Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2024; 14(1): 90277
Published online Mar 18, 2024. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i1.90277
Published online Mar 18, 2024. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v14.i1.90277
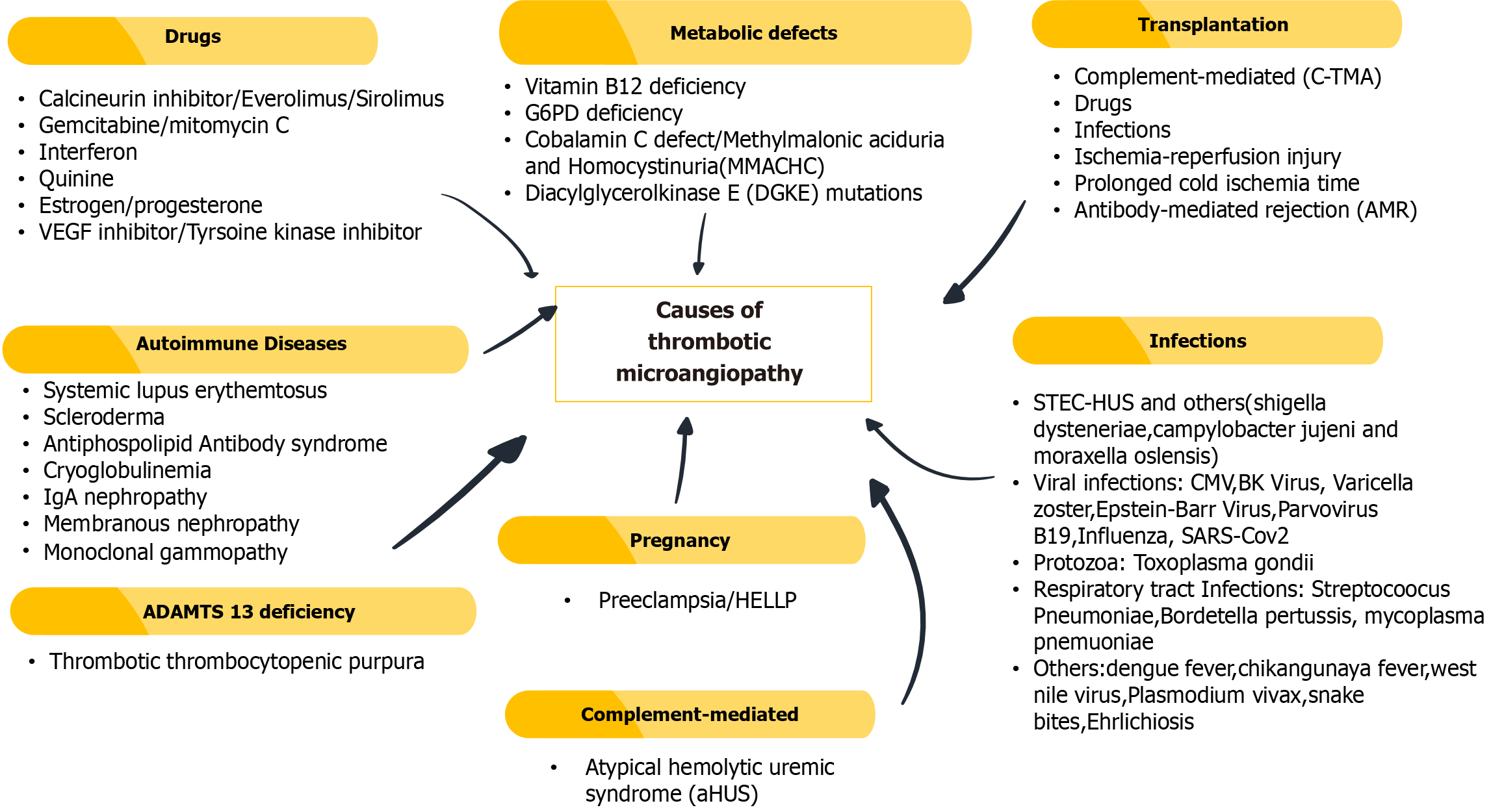
Figure 1 Common causes of thrombotic microangiopathies.
