Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Virol. Jun 25, 2024; 13(2): 91580
Published online Jun 25, 2024. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i2.91580
Published online Jun 25, 2024. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v13.i2.91580
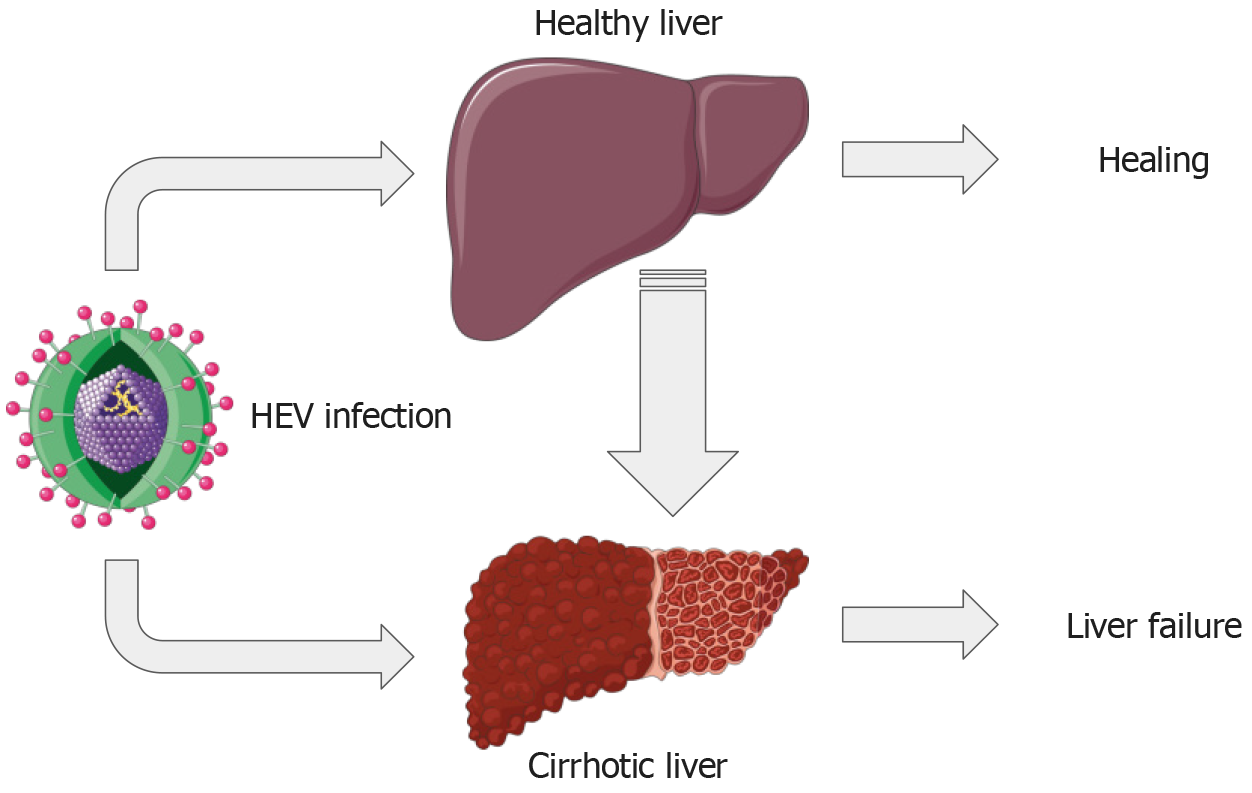
Figure 1 Varying consequences of hepatitis E infection in individuals with healthy and distressed livers.
HEV: Hepatitis E virus. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/3.0/).
