Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Virol. Nov 25, 2022; 11(6): 399-410
Published online Nov 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i6.399
Published online Nov 25, 2022. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v11.i6.399
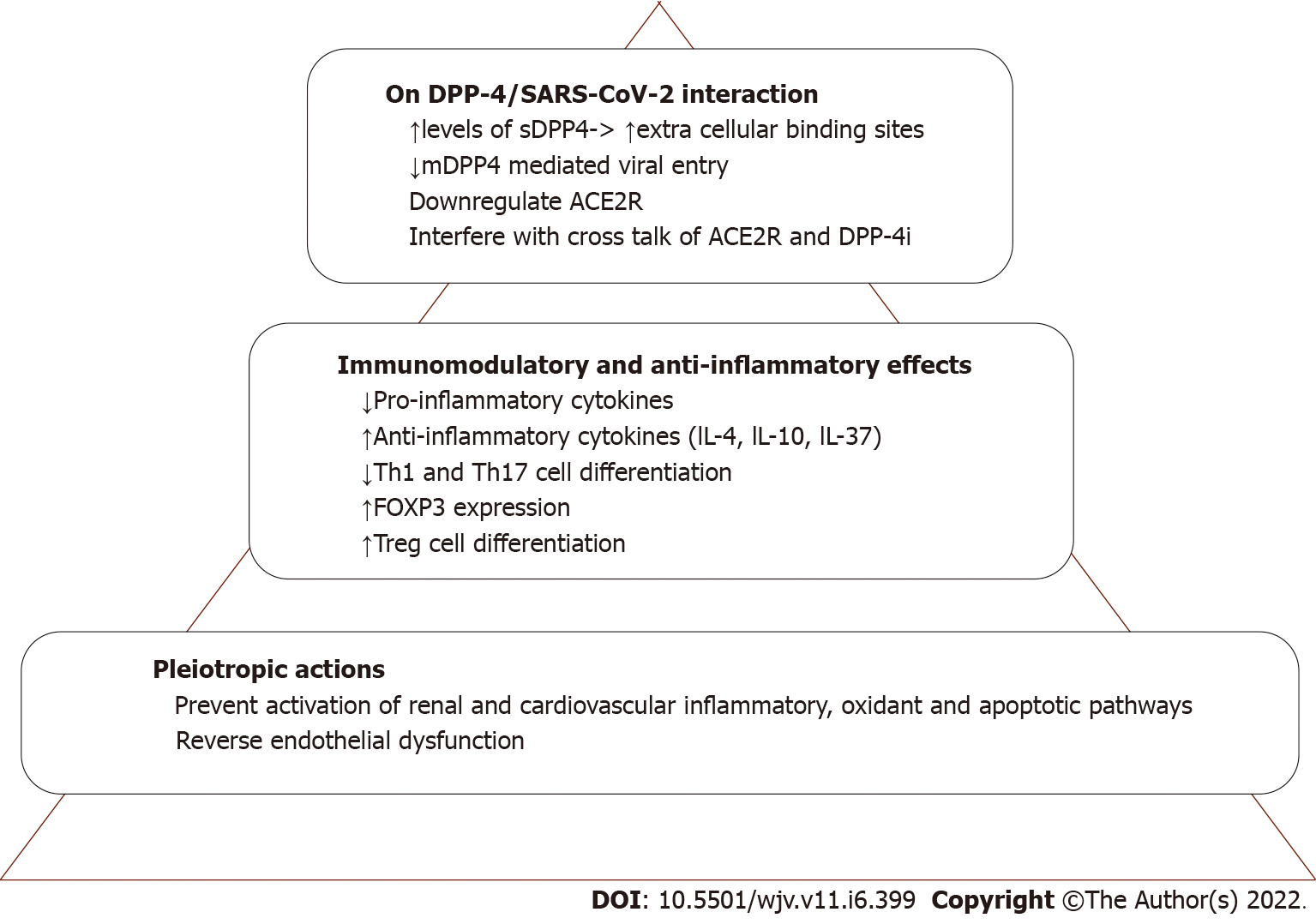
Figure 1 Proposed mechanisms of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in coronavirus disease 2019 infection.
ACE2R: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor; COVID-19: Coronavirus disease 2019; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; FOXP3: Forkhead box P3; IL: Interleukin; mDPP4: Membrane bound DPP4; sDPP4: Soluble DPP4; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor beta.
