Published online Feb 18, 2021. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i2.7
Peer-review started: January 14, 2021
First decision: January 25, 2021
Revised: January 28, 2021
Accepted: January 30, 2021
Article in press: January 30, 2021
Published online: February 18, 2021
Processing time: 35 Days and 3.3 Hours
World Journal of Transplantation (WJT) was launched in December 2011. While we are celebrating WJT’s 10-year anniversary, we are very proud to share with you that since its first issue, WJT has published 312 articles, which have been cited 2786 times (average cites per article of 9.0). Together with an excellent team effort by our authors, Editorial Board members, independent expert referees, and staff of the Editorial Office, WJT advanced in 2020. In this editorial, we summarize the journal’s bibliometrics, including its citation report, published articles in 2020, peer review rate and manuscript invitation metrics, as well as its Editorial Board members and existing problems of WJT. The overall aim of this editorial is to promote the development of WJT in 2021. We appreciate the continuous support and submissions from authors and the dedicated efforts and expertise by our invited reviewers. This collective support will allow us to be even more productive in 2021. In addition, we commit to working with you all to raise the academic influence of WJT over the upcoming year. Finally, on behalf of WJT, we wish you and your families the best for the New Year.
Core Tip: World Journal of Transplantation (WJT) was launched in December 2011. Since then, WJT has published 312 articles, which have been cited 2786 times. In this editorial, we summarize the citation report, published articles in 2020, peer review rate, Editorial Board members, manuscript invitations, and existing problems of WJT. We appreciate the support from our authors, Editorial Board members, independent expert referees, and staff of the Editorial Office. With such great support, we expect to further advance WJT in 2021.
- Citation: Yan JP, Akbulut S, Papalois VE, Salvadori M. New Year's greeting and overview of World Journal of Transplantation in 2021. World J Transplant 2021; 11(2): 7-15
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v11/i2/7.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v11.i2.7
As editors of World Journal of Transplantation (WJT), it is our great pleasure to take this opportunity to wish all our authors, readers, Editorial Board members, independent expert referees, and staff of the Editorial Office a very Happy New Year. On behalf of the Editorial Team, we would like to express our gratitude to all authors who contributed their valuable manuscripts, the independent referees, and our readers for their continuous support, dedication, and encouragement. The collective team effort made by our authors, Editorial Board members, independent expert referees, and staff of the Editorial Office, allowed WJT to advance appreciably in 2020.
As you may remember, WJT published its first issue in December 2011. Reflecting on that history today, as we celebrate WJT’s 10-year anniversary, we are very proud to share with you that since its launch, WJT has published 312 articles that have been cited 2786 times, with average cites per article of 9.0. As a global academic journal in the field of transplantation, our authors hail from various countries and regions, reflecting a diversified contribution profile that underlies our goals of having an effective platform by which we may help to promote the worldwide medical research, sharing and exchanging innovative and substantive knowledge.
The highest number of citations of an article published by WJT is 141, and the title of that article is "Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Etiology and treatment"[1], which is a review of kidney transplantation published in June 2015. The corresponding author is Maurizio Salvadori, one of the Editors-in-Chief of WJT.
In 2020, WJT published 37 articles, of which 5 have been cited, as follows: (1) “Therapeutics administered during ex vivo liver machine perfusion: An overview” (Special Issue, times cited: 4); (2) “Machine perfusion in abdominal organ transplantation: Current use in the Netherlands” (Special Issue, times cited: 3); (3) “Post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders: Current concepts and future therapeutic approaches” (times cited: 3); (4) “Novel alternative transplantation therapy for orthotopic liver transplantation in liver failure: A systematic review” (times cited: 1); and (5) “Emerging and neglected zoonoses in transplant population” (times cited: 1). Among these articles published in 2020, two appeared in the Special Issue "Machine Perfusion" published in January, are highly cited, and focused mainly on the machine perfusion of isolated liver; both papers’ authors aimed to provide information that would reduce the effects of ischemia-reperfusion injury in the liver transplantation process. Submissions for this Special Issue were invited by Vassilios Papalois (Editor-in-Chief of WJT) and arranged by Maria Irene Bellini (Associate Editor of WJT).