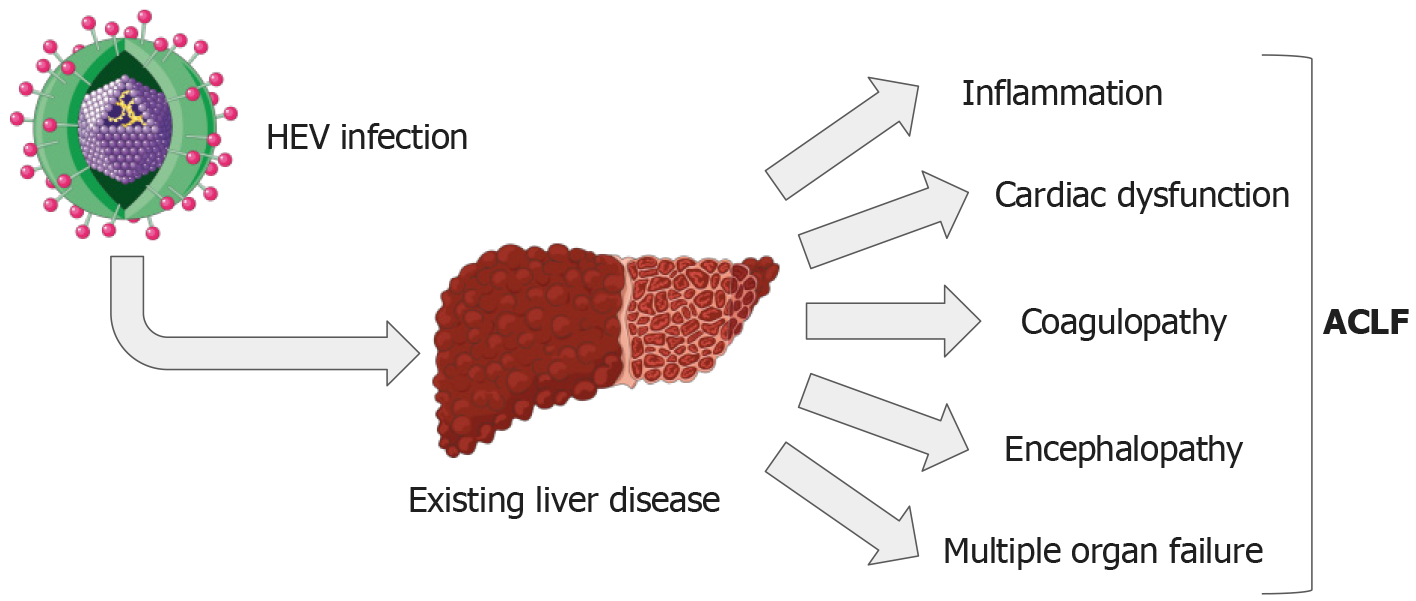
Figure 2 Overview of the impacts of acute-on-chronic liver failure resulting from hepatitis E virus infection in the context of pre-existing liver disease.
HEV: Hepatitis E virus; ACLF: Acute-on-chronic liver failure. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/3.0/).
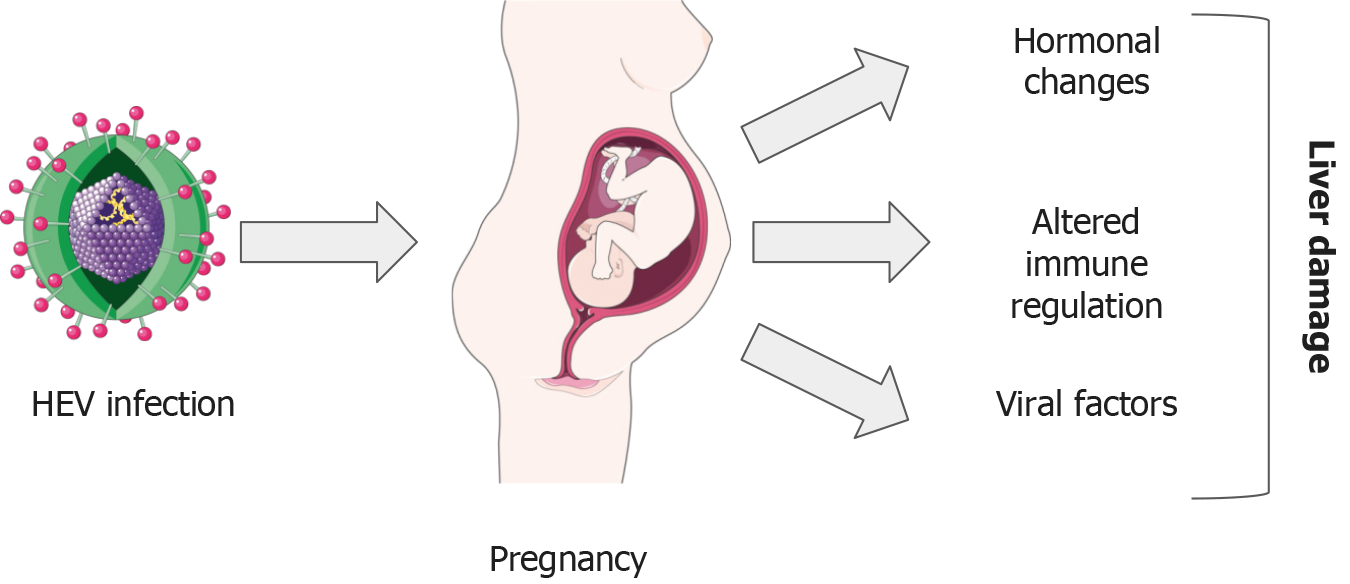
Figure 3 Summary of the adverse effects of hepatitis E infection during pregnancy.
