Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
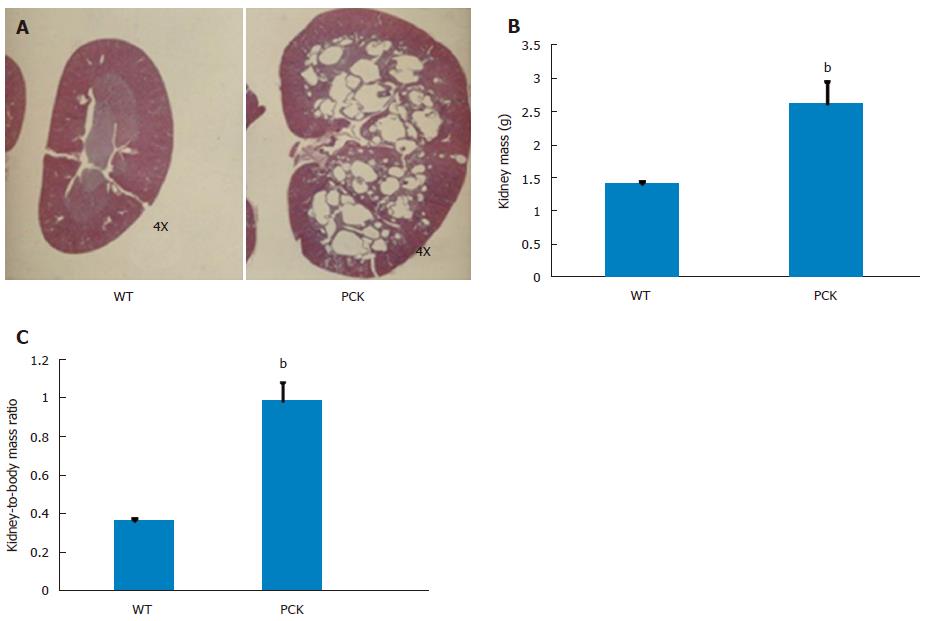
Figure 1 Renal characteristics in the PCK rat.
A: Renal sagittal sections from 6 wk old wild-type (WT, Sprague-Dawley) and PCK rats showing an enlarged renal parenchyma and the medulla almost completely occupied with numerous cysts in the latter; B, C: At this time point, both kidney mass (B) and kidney-to-body mass ratio (C) were greater in the PCK rat (bP < 0.01, vs WT).
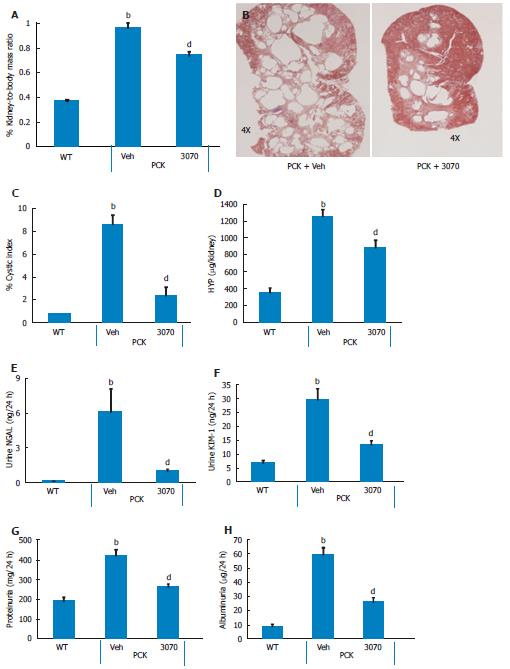
Figure 2 ANG3070 therapy attenuates renal mass, cystic index, renal injury, fibrosis and renal dysfunction.
A, C: By approximately 10 wk of age, PCK rats [vehicle (Veh) cohort] had significantly larger renal mass and renal-to-body mass ratio (A) and increased cystic index (C) compared to the age-matched WT cohort (bP < 0.01); B: Representative hematoxylin and eosin (HE)-stained renal sagittal sections (B) from PCK + Veh and a PCK + ANG3070 rats demonstrating cystic distribution across the renal parenchyma. Treatment of PCK rats with ANG3070 from weeks six to ten was associated with reduced kidney mass and kidney-to-body mass ratio (A) (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); C: Treatment with ANG3070 reduced renal cystic index (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); D: Total kidney hydroxproline (a marker of collagen) content was increased at week ten in the PCK (Veh) rat, treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in this marker of kidney fibrosis (bP < 0.01, vs WT; dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); E, F: Compared to the WT cohort, PCK (Veh) rats exhibited renal injury evidenced by increased urine neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) (E) and urine kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) (F) (bP < 0.01, vs WT). Treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in these urinary markers (E and F) of renal injury; G, H: Renal dysfunction, evidenced by elevated proteinuria (G) and albuminuria (H) was reduced with ANG3070 treatment (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh). HYP: Collagen marker.
