Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Transl Med. Dec 12, 2015; 4(3): 101-112
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.101
Published online Dec 12, 2015. doi: 10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.101
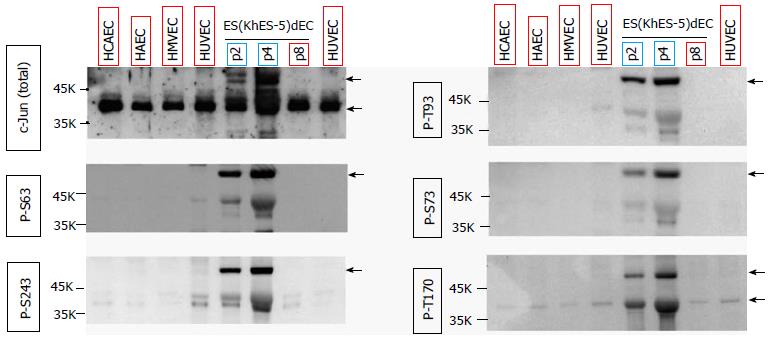
Figure 1 Western blotting assays.
HCAEC, HAEC, HMVEC, HUVEC and ESdECs were subjected to western blotting using indicated antibodies. Arrows indicate the specific bands recognized by the antibodies. HCAEC: Human adult coronary arterial endothelial cells; HAEC: Human adult aortic endothelial cells; HMVEC: Human neonatal dermal microvascular endothelial cells; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ESdECs: Embryonic stem cells-derived vascular endothelial cells.
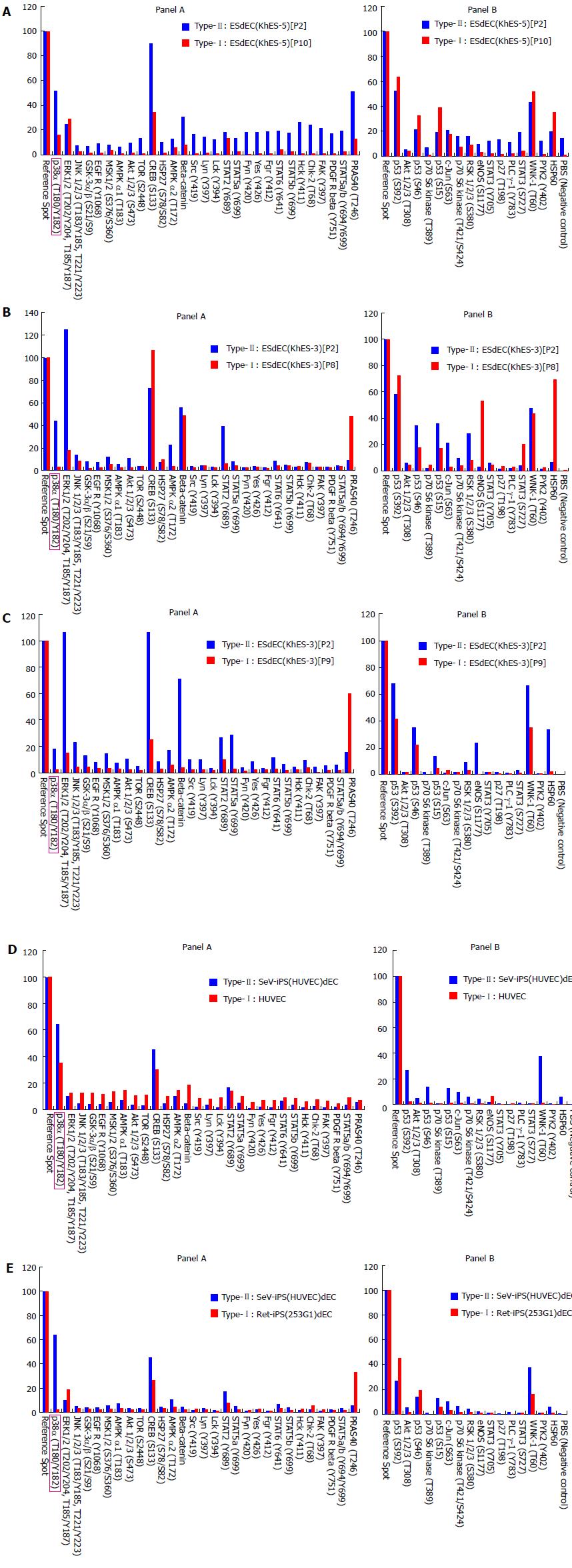
Figure 2 Proteomic kinase assays.
