Published online Jul 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i4.198
Peer-review started: December 24, 2021
First decision: March 16, 2022
Revised: May 1, 2022
Accepted: June 21, 2022
Article in press: June 21, 2022
Published online: July 25, 2022
Processing time: 209 Days and 22.4 Hours
Persistent hiccups, lasting more than 48 h, have been described as an atypical presentation of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) in the general population. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of persistent hiccups and non-ST elevation myocardial injury (NSTEMI) as an atypical presentation of COVID-19 in a peritoneal dialysis (PD) patient.
A 70-year old man, who had been on PD for 3 years with a history of ischemic heart failure and reduced ejection fraction, presented for a scheduled radionuclide myocardial scan. Upon arrival, he complained of anorexia, nausea for 5 d, and unremitting hiccups for the previous 48 h. Clinical and laboratory examinations revealed an NSTEMI plus a positive nasopharyngeal reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. COVID-19 lung involvement was mild and was resolved without specific treatment. Myocardial injury was managed by coronary catheterization and stenting, while hiccups responded only to baclofen per os.
Persistent hiccups and NSTEMI can be atypical presentations of COVID-19 in peritoneal dialysis patients, which may be due to involvement of the central nervous system and myocardial injuries.
Core Tip: A 70-year old man with end-stage kidney disease on peritoneal dialysis, presented for a scheduled myocardial scan due to ischemic heart failure. Upon arrival, he complained of persistent hiccups during the last 2 d along with anorexia and vomiting for the last 5 d. He was diagnosed with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI). Hiccups and NSTEMI are postulated to represent atypical COVID-19 manifestations involving the nervous system and the heart.
- Citation: Bacharaki D, Giannakopoulos P, Markakis K, Papas C, Theodorou A, Zoi V, Tsivgoulis G, Lionaki S. COVID-19 presenting with persistent hiccup and myocardial infarction in a peritoneal dialysis patient: A case report. World J Virol 2022; 11(4): 198-203
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i4/198.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i4.198
The usual presentation of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19) includes fever and cough in the general population and in dialysis patients[1]. Gastrointestinal symptoms including anorexia, nausea, and vomit have also been described, although more rarely than in chronic renal patients[2]. Persistent hiccups, i.e., lasting more than 48 h, have been infrequently described in the general population with COVID-19[3,4]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of COVID-19 presenting with persistent hiccups and non-ST elevation myocardial injury (NSTEMI) in a peritoneal dialysis (PD) patient.
A 70-year-old man with end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) maintained on PD, presented in April 2021 for a scheduled myocardial scan, having ischemic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (35%). Upon arrival, he complained for anorexia, nausea, and vomit tendency and unremitting hiccups.
Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms started 5 d ago and persistent hiccups 2 d ago, preventing him from eating and considerable sleeping. He denied any abdominal pain, stool change, cloudy PD fluids, fever, chest discomfort, symptoms suggestive of gastroesophageal reflux, or change of his custom PD regimen. His medications included metoprolol, monosorbide, ramipril, simvastatin/ezetimibe, furosemide, acetylsalicylic acid, pantoprazole, folic acid, and darbepoetin injections. He denied any new drug initiation or new dietary habits.
The patient’s past medical history was significant for cardiorenal syndrome following myocardial infarction in 2000, with coronary angioplasty and stent insertion, arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia, and a recent diagnosis (one month) of seronegative rheumatoid arthritis. Notably, 15 d prior to presentation, he had been admitted due to anemia (hemoglobin fall to 7.7 g/dL), nausea, and appetite loss, all attributed to recent initiation of leflunomide 10 mg daily for rheumatoid arthritis. At that time, C reactive protein was 141mg/L (reference < 6 mg/L), white blood cell count 6280/μL, serum urea 89 mg/dL, creatinine 6.5 mg/dL, and ferritin 642 ng/mL.
