Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Transplant. Jun 18, 2024; 14(2): 90202
Published online Jun 18, 2024. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i2.90202
Published online Jun 18, 2024. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i2.90202
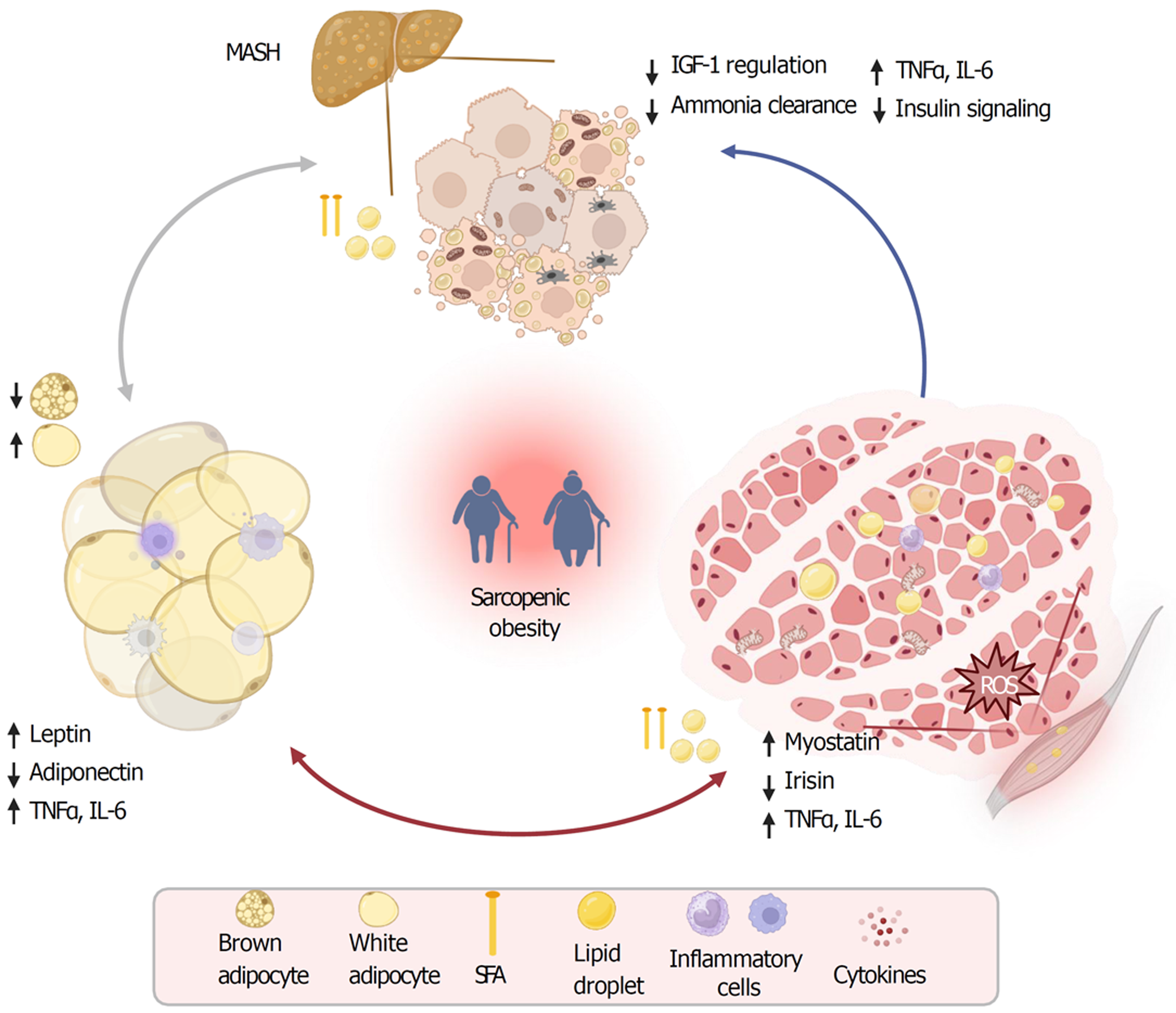
Figure 1 A Pathophysiology of sarcopenic obesity.
Obesity and sarcopenia share biological alterations such as insulin resistance, increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress and age-associated hormonal changes. Adipocyte hypertrophy induces a state of systemic inflammation characterized by decreased adiponectin and elevated levels of leptin, tumor necrosis factor, and interleukin 6 (red arrow). Also, obesity and aging contribute to changes in skeletal muscle homeostasis, leading to increased expression of myostatin and reduced irisin, which ultimately favors muscle wasting (red arrow). Concomitantly, excess delivery of fatty acids to the liver leads to fat deposition into the hepatocytes which results in hepatic insulin resistance as well as decreased insulin-like growth factor production. These processes contribute to a vicious cycle leading to adipose tissue expansion, muscle loss and hepatic dysfunction (gray and blue arrows). TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor; GH: Growth hormone; SFA: Saturated fatty acid; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; MASH: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis. Adapted from “Cycle Diagram”, by BioRender.com (2023). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates with permission for re-publication.