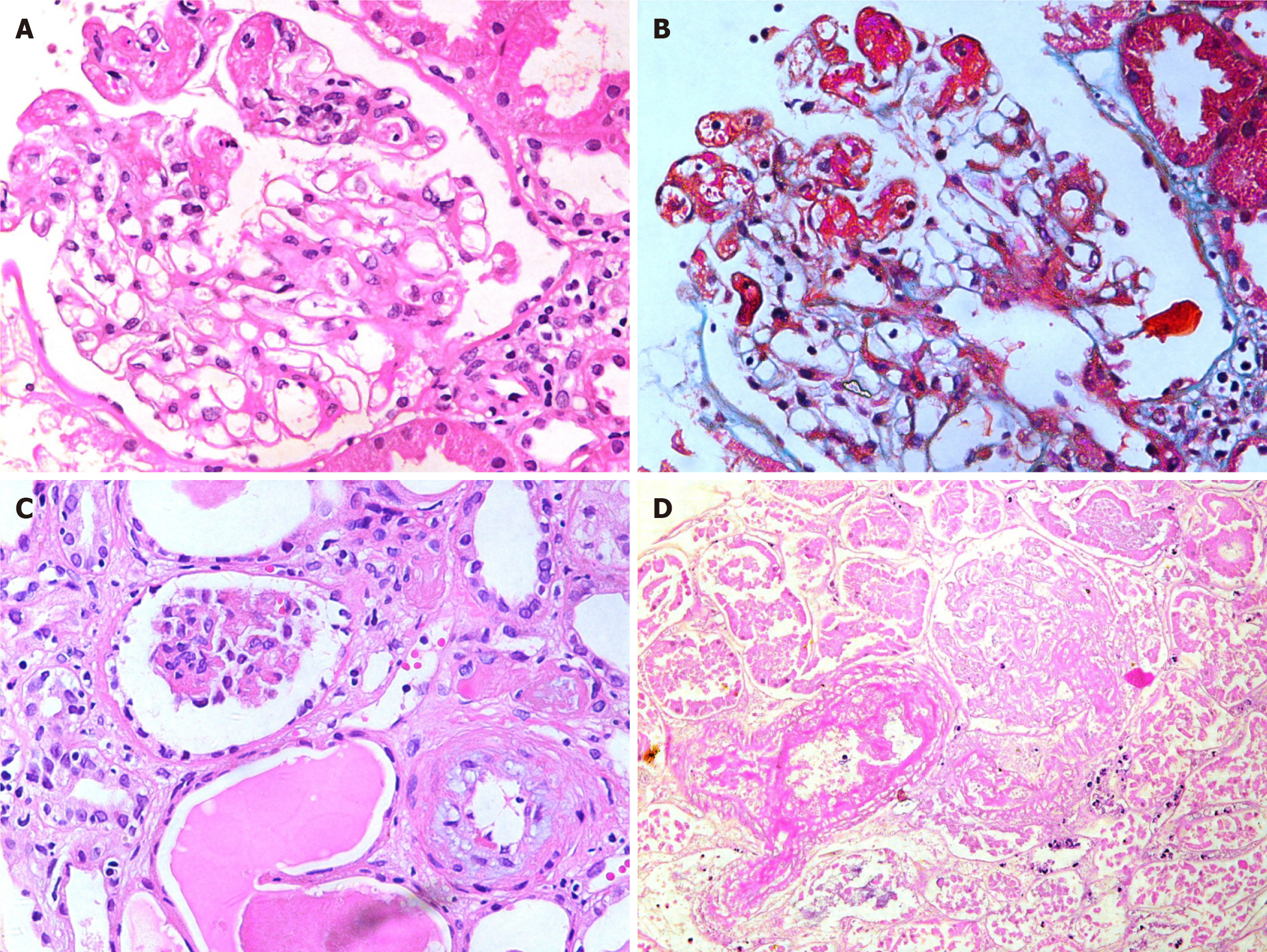
Figure 2 Glomerular lesions in thrombotic microangiopathies.
A: High-power view showing a glomerulus containing fibrin thrombi in dilated capillaries at 9 to 12’O clock position (H&E, × 400); B: The same glomerulus on trichrome staining showing fibrin thrombi staining red with this stain (Masson’s Trichrome, × 400); C: Medium-power view showing one ischemic glomerulus and an arteriole exhibiting mucinous intimal thickening (H&E, × 200); D: Medium-power view showing completely infarcted glomerulus and an adjacent infarcted arteriole containing intraluminal fibrin thrombus. (H&E, × 200).
