Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Virol. May 25, 2021; 10(3): 97-110
Published online May 25, 2021. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i3.97
Published online May 25, 2021. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i3.97
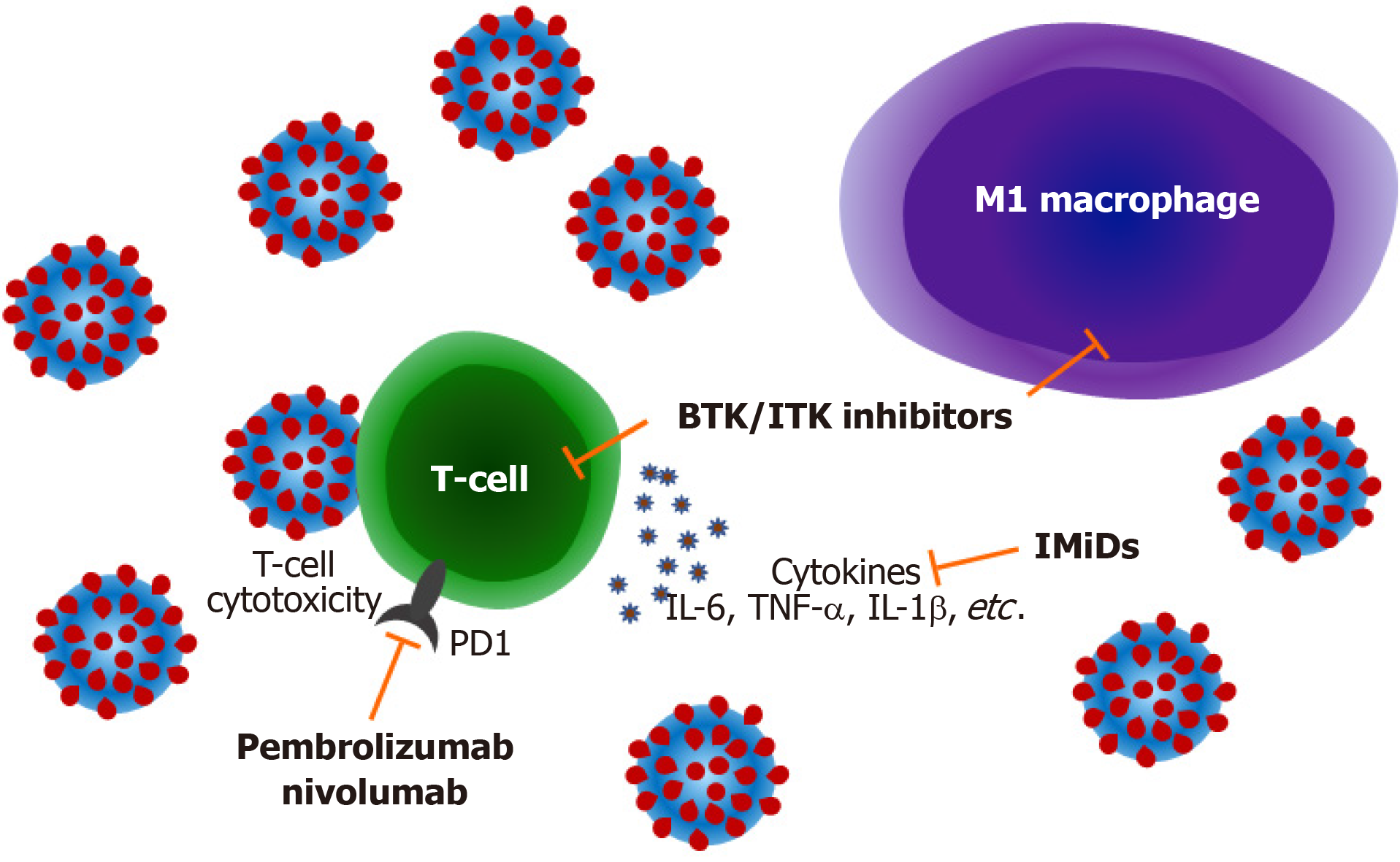
Figure 1 Mechanisms by which lymphoma treatments may modulate coronavirus disease 2019 infection.
Inhibition of Burton's tyrosine kinase and interleukin-2 inducible T-cell kinase modulates T-cell immune responses decreasing production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6, tumour necrosis factor α and interleukin-1b and also attenuating M1 macrophage polarization reducing pulmonary inflammation. Immune checkpoint blockade with drugs targeting programmed cell death 1 may improve antiviral cytotoxic T-cell responses. Immunomodulatory imide drugs can also block cytokine responses and improve T-cell function. BTK: Burton's tyrosine kinase; ITK: Interleukin-2 inducible T-cell kinase; PD1: Programmed cell death 1; IMiDs: Immunomodulatory imide drugs; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumour necrosis factor α.
- Citation: Riches JC. Impact of COVID-19 in patients with lymphoid malignancies. World J Virol 2021; 10(3): 97-110
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3249/full/v10/i3/97.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5501/wjv.v10.i3.97