Lysates of various pairs of type-I and type-II vascular endothelial cells were prepared as indicated and used for proteomic kinase assays. ESdECs: Embryonic stem cells-derived vascular endothelial cells; iPS: Induced pluripotent stem cells.
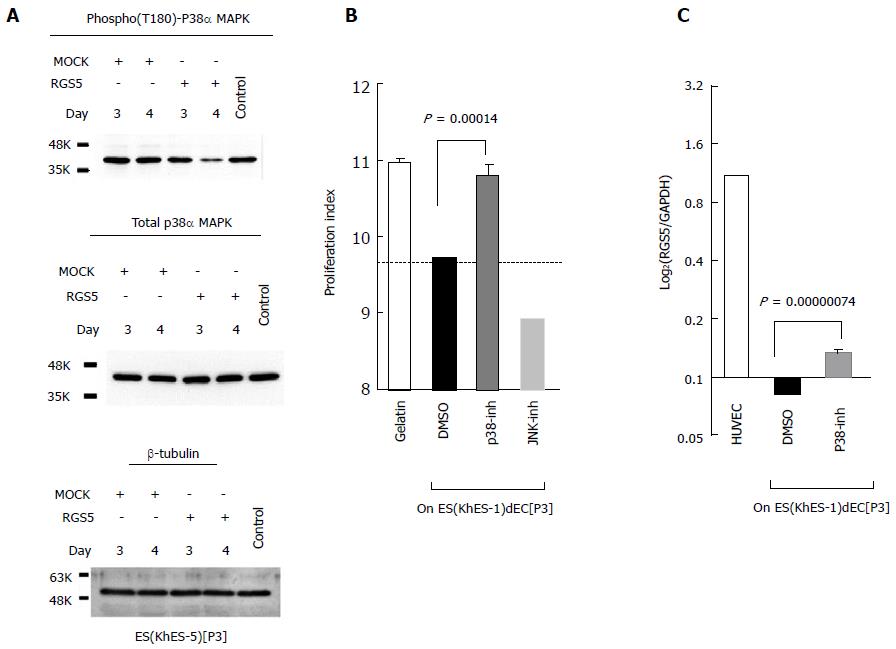
Figure 3 Involvement of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the phenotype regulation of human vascular endothelial cells.
A: Type-II ESdECs were transfected with either an RGS5 expression vector or an empty vector by nucleofection and subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies after 3 or 4 d; B: Type-II ESdECs were treated with either 0.1% DMSO, a p38 MAPK inhibitor (10 μmol/L) or a JNK inhibitor (10 μmol/L) for three days and subjected to co-cultures with human aortic smooth muscle cells (n = 3, AV ± SD); C: Type-II ESdECs were treated by a p38 MAPK inhibitor (10 μmol/L). Next day, RGS5 expressions were examined by qRT-PCR (n = 4, AV ± SD). RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; ESdECs: Embryonic stem cells-derived vascular endothelial cells; DMSO: Dimethylsulfoxide; JNK: Jun N-terminal kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; qRT-PCR: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