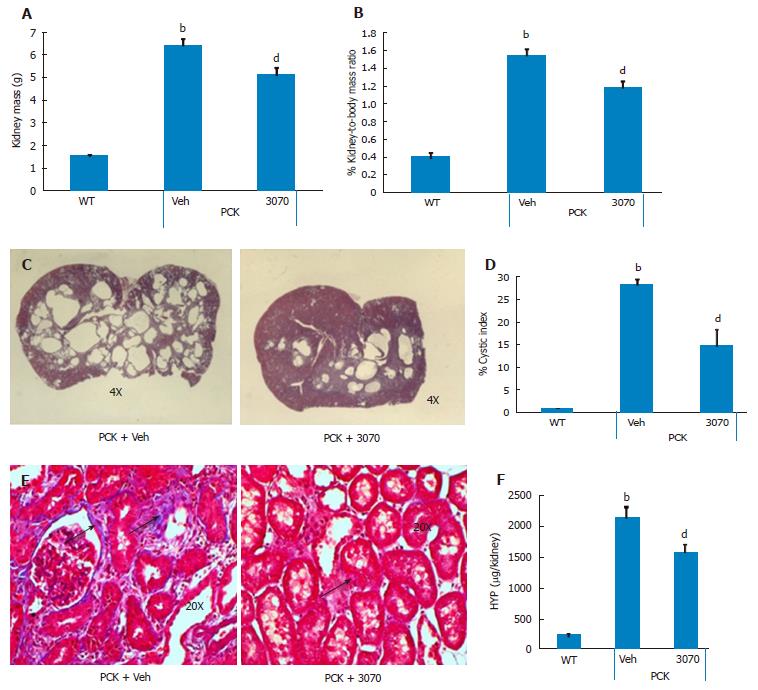
Figure 3 ANG3070 attenuates renal pathology and fibrosis in the PCK rat.
A, B and D: By week 14, kidney mass (A), kidney-to-body mass ratio (B) and renal cystic index (D) were several-fold higher in PCK [vehicle (Veh)] rats compared to the WT cohort (bP < 0.01, vs WT). ANG3070 therapy from weeks 6-14, mitigated renomegaly (A and B); C: Representative H and E-stained renal transverse sections from PCK + Veh and a PCK + ANG3070 rats demonstrating cystic distribution across the renal parenchyma at week 14; D: Treatment with ANG3070 reduced renal cystic index (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + veh); E: Representative Masson’s trichrome stained renal sections from PCK rats showing scarring within the renal interstitium (arrows) of PCK rats; F: Total kidney hydroxyproline (HYP-a marker of collagen) content was increased at week 14 in the PCK (Veh) rat (bP < 0.01, vs WT). Treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in HYP, marker of kidney fibrosis (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh).
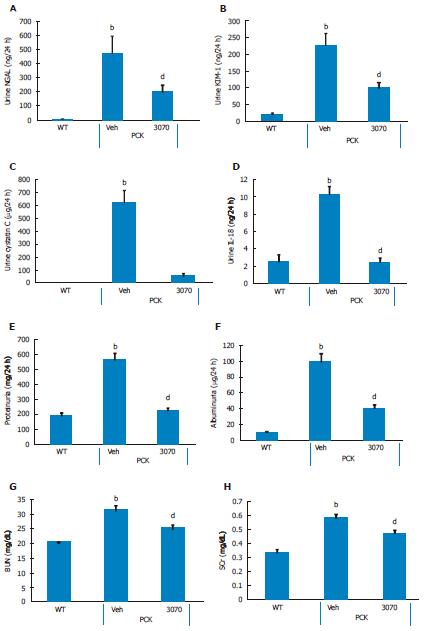
Figure 4 ANG3070 attenuates renal injury biomarkers and renal dysfunction.
