Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Transplant. Mar 18, 2022; 12(3): 27-41
Published online Mar 18, 2022. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v12.i3.27
Published online Mar 18, 2022. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v12.i3.27
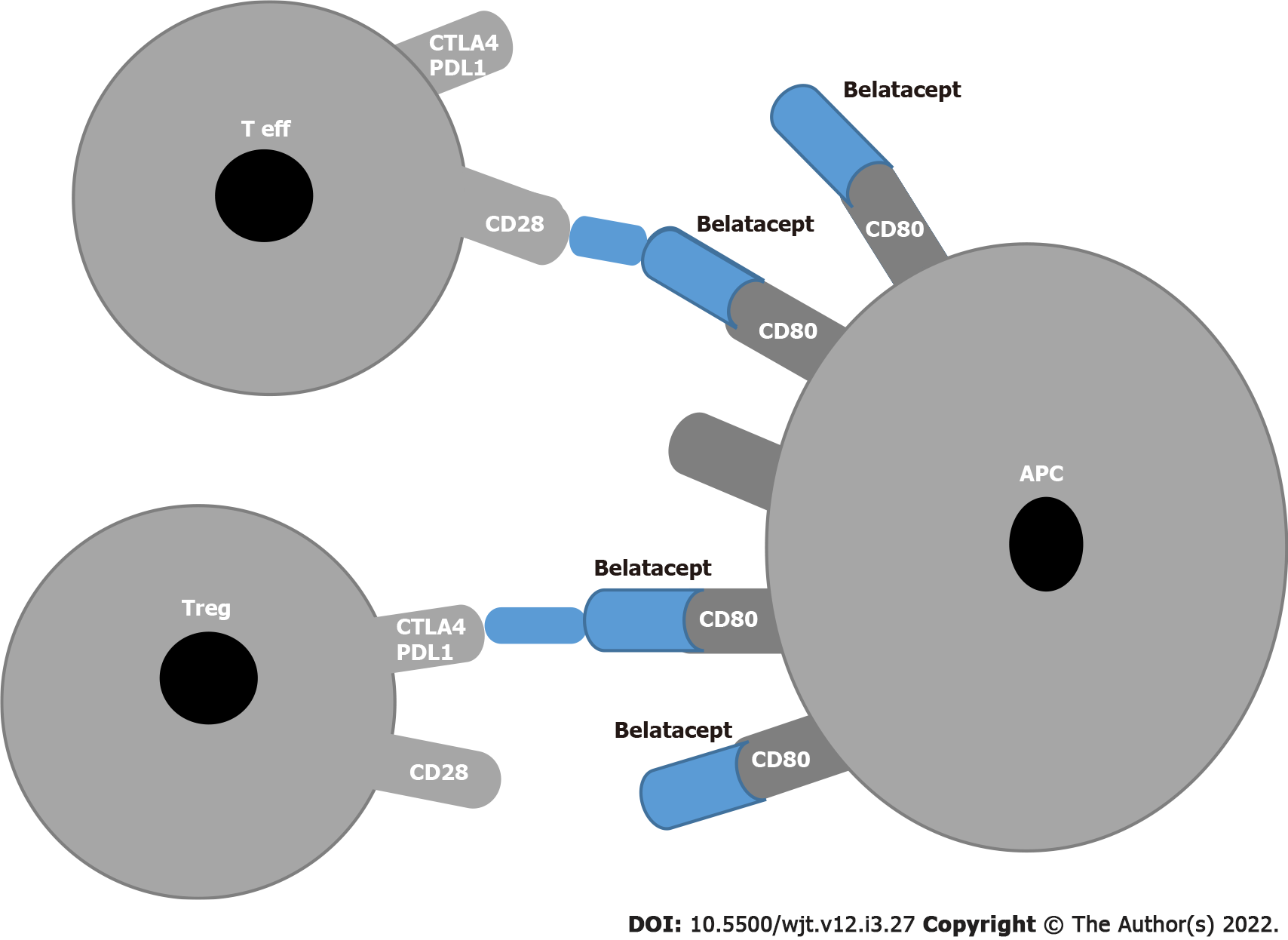
Figure 1 Block of co-stimulation with Belatacept.