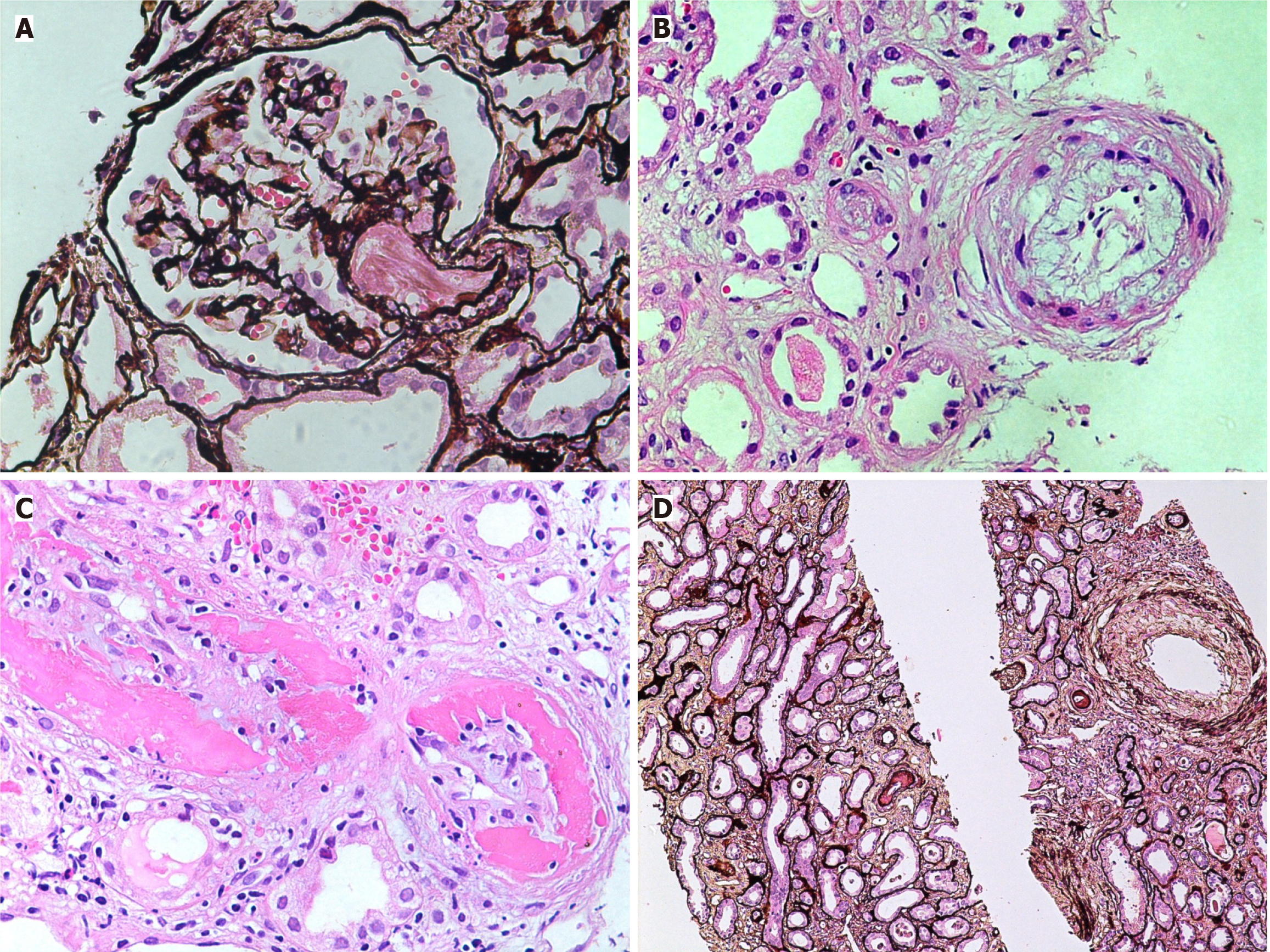
Figure 3 Vascular lesions in thrombotic microangiopathies.
A: Medium-power view showing a glomerulus with an arteriole containing fibrin thrombi in acute phase of thrombotic microangiopathies (TMAs) (H&E, × 200); B: High-power view showing an arteriole with endothelial swelling and complete occlusion of the lumen. An adjacent small artery shows marked mucinous thickening of the intima with narrowing of the lumen (H&E, × 400); C: High-power view showing a small artery with fibrinoid necrosis of the vessel wall and intimal proliferation (H&E, × 400); D: Medium-power view showing fibrointimal thickening of an interlobular size artery in chronic phase of TMA. Mild tubular atrophy is seen in the background (Silver stain, × 200).
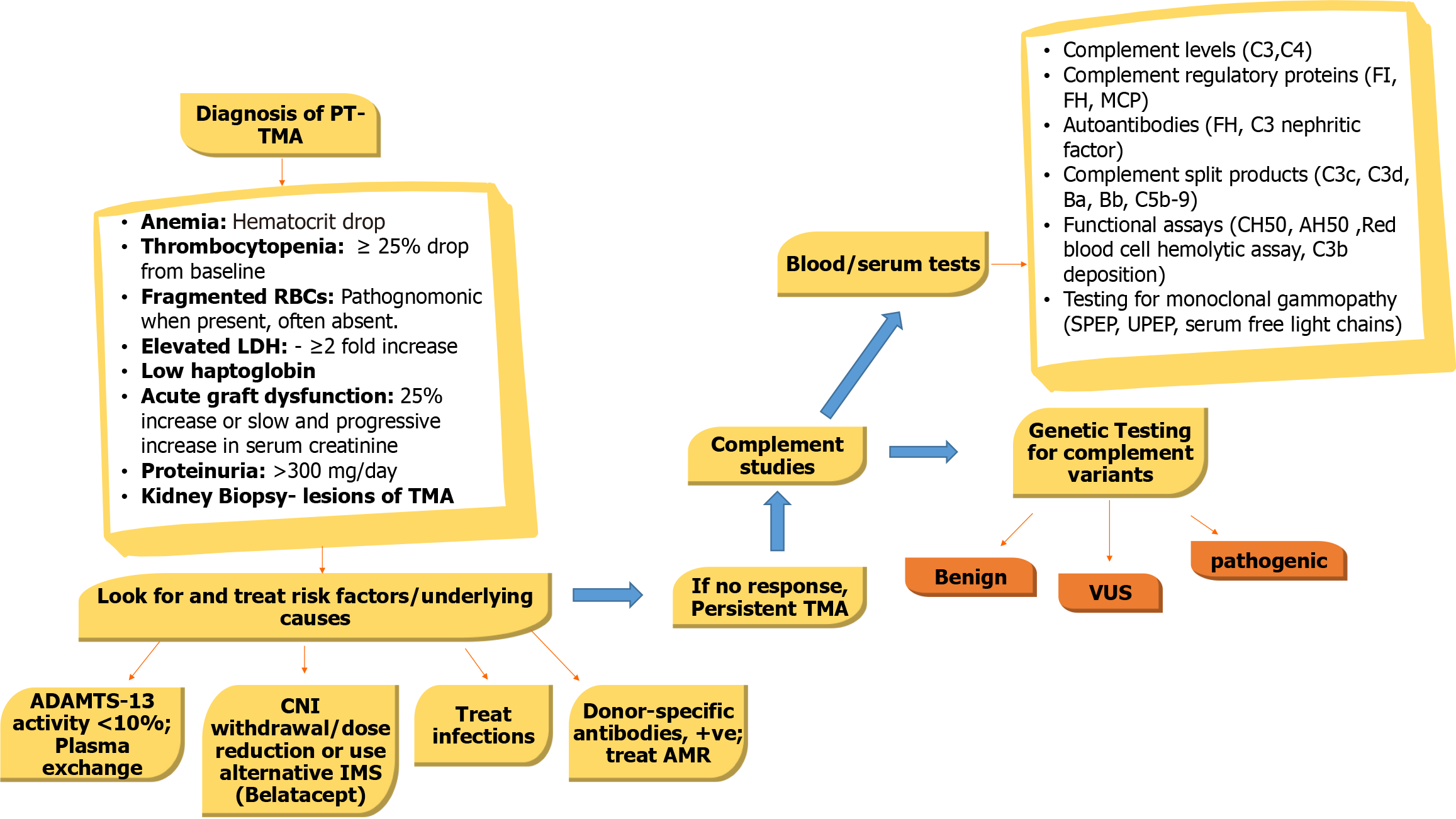
Figure 4 An algorithmic approach to diagnosis, classification and treatment of posttransplant thrombotic microangiopathy.
ADAMTS13: A disintegrin-like and metalloprotease with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 13; AMR: Antibody-mediated rejection; IMS: Immunosuppression; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; MCP: Membrane cofactor protein; PT-TMA: Posttransplant thrombotic microangiopathy; SPEP: Serum protein electrophoresis; TMA: Thrombotic microangiopathy; UPEP: Urine protein electrophoresis; VUS: Variant of unknown significance.
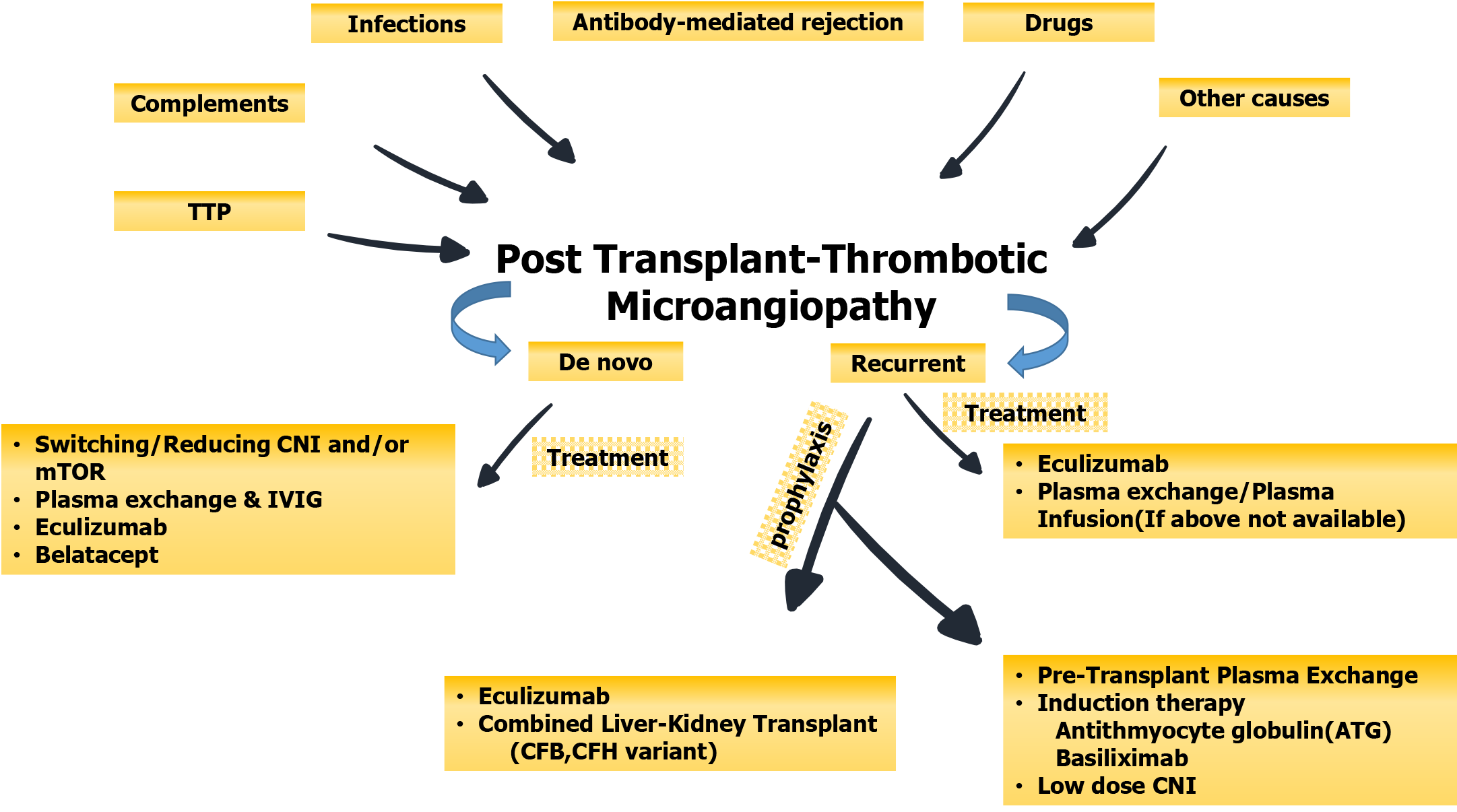
Figure 5 Summary of the main etiologic agents and types of posttransplant thrombotic microangiopathy and their treatment and preventive strategies.
CFB: Complement factor B; CFH: Complement factor H; CNI: Calcineurin inhibitor; IVIG: Intravenous immunoglobulin; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; TTP: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
- Citation: Mubarak M, Raza A, Rashid R, Sapna F, Shakeel S. Thrombotic microangiopathy after kidney transplantation: Expanding etiologic and pathogenetic spectra. World J Transplant 2024; 14(1): 90277
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v14/i1/90277.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v14.i1.90277