Copyright
©2012 Baishideng.
World J Nephrol. Dec 6, 2012; 1(6): 184-194
Published online Dec 6, 2012. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v1.i6.184
Published online Dec 6, 2012. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v1.i6.184
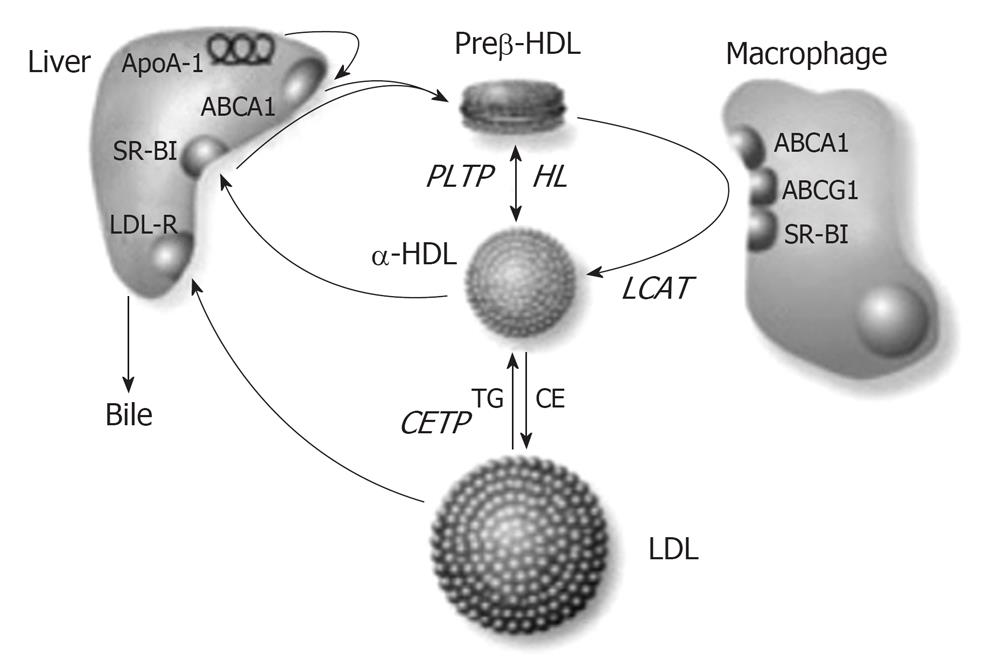
Figure 1 Diagram of the lecithin: cholesterol acyltransferase reaction[18].
Cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) cleaves the fatty acid (R2) from the sn-2 position of phosphatidylcholine and then transesterifies it to the A-ring of cholesterol, producing lysophosphatidylcholine and cholesteryl ester. CE: Cholesteryl ester; CETP: Cholesteryl ester transfer protein; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; TG: Triglyceride; SR-BI: Scavenger receptor class B type I.
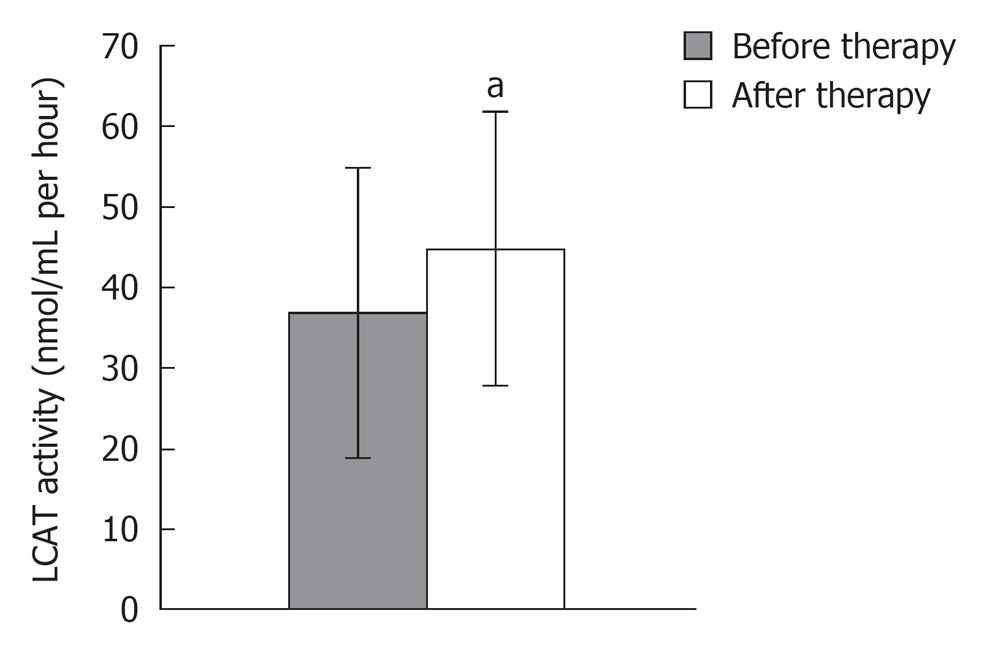
Figure 2 The impact of atorvastatin on the activity of lecithin: Cholesterol acyltransferase enzymes of high-density-lipoprotein remodelling[21].
LCAT: Cholesterol acyltransferase. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Scarpioni R, Ricardi M, Albertazzi V, Melfa L. Treatment of dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease: Effectiveness and safety of statins. World J Nephrol 2012; 1(6): 184-194
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-6124/full/v1/i6/184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v1.i6.184