Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
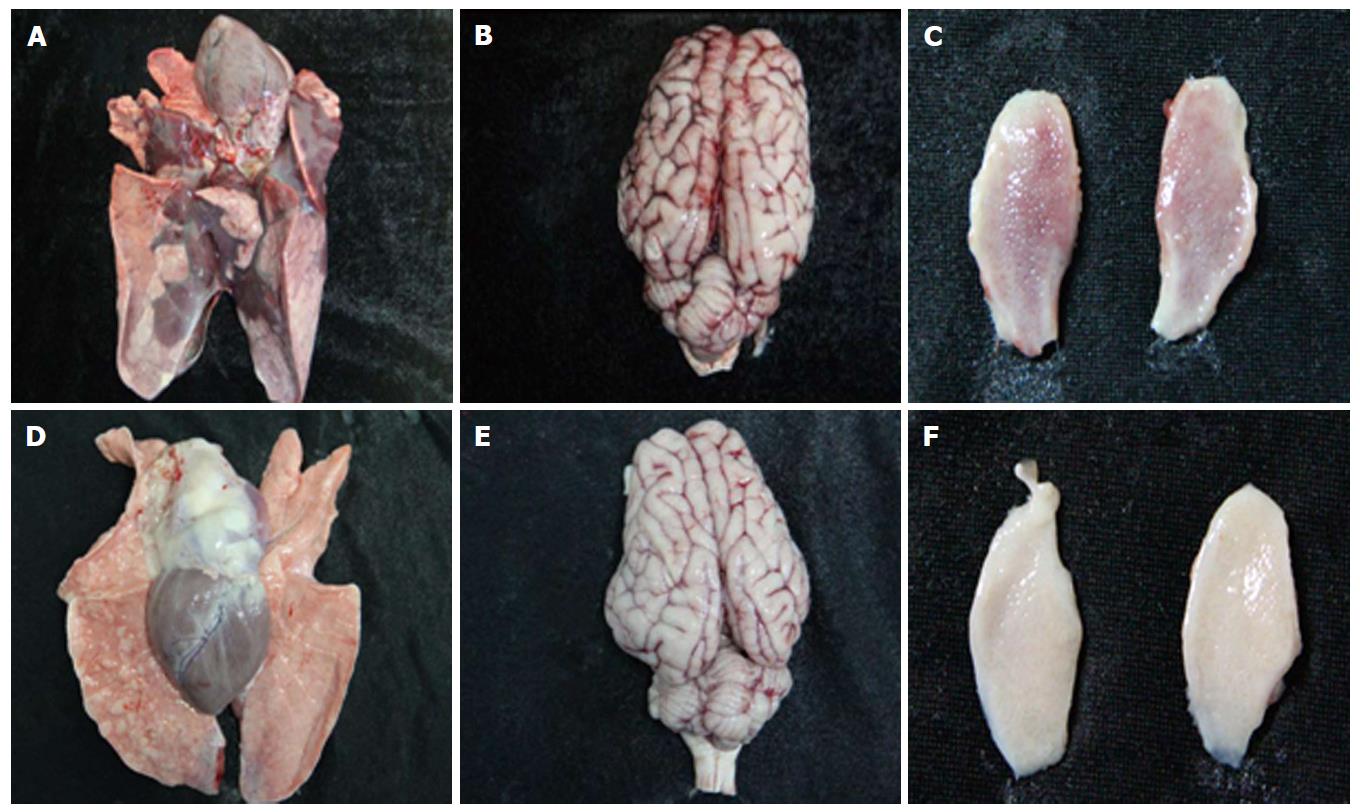
Figure 1 Gross pathology examination at necropsy.
Lung, brain, and tonsil samples after PRV HN1201 (A-C) or Fa strain infection (D-F). PRV: Pseudorabies virus.
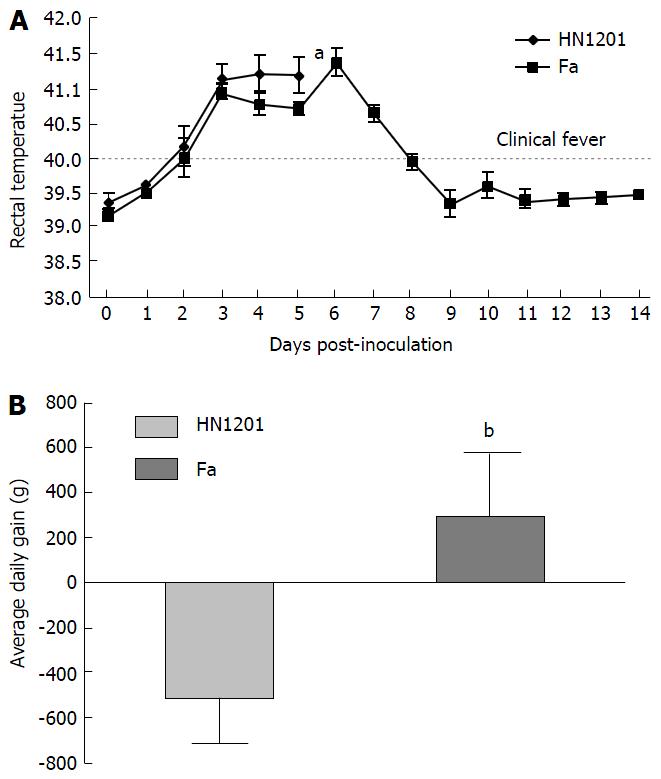
Figure 2 Rectal temperature (A) and average daily (B) body weight gain (6 d post-inoculation) of pigs after pseudorabies virus HN1201 or Fa infection.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001.
