Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Transplant. Jun 18, 2024; 14(2): 92528
Published online Jun 18, 2024. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i2.92528
Published online Jun 18, 2024. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i2.92528
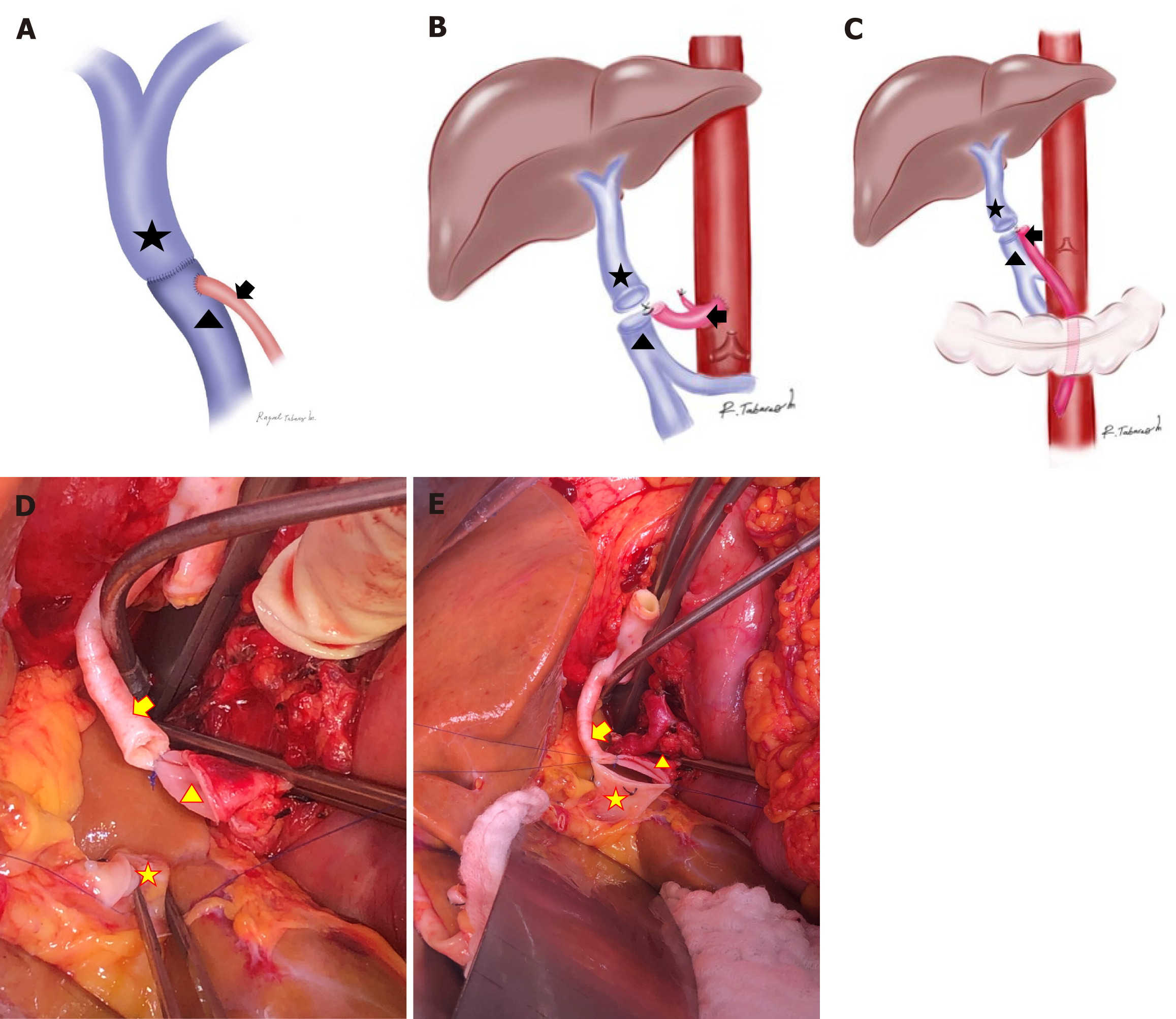
Figure 1 Portal vein arterialization reconstruction techniques.
A: Arterioportal illustration depicting the distal terminolateral anastomoses used to anastomose the portal vein (PV) and the arterial allograft during portal vein arterialization (PVA); B: Supraceliac PVA: the proximal end of the arterial allograft could be anastomosed to the abdominal aorta, superior to the celiac trunk; C: Infrarenal PVA: the proximal end of the arterial allograft could also be anastomosed to the abdominal aorta, inferior to the renal arteries. During this reconstruction, the arterial allograft is passed through the mesocolon; D: Photography demonstrating how the recipient PV (star) is attached to the donor iliac artery graft (arrow) previously anastomosed to the supraceliac aorta; E: Photograph depicting how both donor (arrowhead) and recipient PV (star) are approached terminoterminally, whereas the distal end of the donor iliac artery graft (arrow) arises laterally from the supraceliac aorta.
- Citation: Cortes-Mejia NA, Bejarano-Ramirez DF, Guerra-Londono JJ, Trivino-Alvarez DR, Tabares-Mesa R, Vera-Torres A. Portal vein arterialization in 25 liver transplant recipients: A Latin American single-center experience. World J Transplant 2024; 14(2): 92528
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v14/i2/92528.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v14.i2.92528