A-D: Compared to the WT cohort, at 14 wk of age, PCK [vehicle (Veh)] rats exhibited severe renal injury evidenced by increased urine - neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) (A), kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) (B), cystatin C (C) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) (D) (bP < 0.01, vs WT). Treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in these urinary markers (A-D) of renal injury (dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh); E-H: Renal dysfunction, evidenced by elevated proteinuria (E), albuminuria (F), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) (G) and serum creatinine (SCr) (H), was reduced with ANG3070 treatment (bP < 0.01, vs WT; dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh).
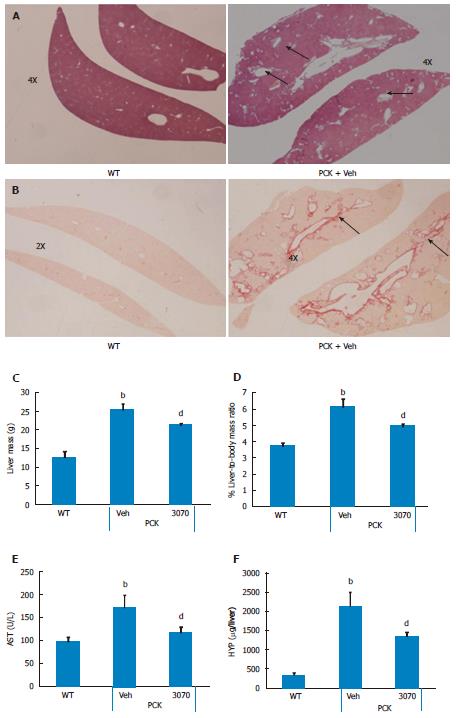
Figure 5 ANG3070 attenuates hepatic lesions, fibrosis and improves liver function in the PCK rat.
A: Compared to the WT cohort, multiple, highly dilated bile ducts (arrows) are visible in H and E-stained PCK [vehicle (Veh)] livers by week 14; B: Representative Picrosirius red-stained liver showing ductal fibrosis (arrows) in the PCK (Veh) cohort; C-F: At sacrifice, PCK rats (Veh) exhibited increased liver mass (C), liver-to-body mass ratio (D) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) (E) compared to the WT cohort. Total liver hydroxyproline content was also increased in the PCK rat (F). Treatment with ANG3070 was associated with a reduction in AST (E), hepatic lesions and fibrosis (HYP: Collagen marker) (A, B, C and F) (bP < 0.01, vs WT; dP < 0.01, vs PCK + Veh).
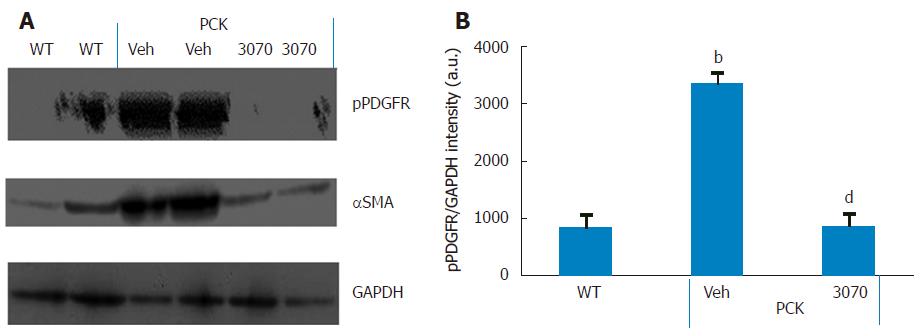
Figure 6 ANG3070 decreases phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor receptor in the PCK rat kidney.
A: Western blot analysis of kidney homogenates showed intense phosphorylated platelet-derived growth factor receptor (pPDGFR) levels in the PCK + vehicle (Veh) cohort compared to the WT and PCK + ANG3070 cohorts. A similar expression profile was seen with the fibrotic marker α smooth muscle actin (αSMA) in these kidneys. GAPDH expression is shown at the bottom; B: pPDGFR in renal homogenates from 10 wk old WT, PCK + Veh and PCK + ANG3070-treated animals was visualized with anti-PDGFR-α antibody and submitted to densitometric analysis with normalization to GAPDH. ANG3070 treatment was associated with a marked reduction in phosphorylated PDGFR levels (bP < 0.01, vs WT; dP <0.01, vs PCK + Veh).
- Citation: Paka P, Huang B, Duan B, Li JS, Zhou P, Paka L, Yamin MA, Friedman SL, Goldberg ID, Narayan P. A small molecule fibrokinase inhibitor in a model of fibropolycystic hepatorenal disease. World J Nephrol 2018; 7(5): 96-107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v7/i5/96.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v7.i5.96