Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Nephrol. Dec 25, 2024; 13(4): 95761
Published online Dec 25, 2024. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v13.i4.95761
Published online Dec 25, 2024. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v13.i4.95761
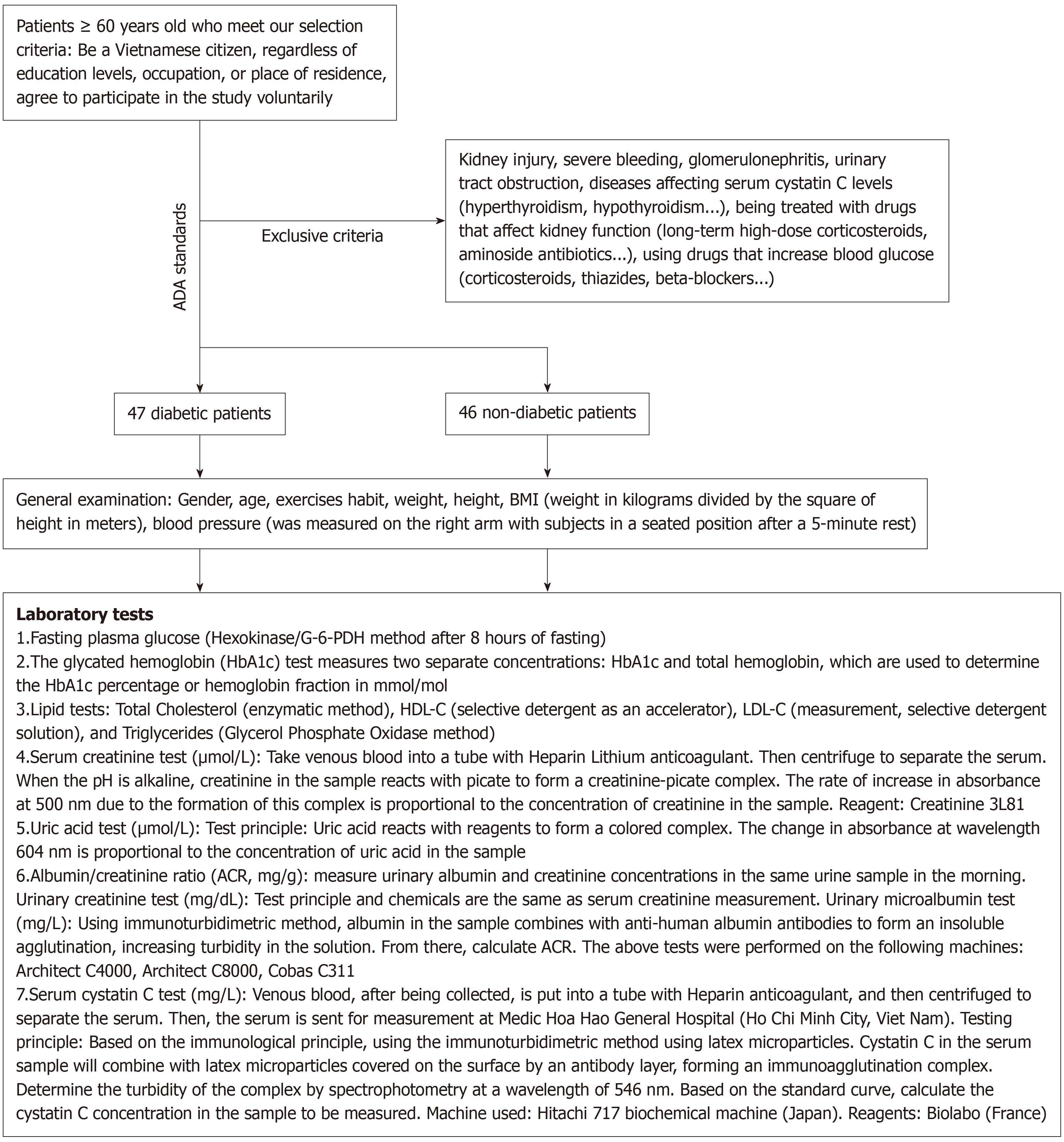
Figure 1 Study flowchart.
ADA: American Diabetes Association; BMI: Body mass index; G-6-PDH: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; HbA1c: Glycated hemoglobin; HDL-C: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; ACR: Albumin/creatinine ratio.