APC: Antigen presenting cell; T eff: T effector; T reg: Regulatory T cells; PDL1: Programmed cell death receptor ligand 1; CTLA4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4.
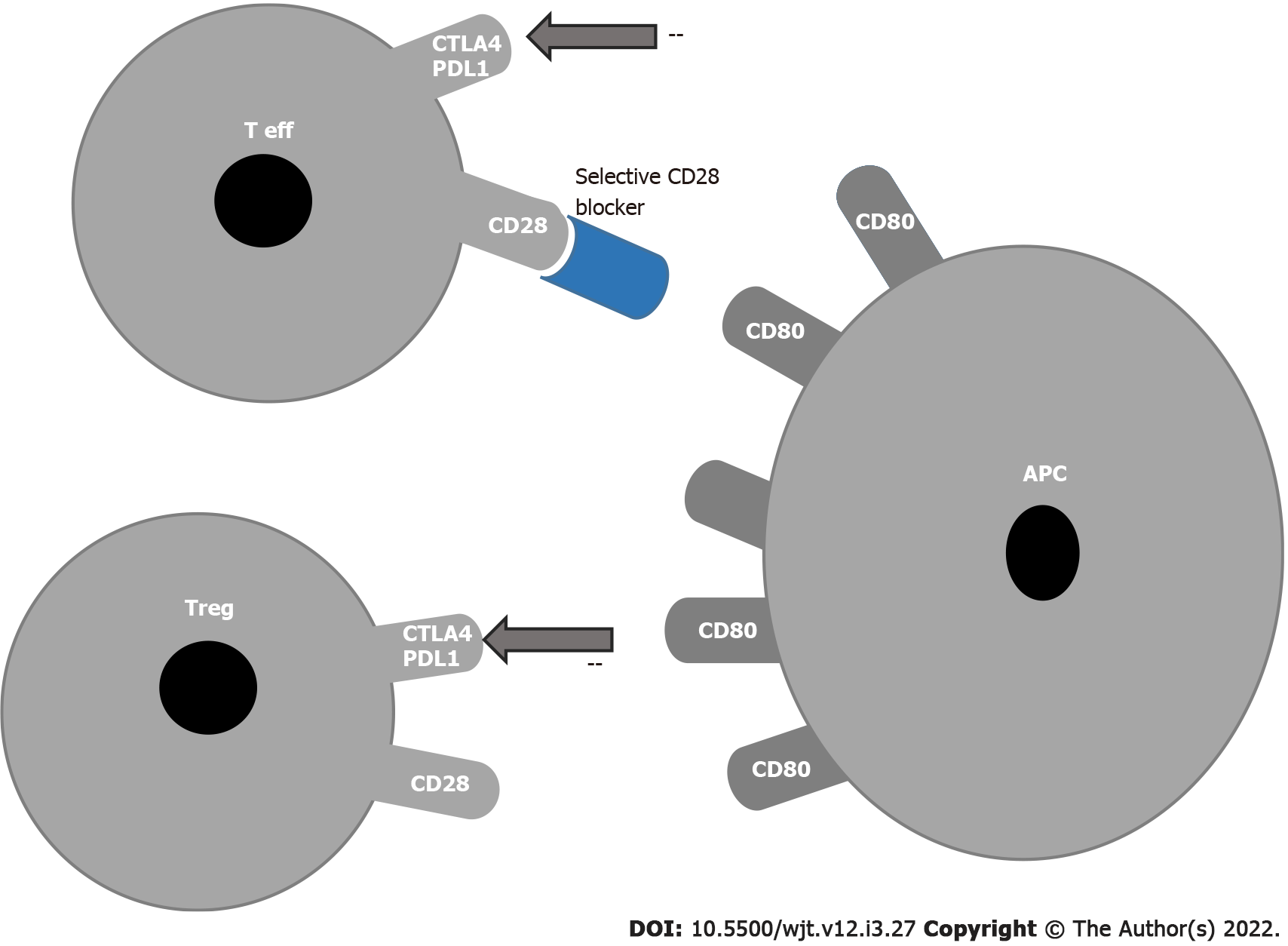
Figure 2 Block of co-stimulation with anti CD28.