He was managed with red blood cells infusions and discontinuation of leflunomide. He was discharged in 2 d with Hb 9.4 g/dL, stable high sensitive troponin 209 pg/mL (reference < 14 pg/mL, while the patient’s high sensitive troponin routine assessment values were between 255-430 pg/mL), free of gastrointestinal symptoms, with good appetite and negative nasopharyngeal reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) testing for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2).
ESKD due to cardiorenal syndrome; PD initiated 3 years ago; carpal tunnel syndrome diagnosed 1 year ago; former truck driver; and no special family history.
Physical examination revealed a weight loss of nearly 2 kg (74 kg), temperature of 36.5 °C, oxygen saturation 98% on room air, and low blood pressure (117/73 mmHg, heart rate 90 beats per minute in sitting position). No signs of peripheral edema nor pulmonary congestion were noted. Abdominal examination was negative, as was heart and lung auscultation. The patient appeared ill with persistent hiccups, weakness, anorexia, and vomit tendency, in contrast with his relatively good clinical condition on discharge 13 d ago.
Peritoneal dialysis fluid analysis revealed a normal cytology and biochemistry and negative Gram staining. Serum laboratory examination revealed C reactive protein of 36.8 mg/L, hemoglobulin of 9.8 g/dL, white blood cell count 4530/μL (neutrophils 58%, lymphocytes 28%), stable serum urea and creatinine, ferritin 855 ng/L, but troponin elevation to 1650 pg/mL.
Electrocardiography showed a sinus rhythm with left bundle branch block, not different compared to previous tracings while echocardiography revealed worsening of ejection fraction to 25%. Routine nasopharyngeal RT-PCR arranged upon admission revealed a positive result and he was transferred to the COVID clinic.
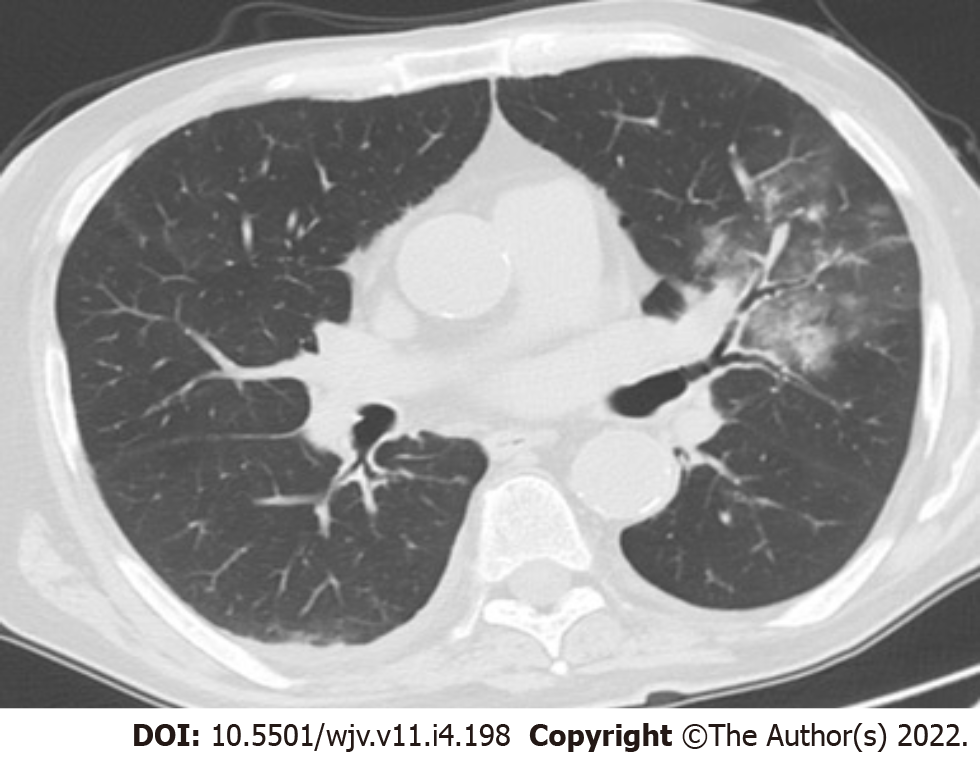
Due to severe co-morbidities and a positive RT-PCR test for SARS-CoV-2, chest computed tomography was performed, showing signs of mild COVID-19 pneumonia, i.e., less than 10% degree of lung infiltration in the right upper lobe, as small areas of ground glass opacities and small areas of atelectasis (Figure 1).