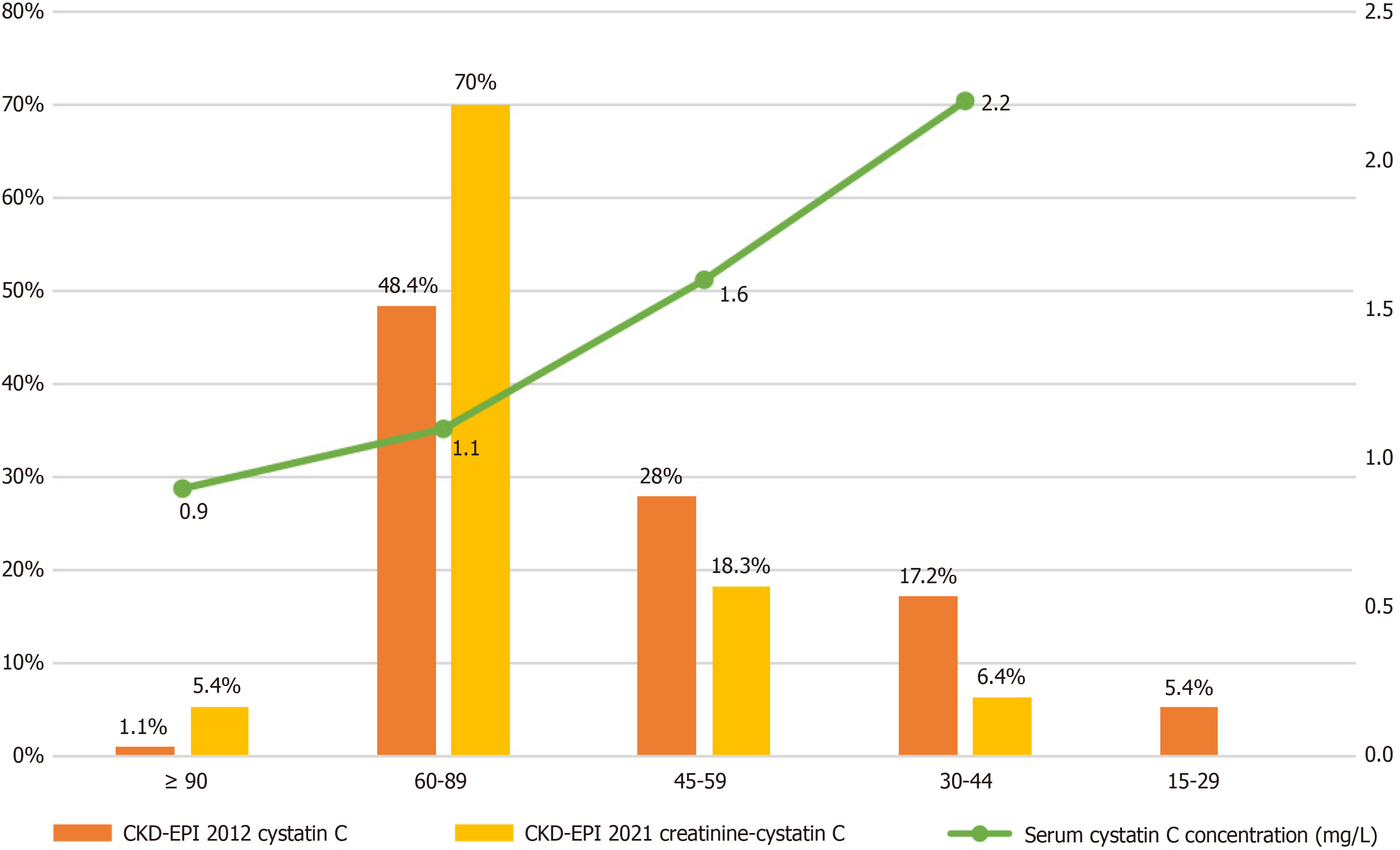
Figure 2 Distribution of study participants in estimated glomerular filtration rate values (mL/min/1.
73m2) according to cystatin C-based equations and the relationship between average serum cystatin C concentration (mg/L) and estimated glomerular filtration rate values. CKD-EPI: Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration.