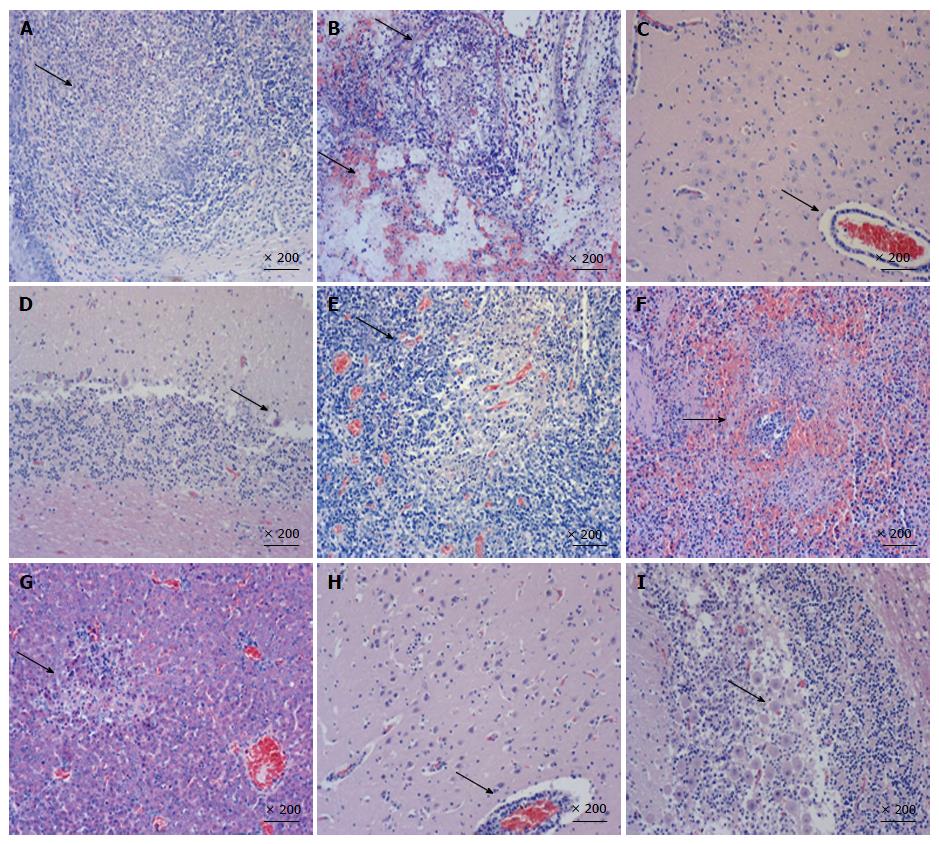
Figure 3 Hematoxylin and eosin staining of multiple tissues of pigs inoculated with HN1201 (A-G) and Fa strain (H and I).
A: Tonsil - tonsillar lymphoid tissue necrosis and formation of large necrotic foci; B: Lung - vascular congestion and hemorrhage (lower arrow), with bronchial epithelial necrosis and necrotic cells within the lumen (upper arrow); C: Brain - lymphocyte infiltration around the small blood vessels in the brain cortex, non-suppurative encephalitis; D: Cerebellum - Purkinje cell degeneration and necrosis; E: Hilar lymph nodes - vascular dilatation and congestion, and lymphatic tissue necrosis; F: Spleen - white pulp structure disappeared and white necrotic marrow lymphocytes formed large necrotic foci; G: Liver - necrotic foci formation; H: Brain - coalescing non-suppurative encephalitis with neuronal degeneration and perivascular cuffing; I: Cerebellum - Purkinje cell degeneration and necrosis.
- Citation: Yang QY, Sun Z, Tan FF, Guo LH, Wang YZ, Wang J, Wang ZY, Wang LL, Li XD, Xiao Y, Tian KG. Pathogenicity of a currently circulating Chinese variant pseudorabies virus in pigs. World J Virol 2016; 5(1): 23-30
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v5/i1/23.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v5.i1.23