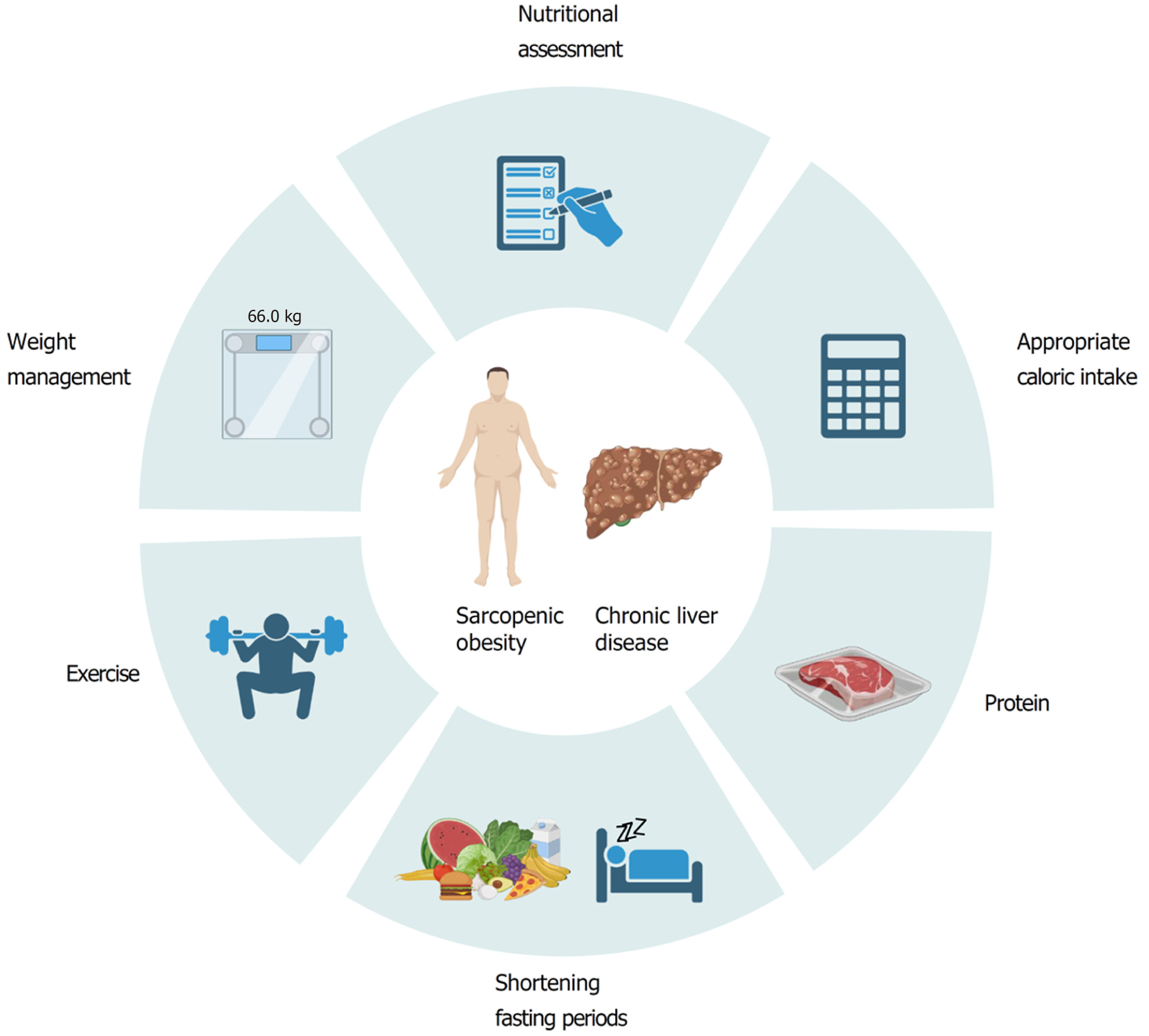
Figure 2 A summary of nutrition and lifestyle recommendations for concurrent chronic liver disease and sarcopenic obesity.
Lifestyle recommendations for patients with chronic liver disease and sarcopenic obesity include thorough nutritional assessments and re-assessments, weight management, and exercise. Nutritional recommendations include maintaining an appropriate caloric, shortening fasting periods, and obtaining and adequate amount of protein through diet. Adapted from “Cycle Diagram”, by BioRender.com (2023). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates with permission for re-publication.
- Citation: Herscovici DM, Cooper KM, Colletta A, Rightmyer M, Shingina A, Feld LD. Sarcopenic obesity in patients awaiting liver transplant: Unique challenges for nutritional recommendations. World J Transplant 2024; 14(2): 90202
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v14/i2/90202.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v14.i2.90202