APC: Antigen presenting cell; T eff: T effector; T reg: Regulatory T cells; PDL1: Programmed cell death receptor ligand 1; CTLA4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4.
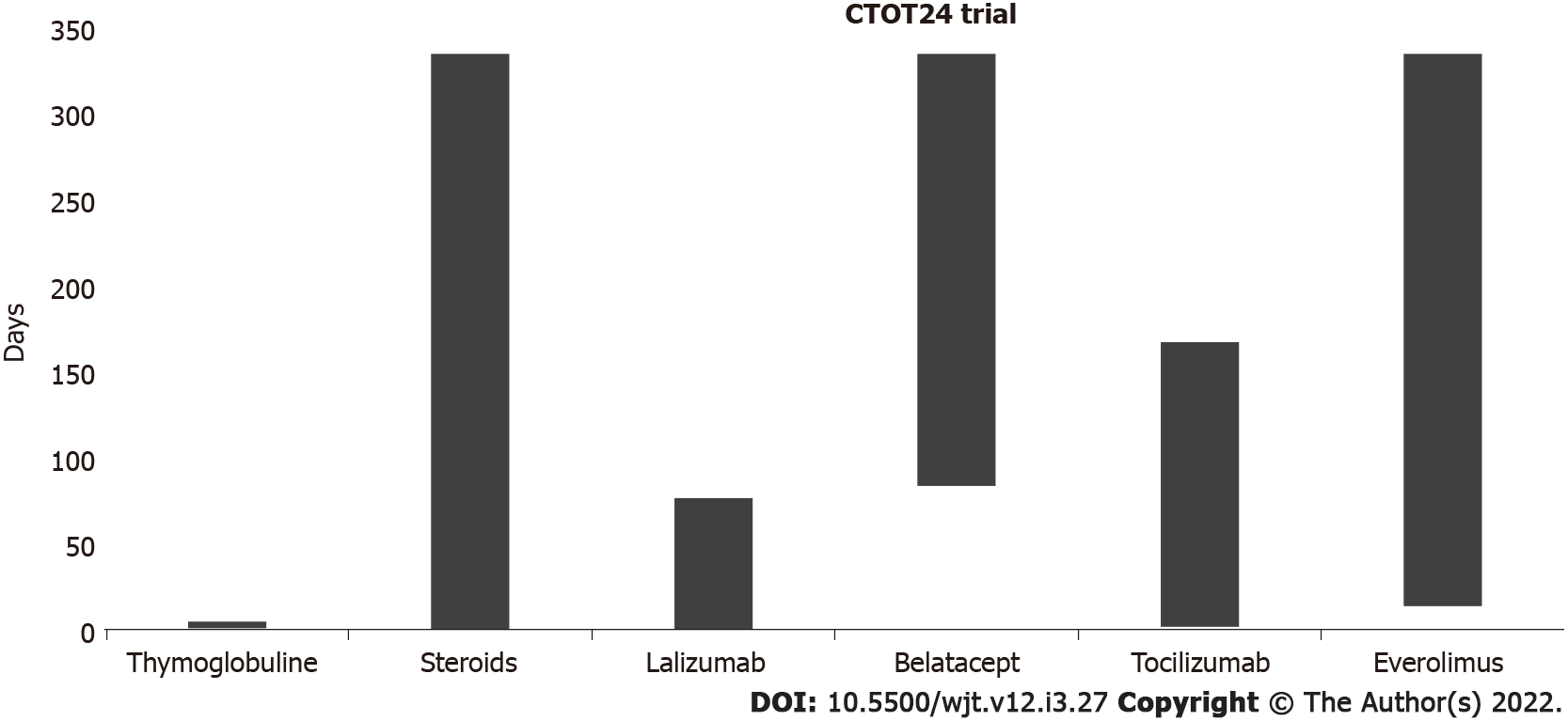
Figure 3 CTOT24 trial.
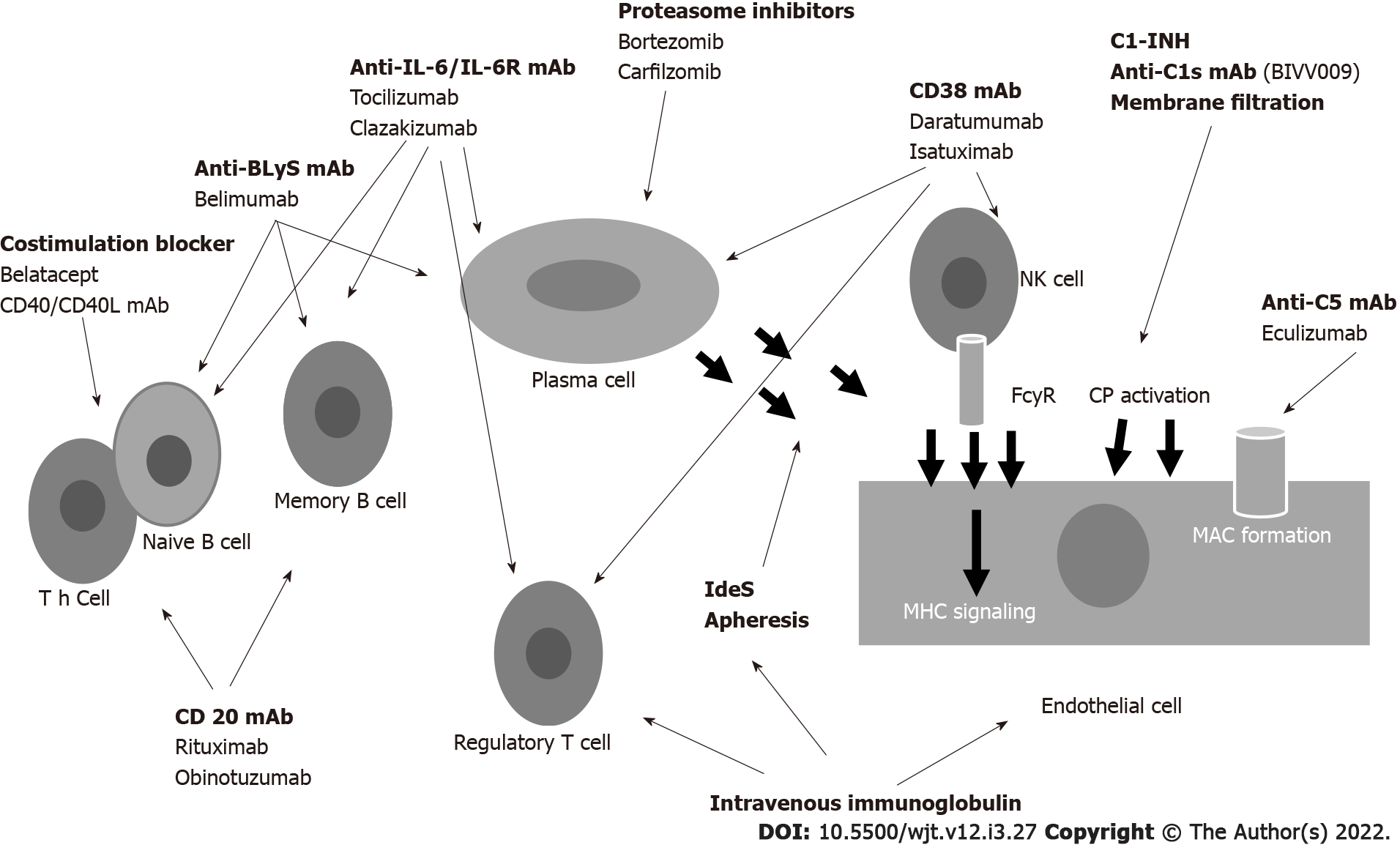
Figure 4 Drugs acting at different levels to control the antibody formation.
BLyS: B Lymphocyte stimulating factor; mAb: Monoclonal antibody; C1-INH: C1 inhibitors; NK: Natural killer; Cp: Complement; FcyR: FcyReceptor; MAC: Membrane attacking complex; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; IL: Interleukin.
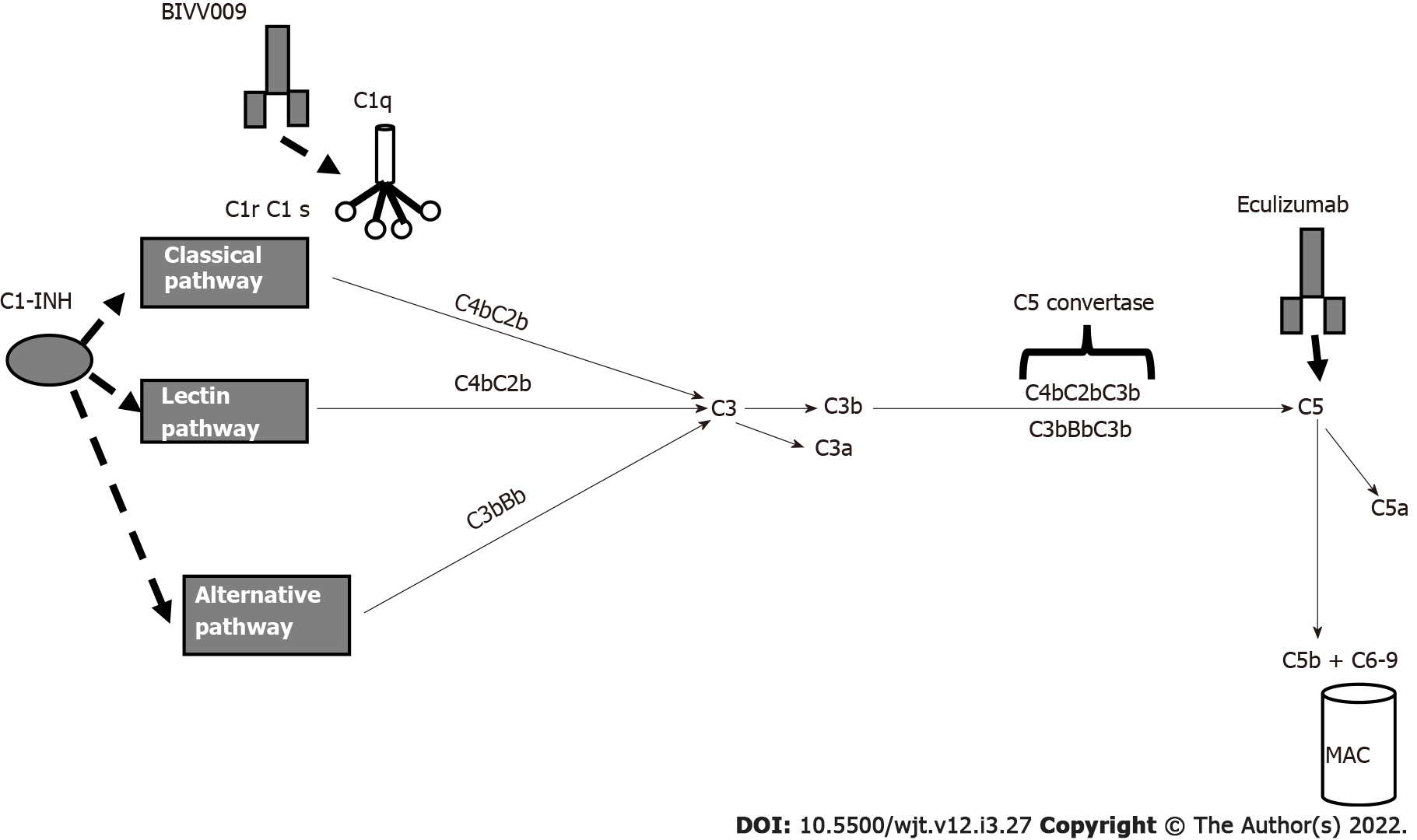
Figure 5 Principal drugs affecting complement.
C1-INH: C1 inhibitor; MAC: Membrane attacking complex.
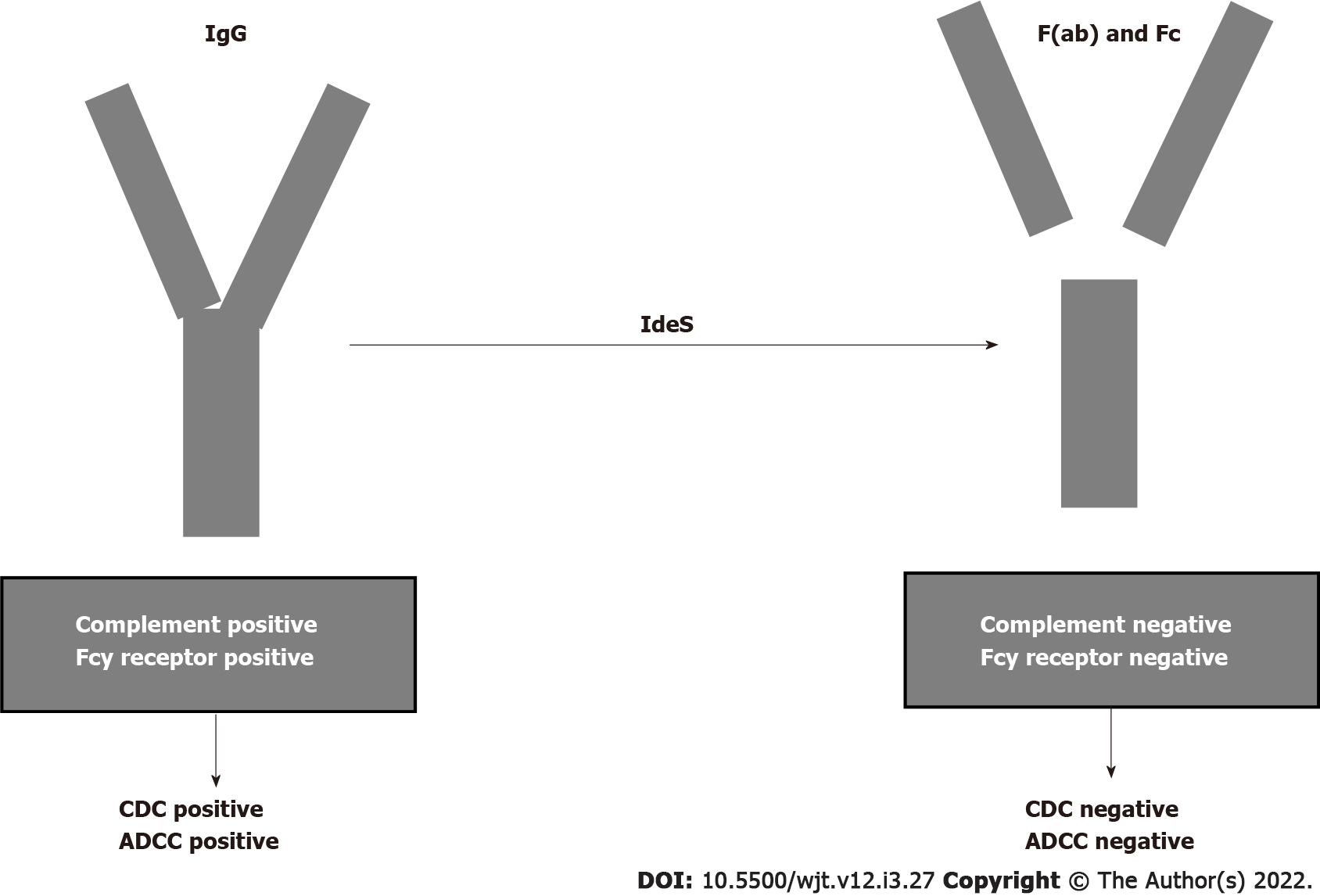
Figure 6 Cleaving intact immunoglobulin G by imlifidase.
CDC: Complement dependent cytotoxicity; ADCC: Antibody dependent cell cytotoxicity; F(ab): Fragment ab; Fc: Fragment c; Ides: Imlifidase; IgG: Immunoglobulin G.
- Citation: Salvadori M, Tsalouchos A. Innovative immunosuppression in kidney transplantation: A challenge for unmet needs. World J Transplant 2022; 12(3): 27-41
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v12/i3/27.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v12.i3.27