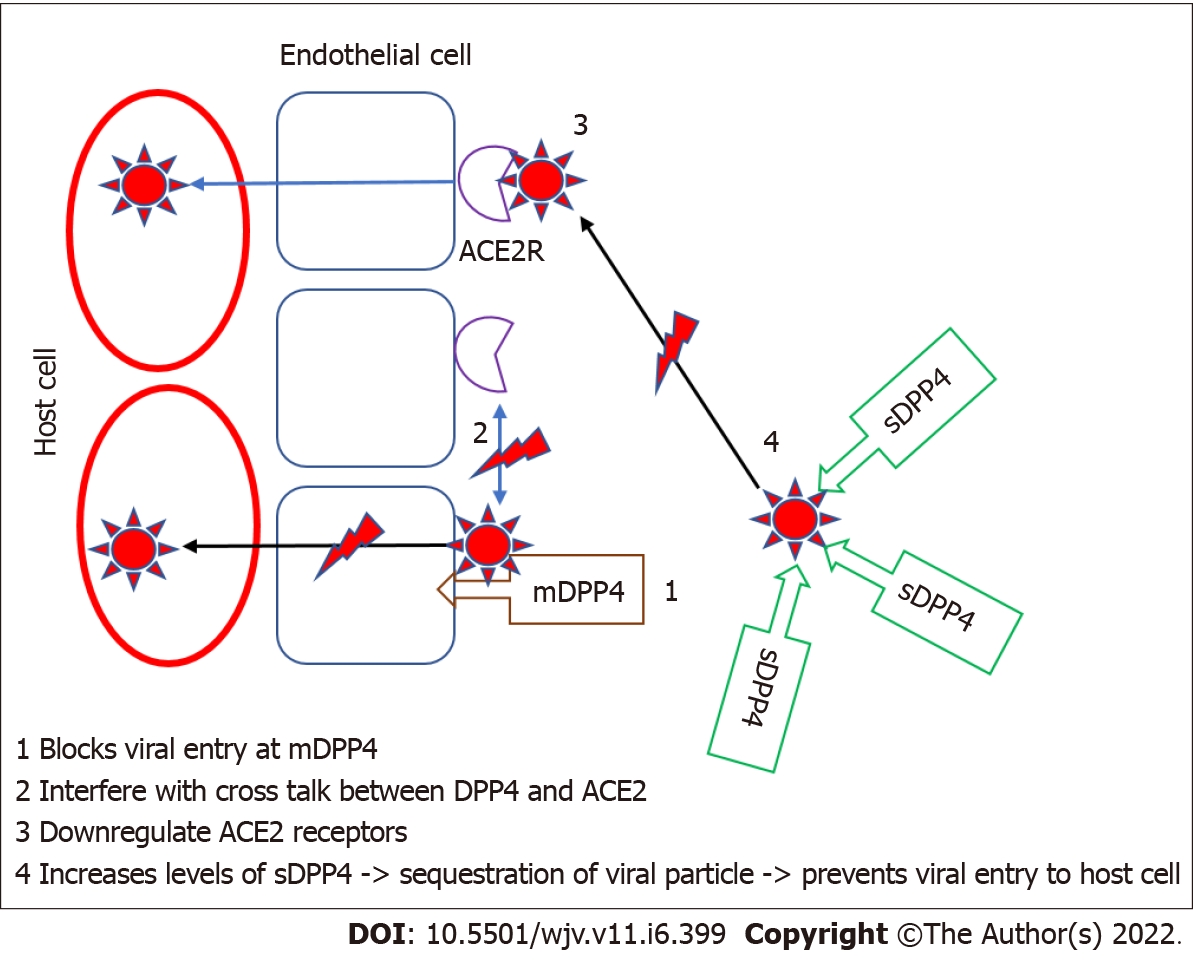
Figure 2 Hypothetical interactions between dipeptidyl peptidase-4 and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 virus.
ACE-2: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ACE2R: Angiotensin converting enzyme 2 receptor; DPP-4: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4; mDPP4: Membrane bound DPP4; sDPP4: Soluble DPP4.
- Citation: Narayanan N, Naik D, Sahoo J, Kamalanathan S. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in COVID-19: Beyond glycemic control. World J Virol 2022; 11(6): 399-410
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v11/i6/399.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v11.i6.399