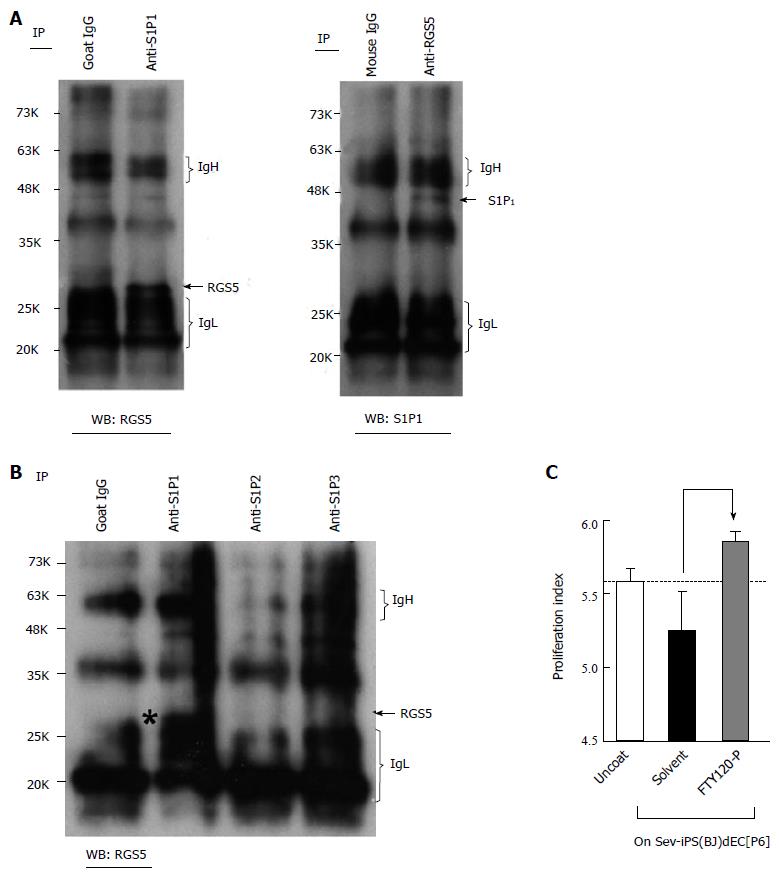
Figure 4 Interaction between sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors and regulator of G-protein signaling 5 in type-I vascular endothelial cells.
A and B: Immunoprecipitation (IP) followed by Western blotting (WB) was performed using HUVEC lysates and indicated antibodies; C: Human aortic smooth muscle cells were subjected contact co-culture experiments with type-II VECs with or without 1 nmol/L FTY720-P (n = 3, AV ± SD). HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; VECs: Vascular endothelial cells; SeV-iPS: Sendai virus vector-based induced pluripotent stem cells; RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5.
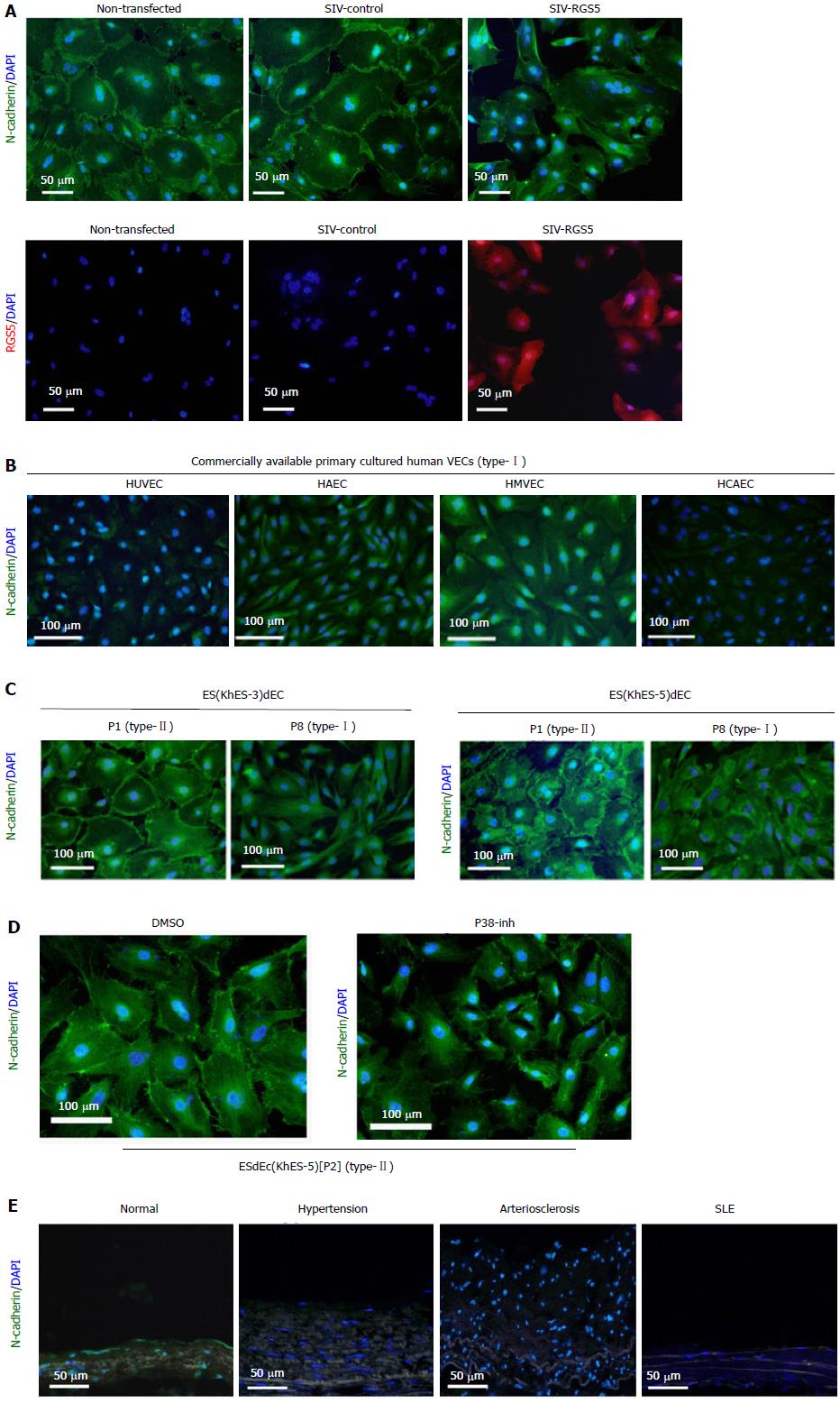
Figure 5 Effects of regulator of G-protein signaling 5 on the intracellular localization of N-cadherin.
A: Type-II VECs were infected with SIV vectors carrying either human RGS5 cDNA (SIV-RGS5) or inverted human RGS5 cDNA (SIV-control) and subjected to immunostaining using an anti-N-cadherin antibody (green) or anti-RGS5 antibody (red); B-E: Immunostaining studies using an anti-N-cadherin antibody (green) with nuclear counterstaining with DAPI (blue) were performed using commercially available primary cultured human VECs (type-I) (B), ESdECs