Mild COVID-19 pneumonia; NSTEMI; and persistent hiccups due to SARS-CoV-2 nervous system involvement.
Due to mild pneumonia, the patient did not receive any specific treatment for COVID-19. Regarding NSTEMI, he received dual antiplatelet therapy and Enoxaparin subcutaneously on a daily basis. He continued his usual ambulatory PD regimen of four daily glucose-based PD exchanges, 2000 mL each (glucose 1.5% and 2.25% alternating) with a daily ultrafiltration of 1000-1200 mL. Due to persistent hiccups and anorexia that prevented him from eating and drinking, he received intravenously one liter of semi-isotonic glucose solution daily with potassium supplementation. Metoclopramide injections three times per day were prescribed for hiccups and then replaced by Chlorpropamide 25 mg three times per day after 2 d of intractable hiccups. On the 7th day, Baclofen tablets was given orally, at a dose of 10 mg per os daily for 5 d.
Upon initiation of baclofen tablets, the patient’s hiccups improved significantly and they ceased completely within 48 h. As a result, the patient was able to eat and sleep, claiming to be in good condition despite NSTEMI and COVID-19. He remained euvolemic with stable arterial pressure records (around 110/70 mmHg, 70 pulses/min). He did not experience any chest discomfort and his troponin values gradually fell to previous baseline levels. Maximum temperature was 37.3 °C but oxygen saturation remained stable at 98% on room air.
A coronary angiogram was performed on the 12th day of hospitalization (on negative COVID-19 PCR), which revealed a significant stenosis at the proximal segment of the first obtuse marginal branch, while the previous stent was intact. A coronary angioplasty was performed 1 mo later with stent implantation and recovering of ejection fraction to 35%.
This patient presented for as scheduled appointment, complaining of nausea, anorexia, and unremitting hiccups. He had not changed his PD regimen, nor his dietary habits or medical prescription. Clinical assessment revealed NSTEMI and mild COVID-19 pneumonia of the upper right lobe. Unremitting hiccups remained his main problem while hospitalized.
Hiccup is caused by diaphragmatic muscle contractions with early glottis closure terminating inspiration. Its pathogenesis is still obscure but lately is considered a deranged neural loop connecting the brain stem and diaphragm[5]. Persistent hiccups, lasting more than 48 h, have been associated with central nervous system, cardiovascular, thoracic, metabolic, and gastrointestinal disorders[5].
Uremia as a potential cause of gastrointestinal symptoms and/or hiccups was excluded, due to stable biochemical parameters and unchanged urinary output or PD regimen. Electrolyte and acid base disturbances were absent. Another potential cause of persistent hiccups could be gastro-esophageal reflux[6], which is a common complication of PD[7], but the symptoms were missing. Pneumonia caused by common pathogens[8] as well as by SARS-CoV-2[3,4] has been reported as a cause of persistent hiccups. Interestingly, apart from cases of lower lobe pneumonia, which would suggest direct irritation of the diaphragm as a potential mechanism resulting in hiccups[8], the association of persistent hiccups with COVID-19 has increasing publications with other sites of lung involvement[9]. Noteworthily, our patient had only minor infiltration in the upper lobe on chest computed tomography (Figure 1). Persistent hiccups have also been reported as an associated symptom in cases of myocardial infarction, primarily in the inferior myocardial wall, thus in proximity with the diaphragm, suggesting that hiccups could be triggered by irrigation of the phrenic nerves or alternatively by the vagus nerve supplying the pericardium, but rarely as the only presenting symptom[10]. There is a case report of persistent hiccups as an atypical presentation of non-ST elevation myocardial injury[11]. In our case, there was a gradual fall of cardiac troponin levels while the hiccup was still persisting, responding eventually only to baclofen. The stenosed vessel, as revealed by angiography (the proximal segment of the first obtuse marginal branch), perfuses the infero-lateral myocardial wall.