HEV: Hepatitis E virus. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/3.0/).
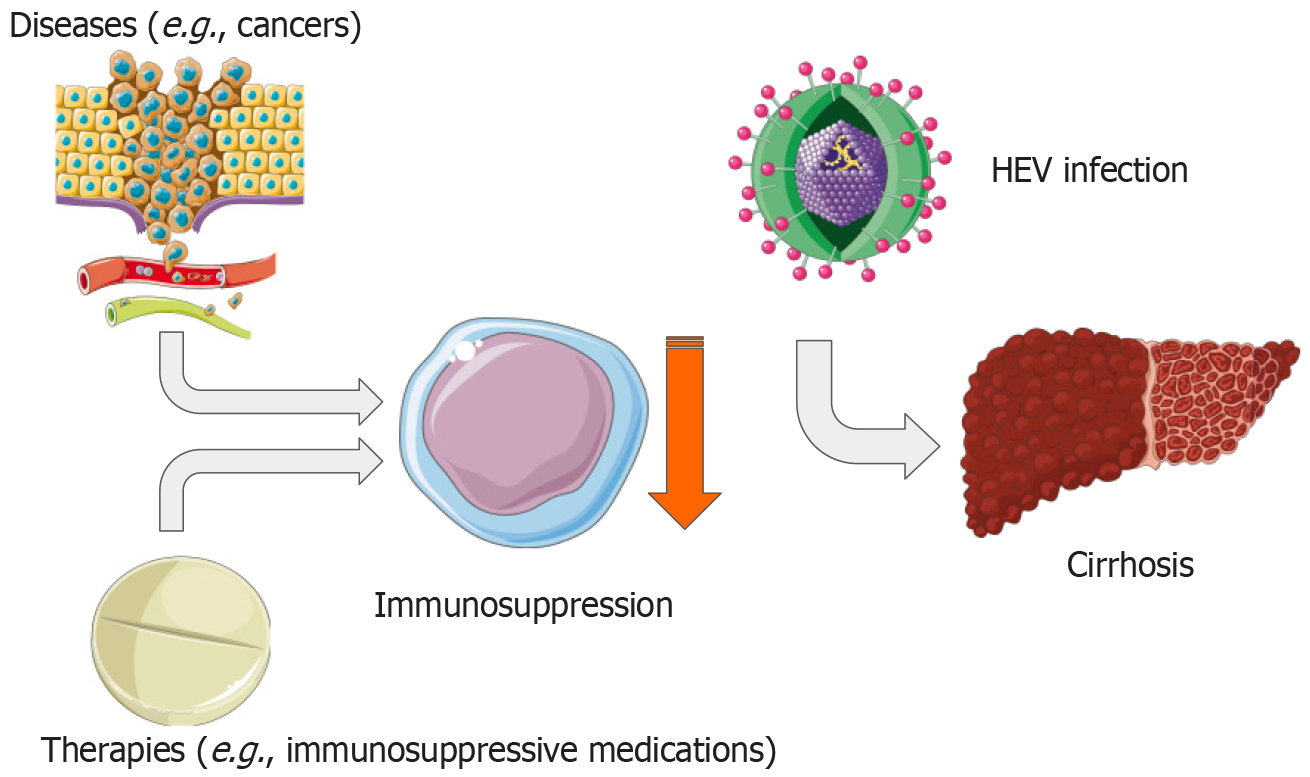
Figure 4 The effects of hepatitis E superinfection on liver health related to disease and therapeutic immunosuppression.
HEV: Hepatitis E virus. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/3.0/).
