Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Sep 25, 2022; 11(5): 310-320
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.310
Published online Sep 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.310
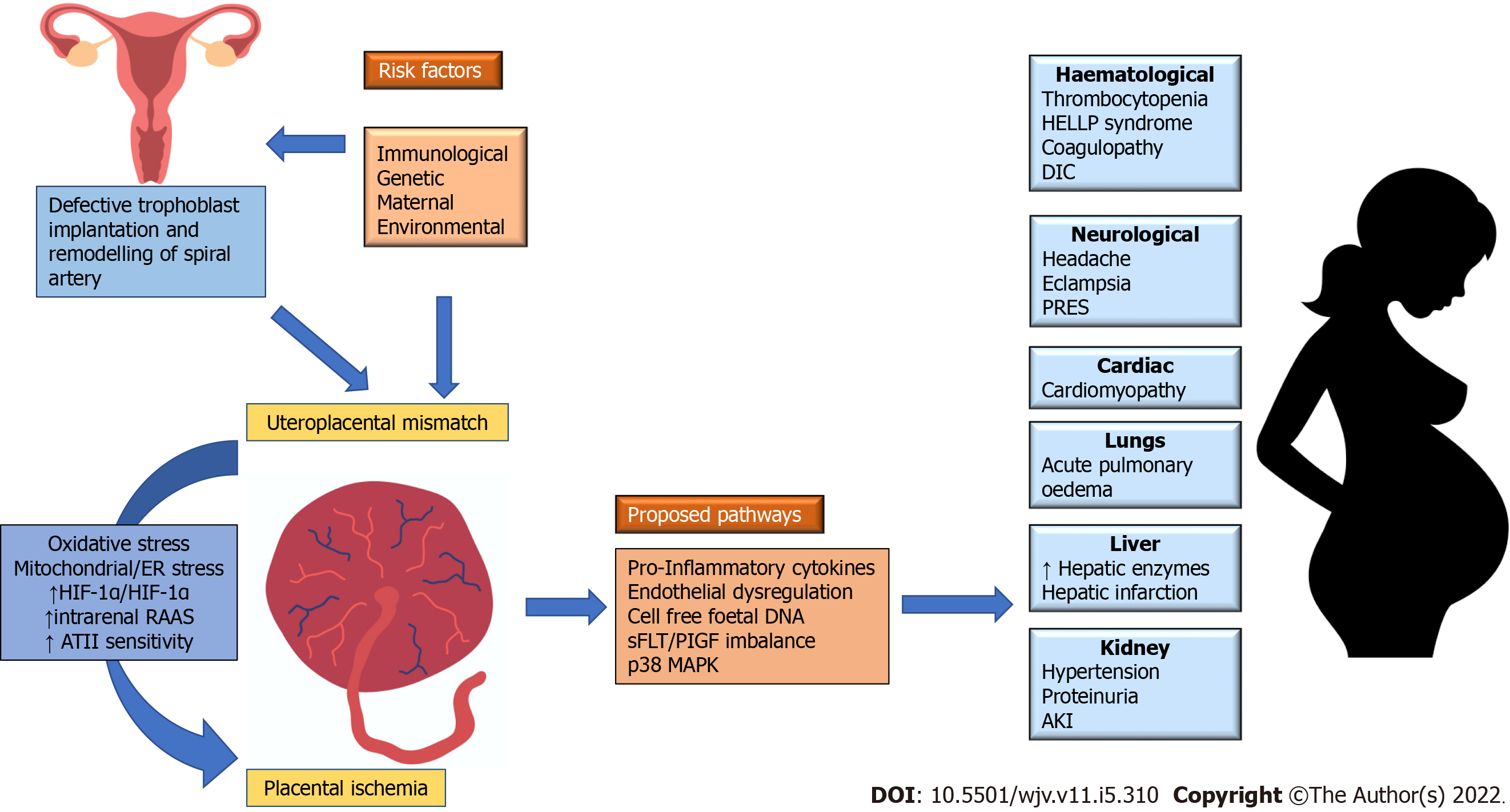
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet syndrome.
Placenta ischemia is central mechanism which is suspected to play a central role in hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet (HELLP) syndrome. Abnormal trophoblast implantation and remodelling of uterine arteries along with genetic, environmental, nutritional, or maternal risk factors cause uteroplacental perfusion mismatch. Various pathways proposed for systemic manifestations of HELLP syndrome include, releases of inflammatory cytokines, endothelial dysfunction, release of cell-free fetal DNA, imbalance of soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase to placental growth factor ratio (sFLT/PIGF ratio). HELLP: Hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and low platelet; ATII: Angiotensin II; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha; RAAS: Renin angiotensin aldosterone system; sFlt/PlGF: Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase and platelet growth factor ratio; ↑: Increased.
- Citation: Nasa P, Juneja D, Jain R, Nasa R. COVID-19 and hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes and thrombocytopenia syndrome in pregnant women - association or causation? World J Virol 2022; 11(5): 310-320
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i5/310.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i5.310