The published articles have been arranged according to their number of citations (Table 1). In total, 248 of the articles have been cited. According to the statistics, 153 papers were cited 1-10 times, followed by 60 papers that were cited 11-20 times and 35 papers that were cited more than 20 times. The overall citation situation will improve as WJT publishes more high-quality papers, further increasing its impact, number of citations, and popularity among readers interested in the field of transplantation.
| Times cited | Number of manuscripts |
| 1-10 | 153 |
| 11-20 | 60 |
| 21-30 | 26 |
| 31-40 | 3 |
| 41-50 | 2 |
| 61-70 | 2 |
| 91-100 | 1 |
| > 100 | 1 |
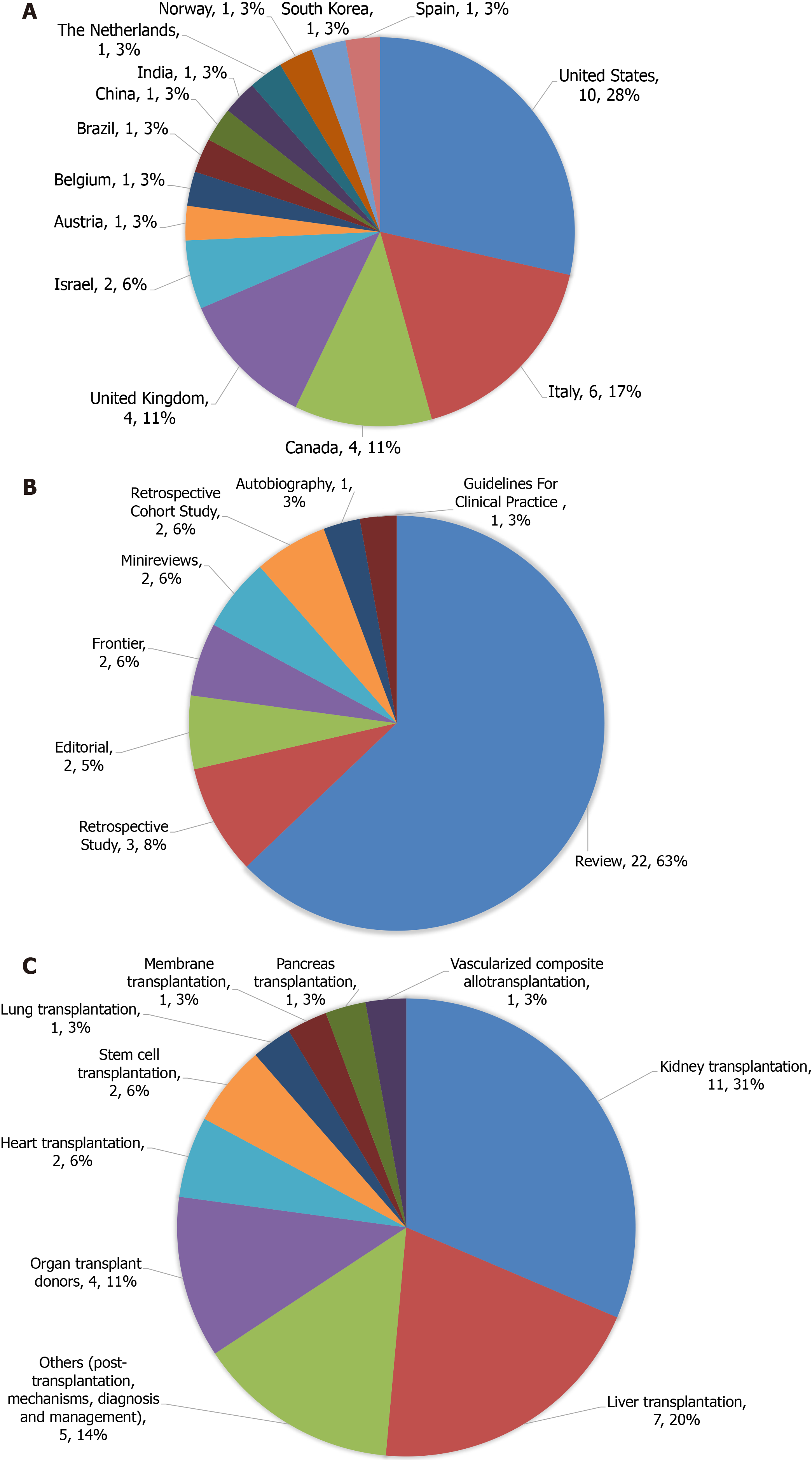
A total of 35 articles were cited more than 20 times, as shown in Table 2. The country/territory information, manuscript type and research topics of these articles are shown in Figure 1. The authors of these 35 articles come from 14 countries/ territories (Figure 1A), including the United States (10/35, 28%), Italy (6/35, 17%), Canada (4/35, 11%), the United Kingdom (4/35, 11%), Israel (2/35, 6%), Austria (1/35, 3%), Belgium (1/35, 3%), Brazil (1/35, 3%), China (1/35, 3%), India (1/35, 3%), the Netherlands (1/35, 3%), Norway (1/35, 3%), South Korea (1/35, 3%), and Spain (1/35, 3%). These 35 articles represented 7 different manuscript types (Figure 1B), including Review (22/35, 63%), Retrospective Study (3/35, 8%), Editorial (2/35, 6%), Frontier (2/35, 6%), Minireviews (2/35, 6%), Retrospective Cohort Study (2/35, 6%), Autobiography (1/35, 3%), and Guidelines For Clinical Practice (1/35, 3%). Considering topical content, these articles represented 9 topics important to the field of transplantation currently (Figure 1C), namely kidney transplantation (11/35, 31%), liver transplantation (7/35, 20%), organ transplant donors (4/35, 11%), heart transplantation (2/35, 6%), stem cell transplantation (2/35, 6%), lung transplantation (1/35, 3%), membrane transplantation (1/35, 3%), pancreas transplantation (1/35, 3%), vascularized composite allotransplantation (1/35, 3%), and others (post-transplantation, mechanisms, diagnosis and management; 5/35, 14%).
| DOI | Article title | Times cited | Country | Manuscript type | Topic |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i2.52 | Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Pathogenesis and treatment | 141 | Italy | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v4.i2.111 | Human amniotic membrane transplantation: Different modalities of its use in ophthalmology | 96 | India | Review | Membrane transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.69 | Survival of encapsulated islets: More than a membrane story | 63 | Israel | Review | Others (post-transplantation, mechanisms, diagnosis, and management) |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i4.183 | Cardiovascular risk factors following renal transplant | 61 | United Kingdom | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i4.48 | Current status of clinical islet transplantation | 44 | Canada | Editorial | Pancreas transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v4.i4.267 | Psychopathological aspects of kidney transplantation: Efficacy of a multidisciplinary team | 42 | Italy | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i3.451 | Deceased organ donation for transplantation: Challenges and opportunities | 37 | United States | Frontier | Organ transplant donors |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.125 | Post-transplant dyslipidemia: Mechanisms, diagnosis and management | 33 | Canada | Review | Others (post-transplantation, mechanisms, diagnosis, and management) |
| 10.5500/wjt.v4.i1.18 | ABO incompatible renal transplants: Good or bad? | 33 | United Kingdom | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i3.505 | Recent insights in the pathogenesis of post-transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders | 30 | Belgium | Review | Others (post-transplantation, mechanisms, diagnosis, and management) |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.291 | Massive haemorrhage in liver transplantation: Consequences, prediction and management | 30 | Canada | Review | Liver transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i4.91 | Role of IL-10 in the progression of kidney disease | 30 | Israel | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.380 | Long term outcomes of cardiac transplant for immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis: The Mayo Clinic experience | 30 | United States | Retrospective Study | Heart transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v2.i4.51 | Current state of renal transplant immunosuppression: Present and future | 30 | United States | Guidelines For Clinical Practice | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i3.517 | Physical rehabilitation for lung transplant candidates and recipients: An evidence-informed clinical approach | 29 | Canada | Review | Lung transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i4.78 | Exercise after heart transplantation: An overview | 29 | Norway | Review | Heart transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i4.68 | Novel immunosuppressive agents in kidney transplantation | 29 | United States | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v2.i6.84 | Polyomavirus-associated nephropathy | 28 | Italy | Review | Others (post-transplantation, mechanisms, diagnosis, and management) |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.183 | Immunosuppressive potency of mechanistic target of rapamycin inhibitors in solid-organ transplantation | 27 | Spain | Minireviews | Organ transplant donors |
| 10.5500/wjt.v7.i3.203 | Developing a donation after cardiac death risk index for adult and pediatric liver transplantation | 27 | United Kingdom | Retrospective Cohort Study | Liver transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i3.594 | Underutilization of palliative care services in the liver transplant population | 27 | United States | Retrospective Study | Liver transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i4.154 | Preservation solutions used during abdominal transplantation: Current status and outcomes | 27 | United States | Review | Others (post-transplantation, mechanisms, diagnosis, and management) |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i2.38 | Changing organ allocation policy for kidney transplantation in the United States | 27 | United States | Editorial | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i4.165 | Reducing transfusion requirements in liver transplantation | 26 | United Kingdom | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i1.91 | Key psychosocial challenges in vascularized composite allotransplantation | 25 | Austria | Review | Vascularized composite allotransplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i4.99 | Optimal stem cell source for allogeneic stem cell transplantation for hematological malignancies | 25 | China | Review | Stem cell transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i3.36 | mTOR signaling in liver regeneration: Rapamycin combined with growth factor treatment | 25 | Netherlands | Autobiography | Liver transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i4.209 | Induced pluripotent stem cells for modeling neurological disorders | 24 | Brazil | Review | Stem cell transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v4.i4.294 | Role of liver transplantation in the management of hepatoblastoma in the pediatric population | 24 | United States | Minireviews | Liver transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v5.i2.44 | Philosophy of organ donation: Review of ethical facets | 23 | United States | Review | Organ transplant donors |
| 10.5500/wjt.v4.i2.43 | Selecting suitable solid organ transplant donors: Reducing the risk of donor-transmitted infections | 23 | United States | Review | Organ transplant donors |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i3.583 | Thromboelastographic reference ranges for a cirrhotic patient population undergoing liver transplantation | 22 | Italy | Retrospective Cohort Study | Liver transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v7.i3.161 | Biomarkers in renal transplantation: An updated review | 21 | Italy | Review | Kidney transplantation |
| 10.5500/wjt.v3.i2.7 | Is it time to give up with calcineurin inhibitors in kidney transplantation? | 21 | Italy | Frontier | |
| 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.411 | Proposal of new expanded selection criteria using total tumor size and 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose - positron emission tomography/computed tomography for living donor liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: The National Cancer Center Korea criteria | 21 | South Korea | Retrospective Study | Liver transplantation |
In 2020, the WJT Editorial Office received a total of 65 manuscripts. Among these, 60 had the first decision made by the Science Editor Development Department, with 30 being edited, processed and advancing to the second decision; ultimately, 13 (20%, 13/65) were rejected and 30 (47.6%, 30/65) were published online by the Production Department. In total, 37 articles were published by WJT in 2020, including 7 articles that had been submitted in 2019. Compared with the number of published articles in 2019 (14 total), the number of published articles was higher by 23 in 2020 (37 vs 14), equating to a 264.29% increase.
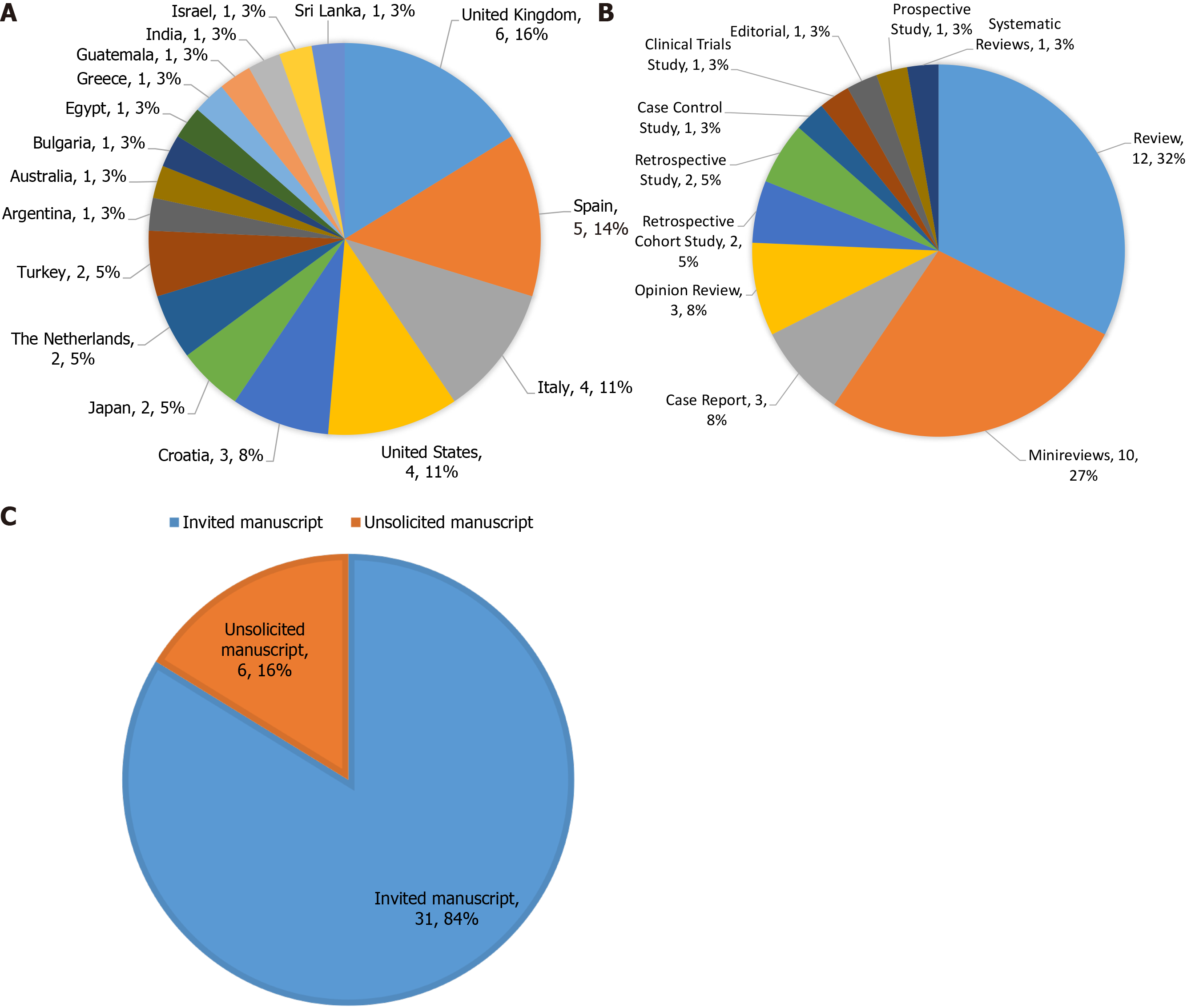
The country/territory information, manuscript type and manuscript source of these 37 articles are shown in Figure 2. The authors of these articles hailed from 17 countries/territories (Figure 2A), including the United Kingdom (6/37, 16%), Spain (5/37, 14%), Italy (4/37, 11%), the United States (4/37, 11%), Croatia (3/37, 8%), Japan (2/37, 5%), the Netherlands (2/37, 5%), Turkey (2/37, 5%), Argentina (1/37, 3%), Australia (1/37, 3%), Bulgaria (1/37, 3%), Egypt (1/37, 3%), Greece (1/37, 3%), Guatemala (1/37, 3%), India (1/37, 3%), Israel (1/37, 3%), and Sri Lanka (1/37, 3%). The articles represented 11 different manuscript types (Figure 2B), including Review (12/37, 32%), Minireviews (10/37, 27%), Case Report (3/37, 8%), Opinion Review (3/37, 8%), Retrospective Cohort Study (2/37, 5%), Retrospective Study (2/37, 5%), Case Control Study (1/37, 3%), Clinical Trials Study (1/37, 3%), Editorial (1/37, 3%), Prospective Study (1/37, 3%), and Systematic Review (1/37, 3%). There were 6 unsolicited manuscripts (6/37, 16%) and 31 invited manuscripts (31/37, 84%) making up these published articles (Figure 2C).
In 2020, 2090 invitations were sent out to peer reviewers and Editorial Board members to conduct peer review of manuscripts, yielding 155 acceptances (7.4%, 155/2090), 314 declines (15%, 314/2090), and 81 non-responses (3.9%, 81/2090). Among the peer reviewers and Editorial Board members who accepted invitations, 150 (7.2%, 150/2090) submitted the peer review report on time, 181 (8.7%, 181/2090) failed to submit the peer review report on time, and 5 have not submitted the peer review report yet.
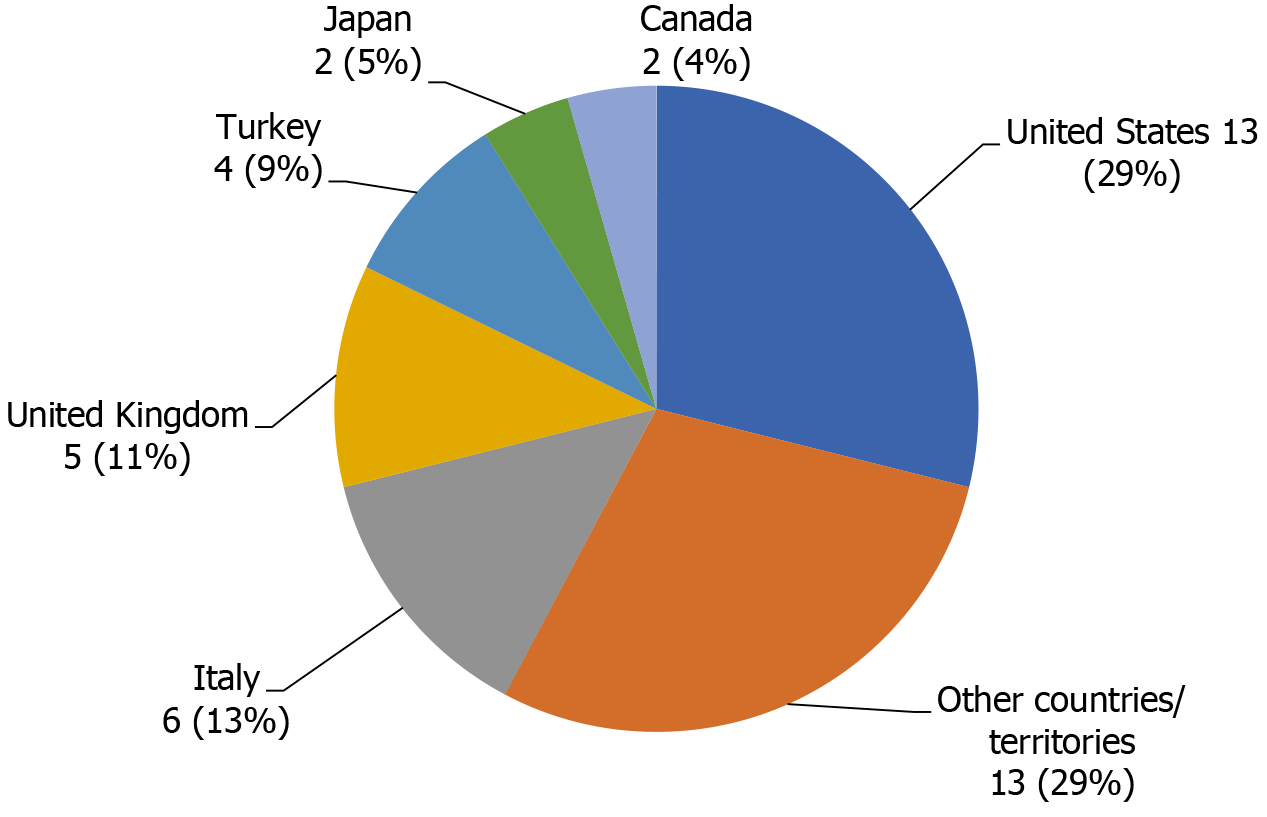
WJT currently has 45 Editorial Board members, including 3 Editors-in-Chief, 5 Associate Editors and 37 Editorial Board members. These 45 Editorial Board members hail from 19 countries/territories (Figure 3), including 13 (28.9%, 13/45) from the United States, 6 (13.3%, 6/45) from Italy, 5 (11.1%, 5/45) from the United Kingdom, 4 (9%, 4/45) from Turkey, 2 (4.4%, 2/45) from Japan, 2 (4.4%, 2/45) from Canada, and 13 (28.9%, 13/45) from other countries/territories (i.e., Chile, China, Colombia, Croatia, Egypt, France, Germany, Norway, Russia, South Korea, Spain, Switzerland, and Brazil). In 2020, 21 Editorial Board members participated in the peer-review work (21/45, 46.7%), providing a review rate of Editorial Board members that is typical but which we aim to improve to an outstanding level.
In 2020, WJT received a total of 86 titles in response to invited manuscript outreach for consideration for publication in the upcoming year of 2021. These included 56 (65.1%, 56/86) Review Articles, 21 (24.4%, 21/86) Original Articles, 4 (4.7%, 4/86) Editorials, and 5 (5.8%, 5/866) other types of articles. We need to invite more original articles in 2021.
Although WJT advanced in 2020, there are some issues that still need to be addressed in our pursuit of maximizing its impact on the field of transplantation: (1) The Editorial Board members submitted few manuscripts, and this number needs to increase in 2021; (2) We published few original articles, and this number needs to increase in 2021; (3) We received few peer-review reports for each manuscript, and this number needs to increase in 2021; and (4) The number of members of the Editorial Board was insufficient and the review rate of Editorial Board members is typical (but should be improved to outstanding).
The number of Editors-in-Chief and Associate Editors has stabilized at a sufficient amount, but the number of Editorial Board members needs to be expanded. In 2021, we need to focus on inviting additional highly influential scientists to join the Editorial Board of WJT, with the aim of growing the number of Editorial Board members to 100. We also need to invite Editorial Board members or highly influential scientists to write high-quality review articles or arrange Special Issues for WJT, to support and promote the journal’s overall academic influence.
Above all, we greatly appreciate the support shown by authors, Editorial Board members, independent expert referees, and staff of the Editorial Office throughout 2020. With this support system in place, we expect to expand our productivity, working with you all to raise the academic influence of WJT in 2021. In order to achieve these goals, we recognize and appreciate the importance of the continuous support and submissions from authors and the dedicated efforts and expertise by our invited reviewers. As editors, we will strive to ensure efficient communication with the authors, providing professional support and answering questions as they arise. We will also remain open to any suggestions that could improve WJT’s operation and publication. Once again, on behalf of WJT, we wish you and your families the best for the New Year.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Transplantation
Country/Territory of origin: United States
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A, A
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Chiu KW, Gangl A, Schmidt N, Soriano-Ursúa MA S-Editor: Wang JL L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Wang LL
| 1. | Salvadori M, Rosso G, Bertoni E. Update on ischemia-reperfusion injury in kidney transplantation: Pathogenesis and treatment. World J Transplant. 2015;5:52-67. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 289] [Cited by in RCA: 270] [Article Influence: 27.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |