Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2023; 13(3): 58-85
Published online Mar 18, 2023. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v13.i3.58
Published online Mar 18, 2023. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v13.i3.58
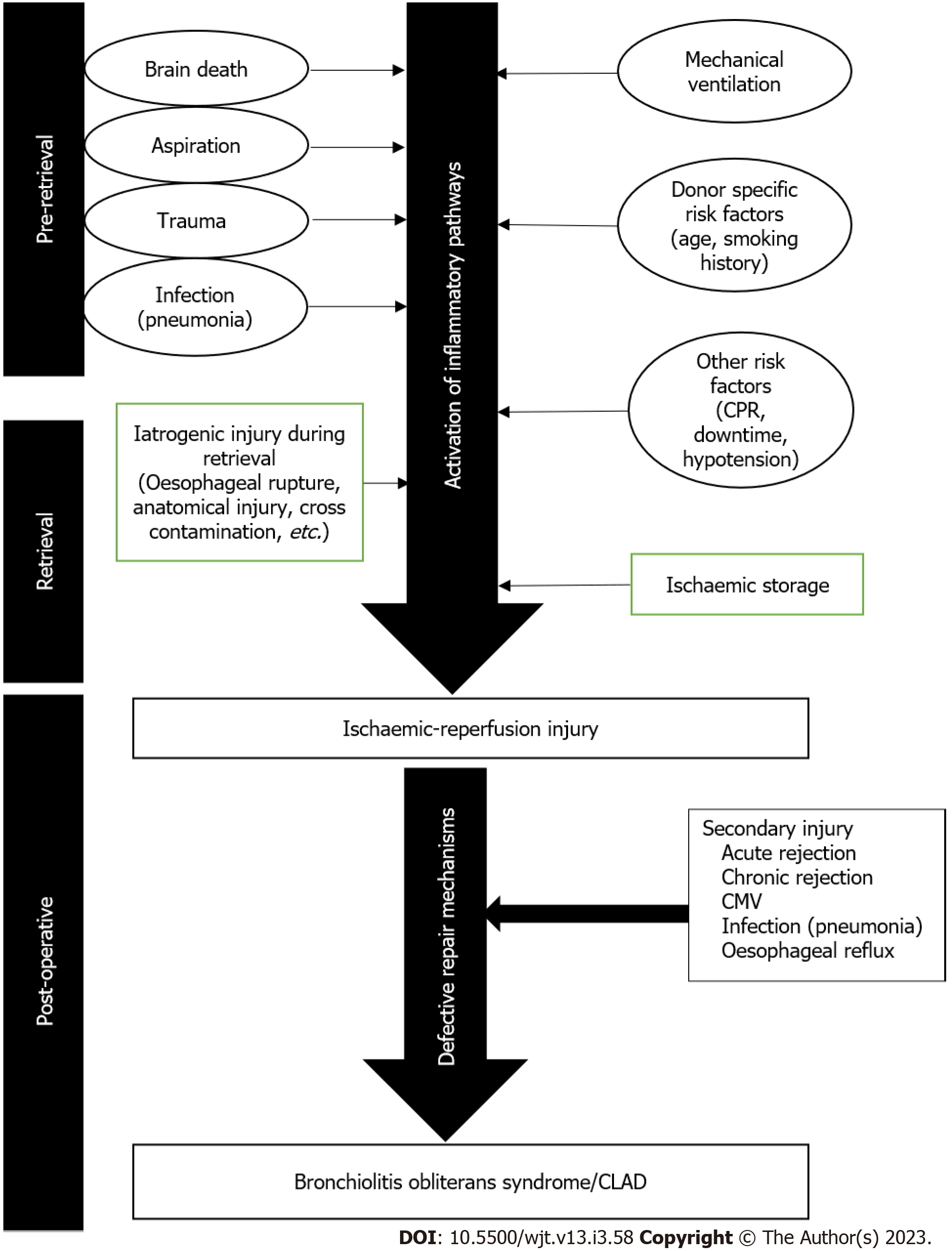
Figure 1 Pathophysiological mechanisms that lead to ischaemic-reperfusion injury and subsequently chronic lung allograft dysfunction.
CLAD: Chronic lung allograft dysfunction.
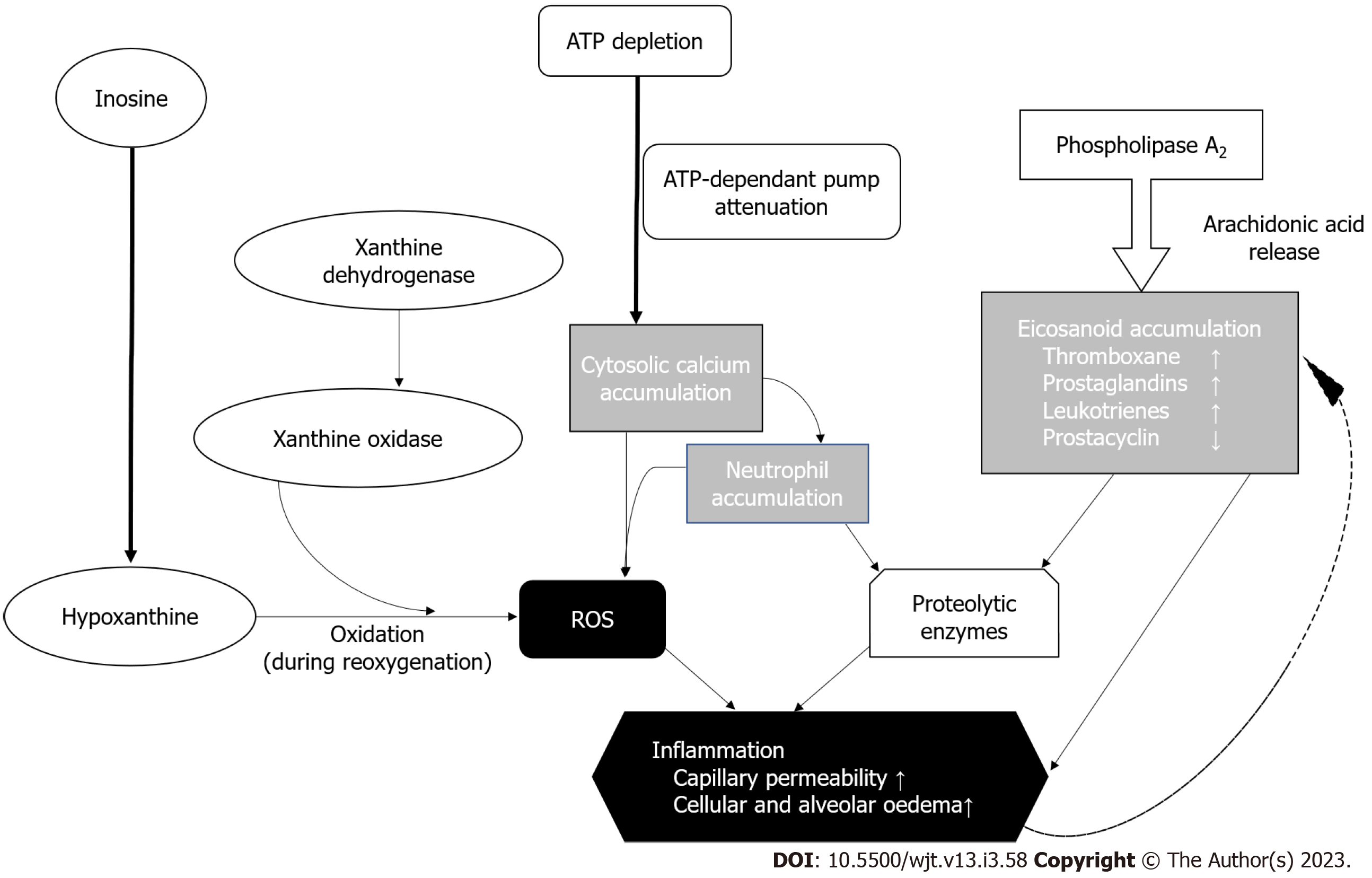
Figure 2 Pathophysiology of lung ischemia-reperfusion injury.
ROS: Reactive oxygen species.
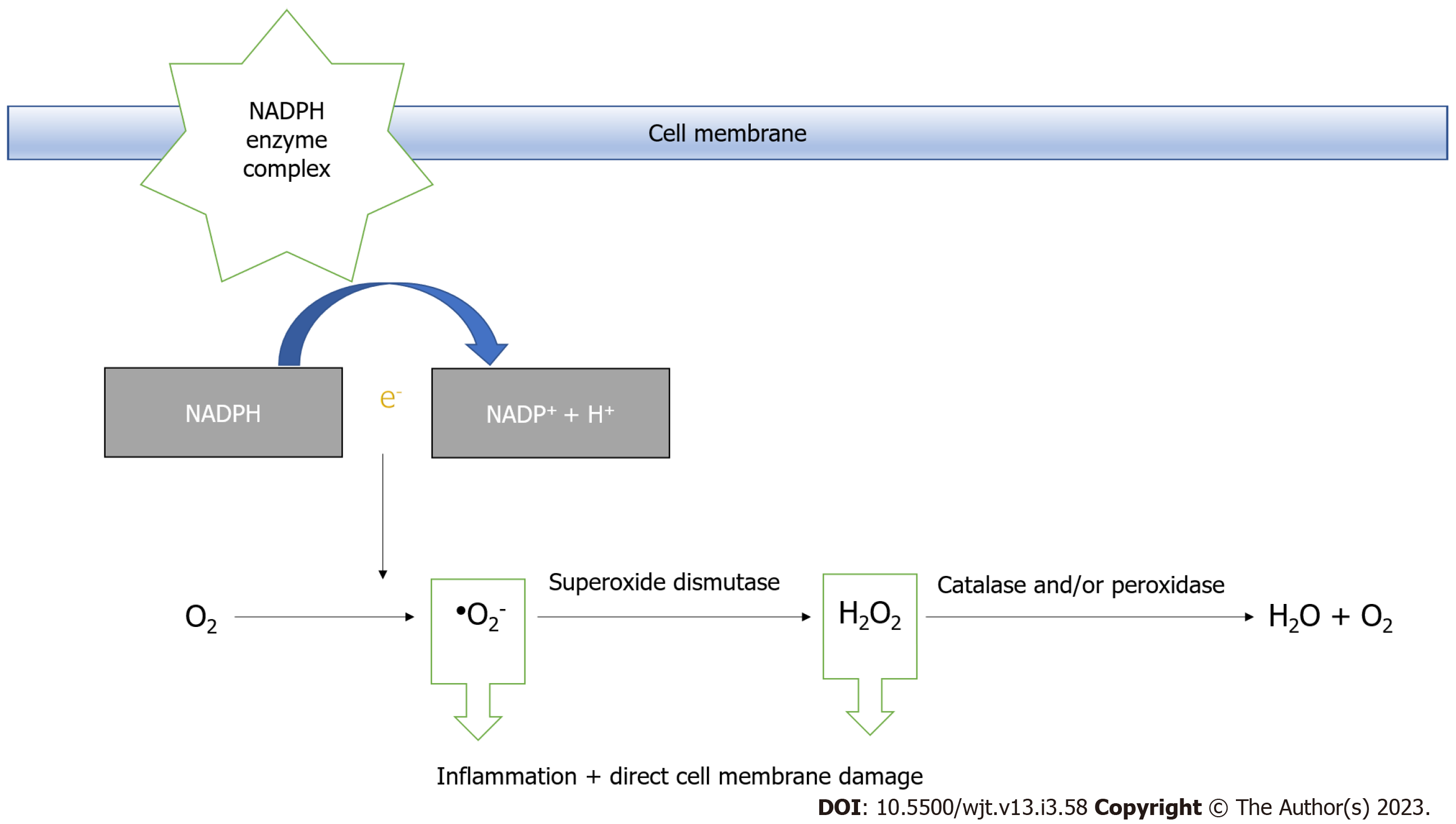
Figure 3 Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase system and the generation of superoxide anion.
NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate.
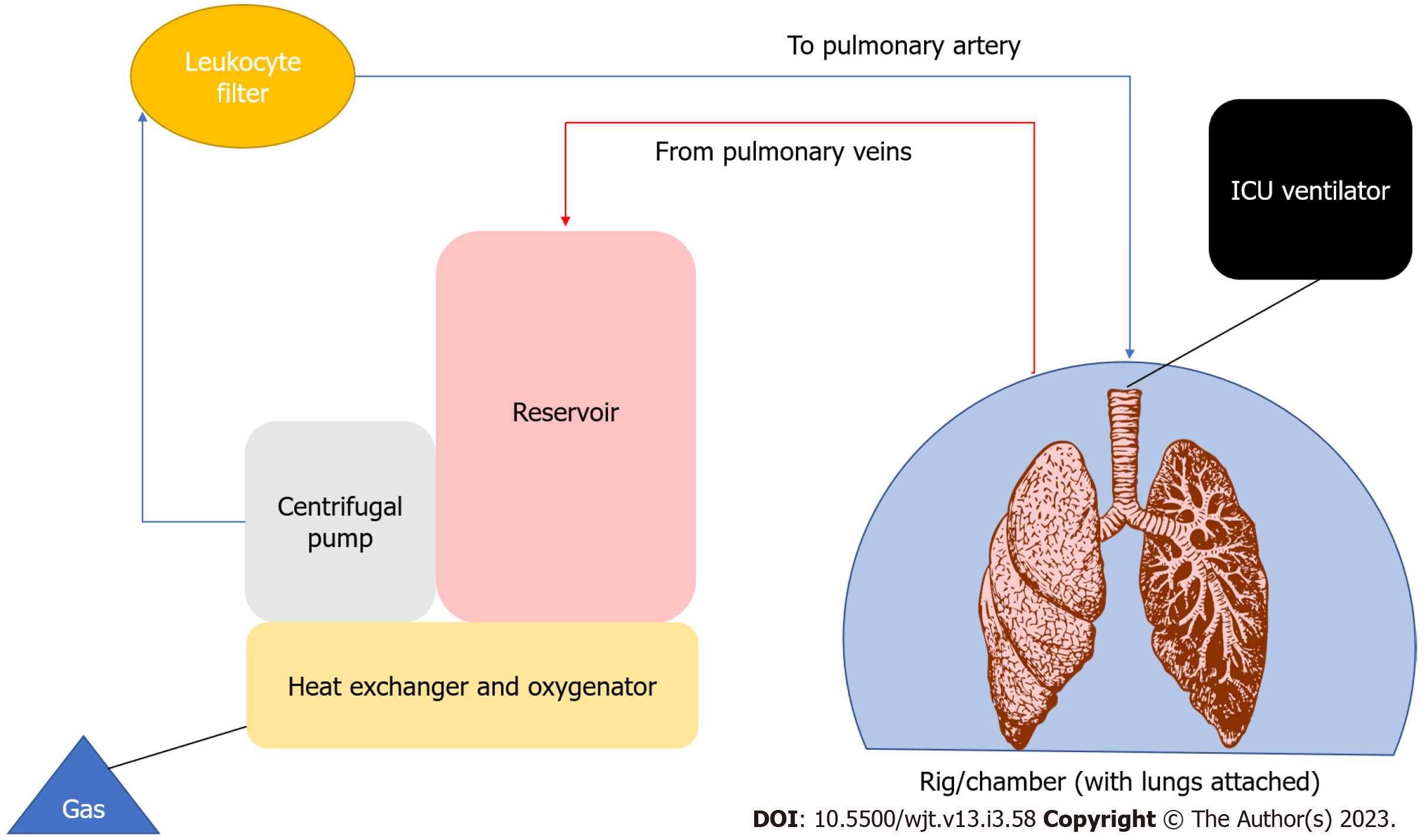
Figure 4 Example of an exvivo lung perfusion circuit.
ICU: Intensive care unit.
- Citation: Avtaar Singh SS, Das De S, Al-Adhami A, Singh R, Hopkins PM, Curry PA. Primary graft dysfunction following lung transplantation: From pathogenesis to future frontiers. World J Transplant 2023; 13(3): 58-85
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v13/i3/58.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v13.i3.58