at early (type-II) and late (type-I) passages (C), ESdECs at early passages (type-II) treated with 0.1% DMSO or a p38 inhibitor (10 μmol/L) (D) and clinical specimens (E). HCAEC: Human adult coronary arterial endothelial cells; HAEC: Human adult aortic endothelial cells; HMVEC: Human neonatal dermal microvascular endothelial cells; HUVEC: Human umbilical vein endothelial cells; ESdECs: Embryonic stem cells-derived vascular endothelial cells; RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; DMSO: Dimethylsulfoxide; VECs: Vascular endothelial cells.
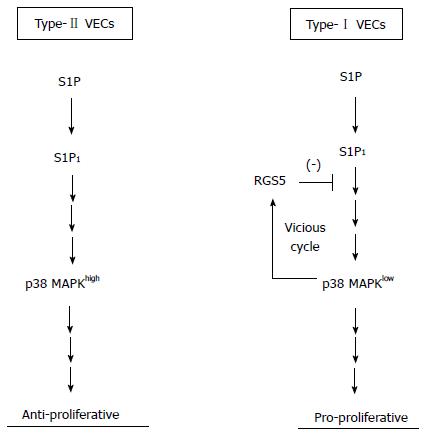
Figure 6 A model for roles of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in the regulation of vascular endothelial cells phenotypes.
MAPK: Mmitogen-activated protein kinase; RGS5: Regulator of G-protein signaling 5; S1P: Sphingosine-1-phosphate; VECs: Vascular endothelial cells.
- Citation: Nakahara M, Nishio M, Saeki K, Yuo A, Saeki K. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase regulates type-I vs type-II phenotyping of human vascular endothelial cells. World J Transl Med 2015; 4(3): 101-112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6132/full/v4/i3/101.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5528/wjtm.v4.i3.101