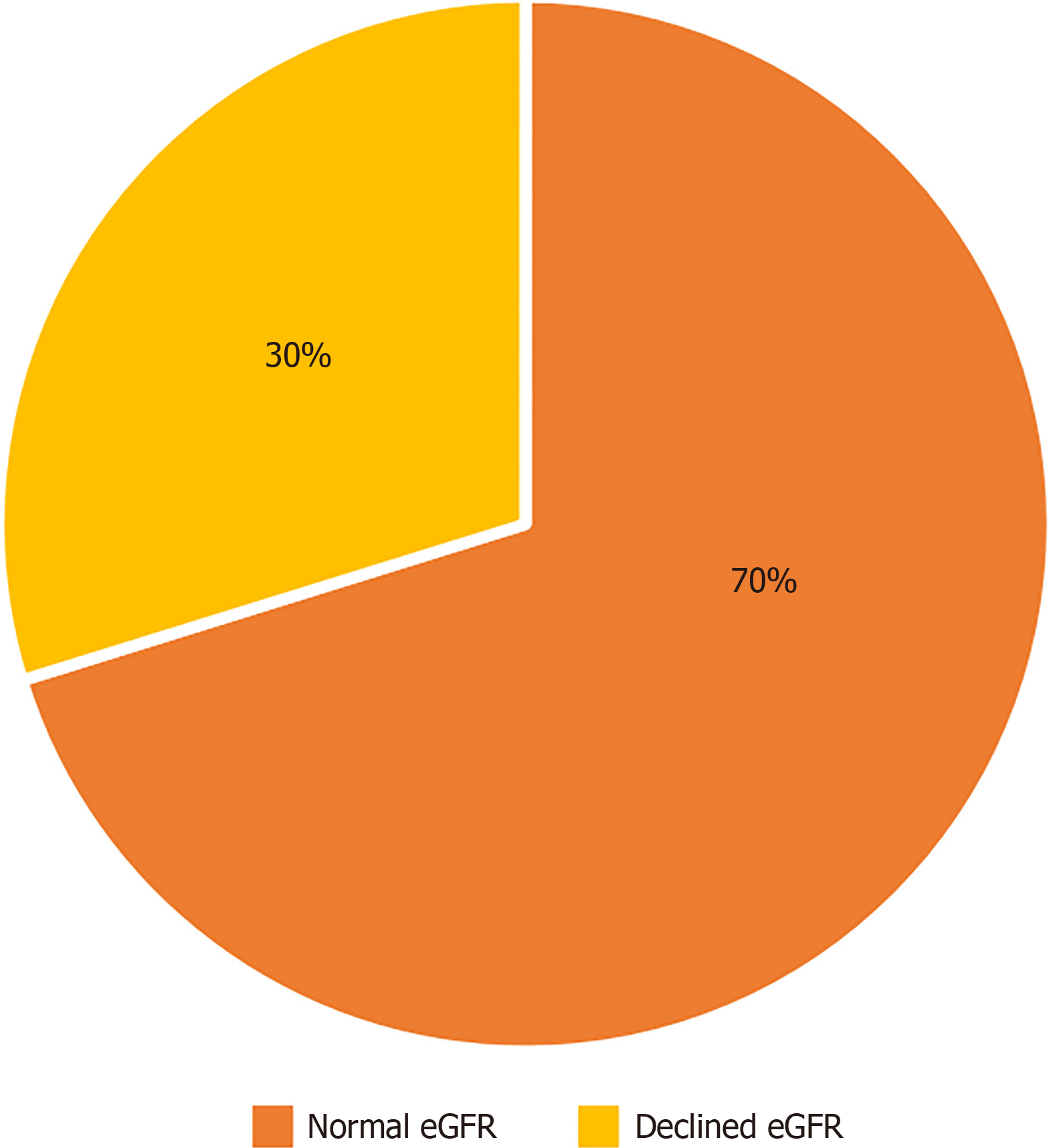
Figure 3 The percentage of estimated glomerular filtration rate decline in elderly diabetic patients.
The estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was determined by the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration 2021 creatinine-cystatin C, then the percentage of patients who have declined eGFR (eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2) was calculated. eGFR: Estimated glomerular filtration rate.
- Citation: Tran TTT, Ha TK, Phan NM, Le MV, Nguyen TH. Detection of decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate in patients with type 2 diabetes by cystatin C-based equations. World J Nephrol 2024; 13(4): 95761
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v13/i4/95761.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v13.i4.95761