Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
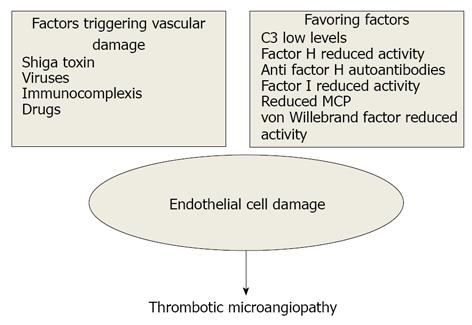
Figure 1 Pathogenetic mechanisms of thrombotic microangiopathy.
MCP: Membrane cofactor protein.
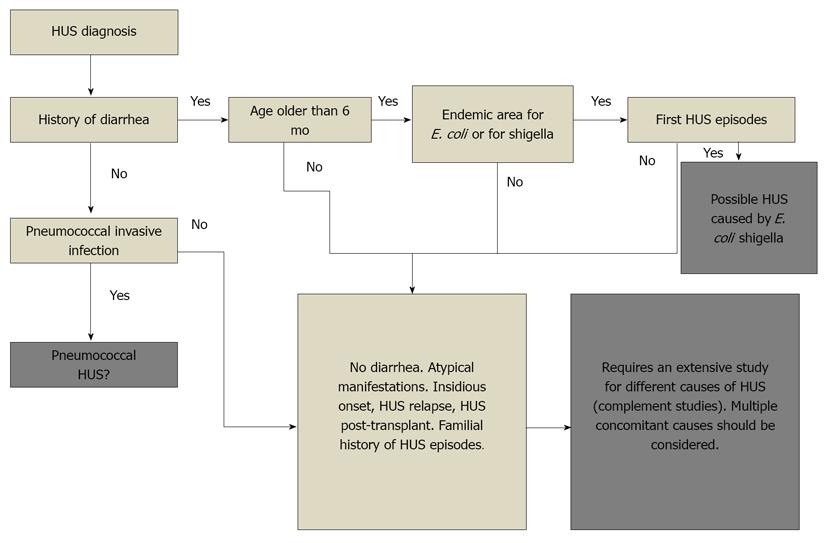
Figure 2 Diagnostic algorithm to distinguish among different Hemolytic uremic syndrome.
HUS: Hemolytic uremic syndrome; E. coli: Escherichia coli.
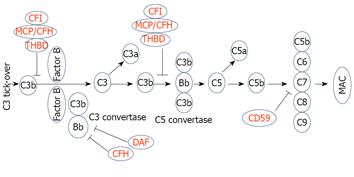
Figure 3 Alternative pathway.
The alternative pathway is triggered by spontaneous activation of C3. Activation of this pathway leads to MAC formation which results in cell lysis (in red complement regulatory proteins; in black complement activating factors). CFH: Complement factor H; CFI: Complement factor I; DAF: Decay accelerating factor; MAC: Membrane attack complex; MCP: Membrane cofactor protein; THBD: Thrombomodulin.
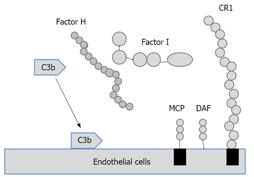
Figure 4 Complement regulatory factors.
CR1: Complement receptor 1; DAF: Decay-accelerating factor; MCP: Membrane cofactor of proteolysis.
- Citation: Salvadori M, Bertoni E. Update on hemolytic uremic syndrome: Diagnostic and therapeutic recommendations. World J Nephrol 2013; 2(3): 56-76
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v2/i3/56.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v2.i3.56