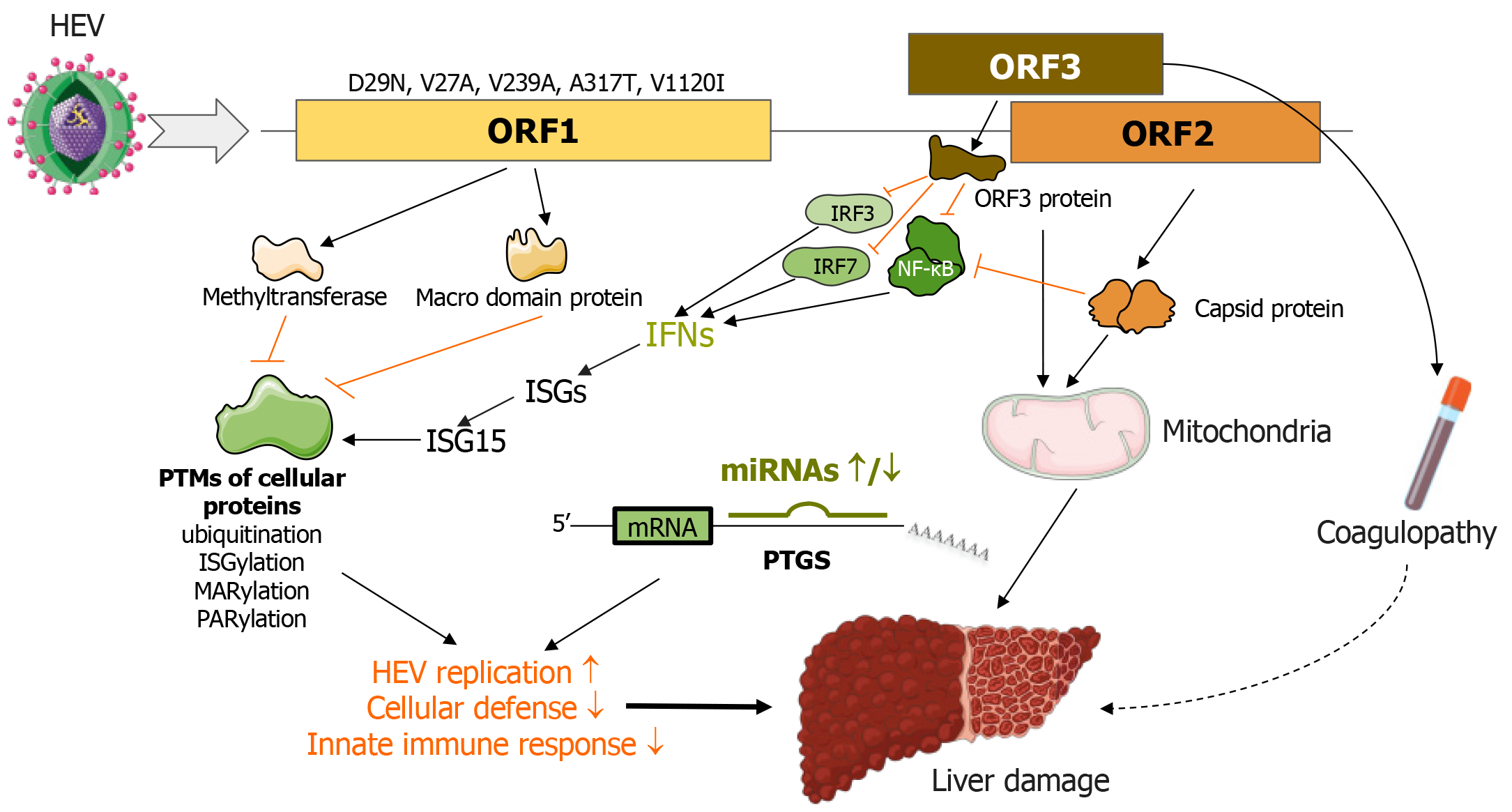
Figure 5 Several viral factors that increase hepatic injury induced by hepatitis E virus.
The solid line with black arrows represents a direct influence, whereas the dashed line with arrows represents an indirect impact. Red lines show inhibitory processes. D29N, V27A, V239A mutations are associated with increased virulence. HEV: Hepatitis E virus; ISGs: Interferon-stimulated genes; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; miRNA: MicroRNA; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB; ORF: Open reading frame; PTM: Post-translational modification; PTGS: Post-transcriptional gene silencing. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/Licenses/by/3.0/).
- Citation: Orosz L, Sárvári KP, Dernovics Á, Rosztóczy A, Megyeri K. Pathogenesis and clinical features of severe hepatitis E virus infection. World J Virol 2024; 13(2): 91580
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v13/i2/91580.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v13.i2.91580