Furthermore, nausea and vomiting can be associated symptoms of myocardial infarction[12] and more rarely the presenting symptom in atypical cases[13].
On the other hand, there are numerous reports associating myocardial injuries and infarctions with COVID-19, with potential causes being direct myocyte injury and prothrombotic effect of SARS-CoV-2 infection[12]. Nevertheless, it is still difficult to differentiate between non-COVID acute coronary syndrome and COVID-19 induced acute myocardial injury[14]. Noteworthy, gastrointestinal symptoms, such as diarrhea (more often) nausea and vomiting, often accompany COVID-19, either by direct infection of GI cells or indirectly[15], although diarrhea was absent in our patient. Since the underlying mechanisms of persistent hiccups are various disorders (structural, infectious, and inflammatory) that impact either the central nervous system or the phrenic nerves or their branches[16], one could speculate that COVID-19 could be linked causally with hiccups by nervous system involvement[17].
Baclofen is a gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptor agonist approved as a medication to control spasticity[18]. It has been used successfully for persistent hiccups of different etiologies with an action attributed to either reduction of dopamine release in the central nervous system, which could interrupt hiccup's reflex arc or induction of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations, by stimulating gamma-aminobutyric acid B receptors in the motor nucleus of the vagal nerve and nucleus tract solitarious[18]. Hiccups attributed to COVID-19 have been managed with hydroxychloroquine, metoclopramide, and chlorpropamide, as well as a combination scheme with baclofen included[3,4,9]. In this case, hiccups did not respond to metoclopropamide nor chlorpropamide, but on the contrary had an immediate and complete response to baclofen.
Based on the above, COVID-19 may be the unifying cause of all. Anorexia, vomit tendency, and hiccup could be manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 gastrointestinal[15] and/or nervous system involvement[16,17,18,19]. Non-ST myocardial infraction could also be a manifestation of COVID-19[11]. COVID-19 induced endotheliitis could be the underlying pathophysiology of nervous system and heart involvement[18,20].
A case of atypical presentation of COVID-19 in a PD patient with persistent hiccups and NSTEMI is described here. We may speculate that they could be the result of SARS-CoV-2 involvement of the nervous system and heart, respectively. Baclofen seems to be the drug of choice for persistent hiccups even in patients with ESKD.
