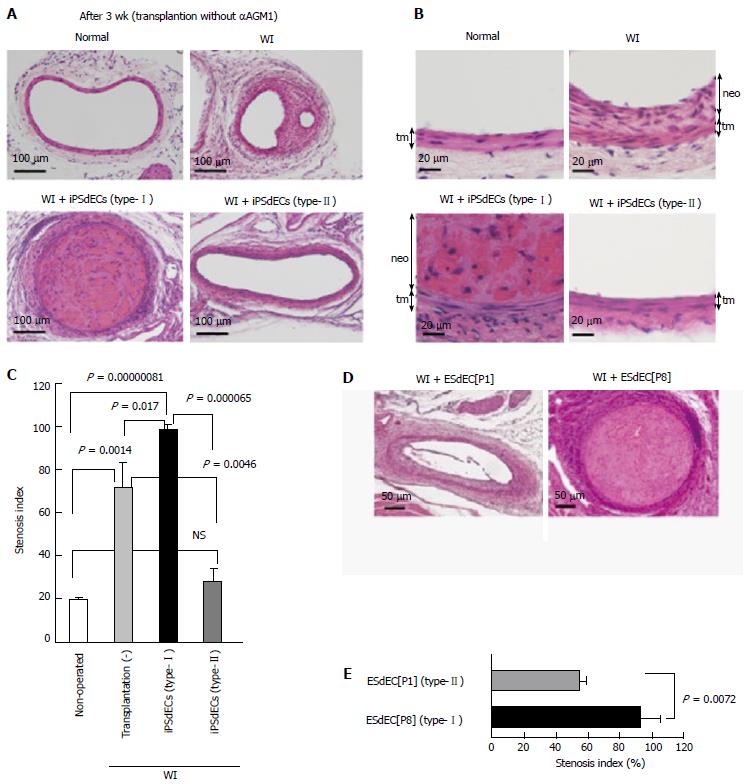
Figure 4 Transplantation without immunosuppression.
A-C: WI-operated femoral arteries transplanted with type-I or type-II iPSdECS were examined after 3 wk from PVVT in mice without αAGM1 administration. Photographs of HE-stained samples at high magnification, those at low magnification and calculated stenosis indexes (Av ± SD, n = 3) (C) were shown; D and E: HE staining (D) and calculated stenosis indexes (n = 3) (E) of WI-operated femoral arteries after 3 wk from ESdECs transplantation without αAGM1 administration. WI: Wire injury; iPSC: Induced pluripotent stem cell; VEC: Vascular endothelial cell; iPSdECs: iPSC-derived VECs; αAGM1: Anti-asialo GM1 monoclonal antibody; ESdECs: ESC-derived VECs.
- Citation: Nishio M, Nakahara M, Saeki K, Fujiu K, Iwata H, Manabe I, Yuo A, Saeki K. Pro- vs anti-stenotic capacities of type-I vs type-II human induced pluripotent-derived endothelial cells. World J Transl Med 2015; 4(3): 113-122
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6132/full/v4/i3/113.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.113