Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Virology. May 12, 2015; 4(2): 36-41
Published online May 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i2.36
Published online May 12, 2015. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v4.i2.36
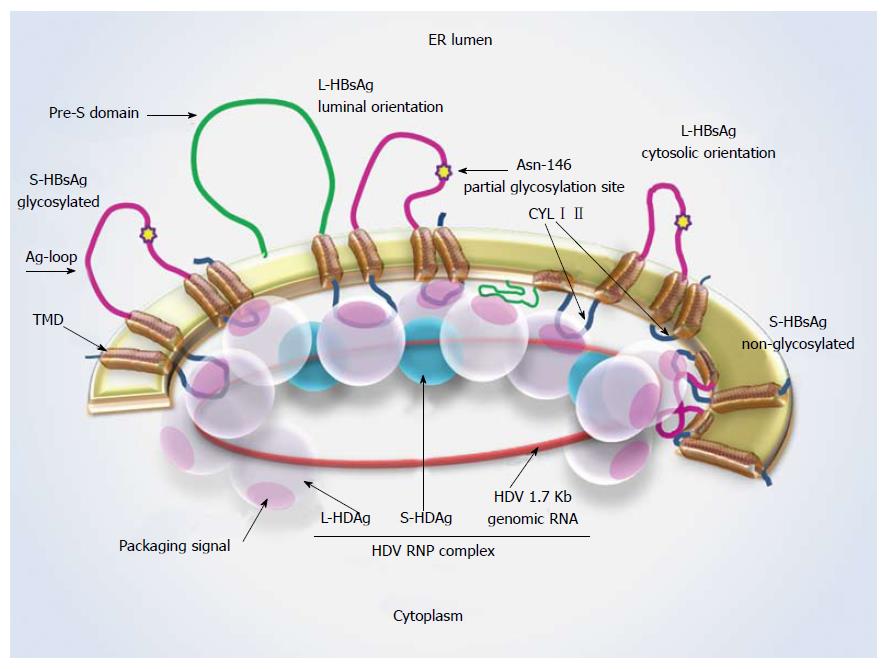
Figure 1 Hepatitis D virus-ribonucleoprotein complex interaction with S-hepatitis B virus surface antigen.
Schematic representation of L- and S-HBsAg locations in the ER membrane and the interaction sites with the HDV-RNP complex. The Asn-146 glycosylation site is highlighted by a star. About half of the residues remain non-glycosylated at this site. A cytosolic orientation has been suggested for the non-glycosylated Ag loop, which may interfere with HBsAg-HDAg interaction. L-HDAg mediates HDV assembly at the late stage of viral replication through forming connections with HDV-RNA, S-HDAg and HBsAg. Ag loop: Antigenic loop; CYL I, II: Cytosolic loop I, II; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; L-/ S-HBsAg: Large and small hepatitis B virus surface antigens; L-/ S-HDAg: Large and small hepatitis D virus proteins; RNP: Ribonucleoprotein; TMD: Transmembrane domain.
- Citation: Shirvani-Dastgerdi E, Tacke F. Molecular interactions between hepatitis B virus and delta virus. World J Virology 2015; 4(2): 36-41
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v4/i2/36.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v4.i2.36