We acknowledge the support and contribution in the management of the COVID-19 patient of the nurses of Hemodialysis and Peritoneal Dialysis Unit: Irene Zorba, Dimitra Siopi, Athina Maniati, Zoi Polymerou, and Lambrini Xoxakou.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Infectious diseases
Country/Territory of origin: Greece
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Chen GX, United States; Rajcani J, Slovakia S-Editor: Yan JP L-Editor: Wang TQ P-Editor: Yan JP
| 1. | Valeri AM, Robbins-Juarez SY, Stevens JS, Ahn W, Rao MK, Radhakrishnan J, Gharavi AG, Mohan S, Husain SA. Presentation and Outcomes of Patients with ESKD and COVID-19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020;31:1409-1415. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 259] [Cited by in RCA: 285] [Article Influence: 57.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Cao C, Chen M, He L, Xie J, Chen X. Clinical features and outcomes of COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms. Crit Care. 2020;24:340. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 4.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Prince G, Sergel M. Persistent hiccups as an atypical presenting complaint of COVID-19. Am J Emerg Med. 2020;38:1546.e5-1546.e6. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 4.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Ali SK, Muturi D, Sharma K. Be Wary of Hiccups: An Unusual Case of COVID-19. Cureus. 2021;13:e12974. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Brañuelas Quiroga J, Urbano García J, Bolaños Guedes J. Hiccups: a common problem with some unusual causes and cures. Br J Gen Pract. 2016;66:584-586. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Fisher MJ, Mittal RK. Hiccups and gastroesophageal reflux: cause and effect? Dig Dis Sci. 1989;34:1277-1280. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Song HJ, Kim SM, Lee YM, Hwang JA, Moon KM, Moon CG, Koo HS, Song KH, Kim YS, Lee TH, Huh KC, Choi YW, Kang YW, Hwang WM, Yun SR. Is there a difference in the prevalence of gastroesophageal reflux disease between peritoneal dialysis and hemodialysis patients? Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013;62:206-212. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Karakonstantis S, Pitsigavdaki S, Korela D, Galani D. Lower lobe pneumonia presenting as singultus (hiccups). Caspian J Intern Med. 2018;9:403-405. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Sene DR, Watashi DM, Bilitardo IO, Moreno CEC, Moreno MFF. COVID-19 presenting as persistent hiccups: a case report. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 2021;63:e62. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Shaikh N, Raj R, Movva S, Mattina C. Persistent Hiccups as the Only Presenting Symptom of ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Case Rep Cardiol. 2018;2018:7237454. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Davenport J, Duong M, Lanoix R. Hiccups as the only symptom of non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Am J Emerg Med. 2012;30:266.e1-266.e2. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Herlihy T, McIvor ME, Cummings CC, Siu CO, Alikahn M. Nausea and vomiting during acute myocardial infarction and its relation to infarct size and location. Am J Cardiol. 1987;60:20-22. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 26] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Brieger D, Eagle KA, Goodman SG, Steg PG, Budaj A, White K, Montalescot G; GRACE Investigators. Acute coronary syndromes without chest pain, an underdiagnosed and undertreated high-risk group: insights from the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events. Chest. 2004;126:461-469. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 336] [Cited by in RCA: 342] [Article Influence: 16.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Bae JY, Hussein KI, Howes CJ, Setaro JF. The Challenges of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction in COVID-19 Patients. Case Rep Cardiol. 2021;2021:9915650. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Cameli M, Pastore MC, Mandoli GE, D'Ascenzi F, Focardi M, Biagioni G, Cameli P, Patti G, Franchi F, Mondillo S, Valente S. COVID-19 and Acute Coronary Syndromes: Current Data and Future Implications. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020;7:593496. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Jin B, Singh R, Ha SE, Zogg H, Park PJ, Ro S. Pathophysiological mechanisms underlying gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with COVID-19. World J Gastroenterol. 2021;27:2341-2352. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 41] [Cited by in RCA: 34] [Article Influence: 8.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Alvarez-Cisneros T, Lara-Reyes A, Sansón-Tinoco S. Hiccups and psychosis: two atypical presentations of COVID-19. Int J Emerg Med. 2021;14:8. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Norouzi M, Miar P, Norouzi S, Nikpour P. Nervous System Involvement in COVID-19: a Review of the Current Knowledge. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58:3561-3574. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Mirijello A, Addolorato G, D'Angelo C, Ferrulli A, Vassallo G, Antonelli M, Leggio L, Landolfi R. Baclofen in the treatment of persistent hiccup: a case series. Int J Clin Pract. 2013;67:918-921. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Calabretta E, Moraleda JM, Iacobelli M, Jara R, Vlodavsky I, O'Gorman P, Pagliuca A, Mo C, Baron RM, Aghemo A, Soiffer R, Fareed J, Carlo-Stella C, Richardson P. COVID-19-induced endotheliitis: emerging evidence and possible therapeutic strategies. Br J Haematol. 2021;193:43-51. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 13.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |