Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Transplant. Jun 24, 2016; 6(2): 255-271
Published online Jun 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.255
Published online Jun 24, 2016. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.255
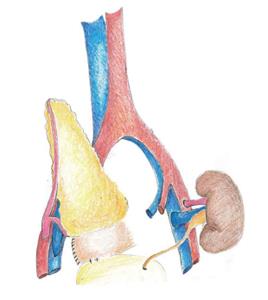
Figure 1 Technique of systemic-bladder drainage with creation of an anastomosis between the allograft duodenal segment and vesical dome of the recipient bladder.
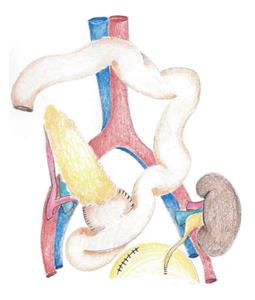
Figure 2 Technique of conversion from bladder to enteric exocrine drainage (enteric conversion) for persistent metabolic, urologic, or other problems.
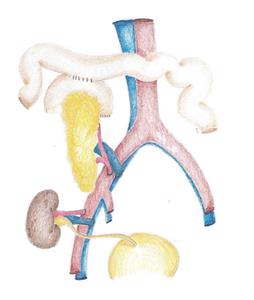
Figure 3 Technique of systemic-enteric drainage with side-to-side anastomosis between allograft duodenum and recipient small bowel.
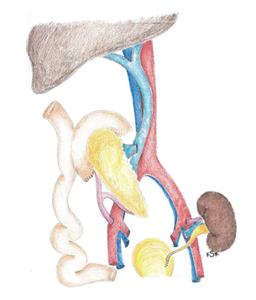
Figure 4 Technique of portal-enteric drainage with side-to-side anastomosis between allograft duodenum and small bowel; this technique is also amenable to using the native duodenum or stomach for exocrine diversion.
- Citation: El-Hennawy H, Stratta RJ, Smith F. Exocrine drainage in vascularized pancreas transplantation in the new millennium. World J Transplant 2016; 6(2): 255-271
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v6/i2/255.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v6.i2.255