Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Transplant. Jun 18, 2021; 11(6): 161-179
Published online Jun 18, 2021. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i6.161
Published online Jun 18, 2021. doi: 10.5500/wjt.v11.i6.161
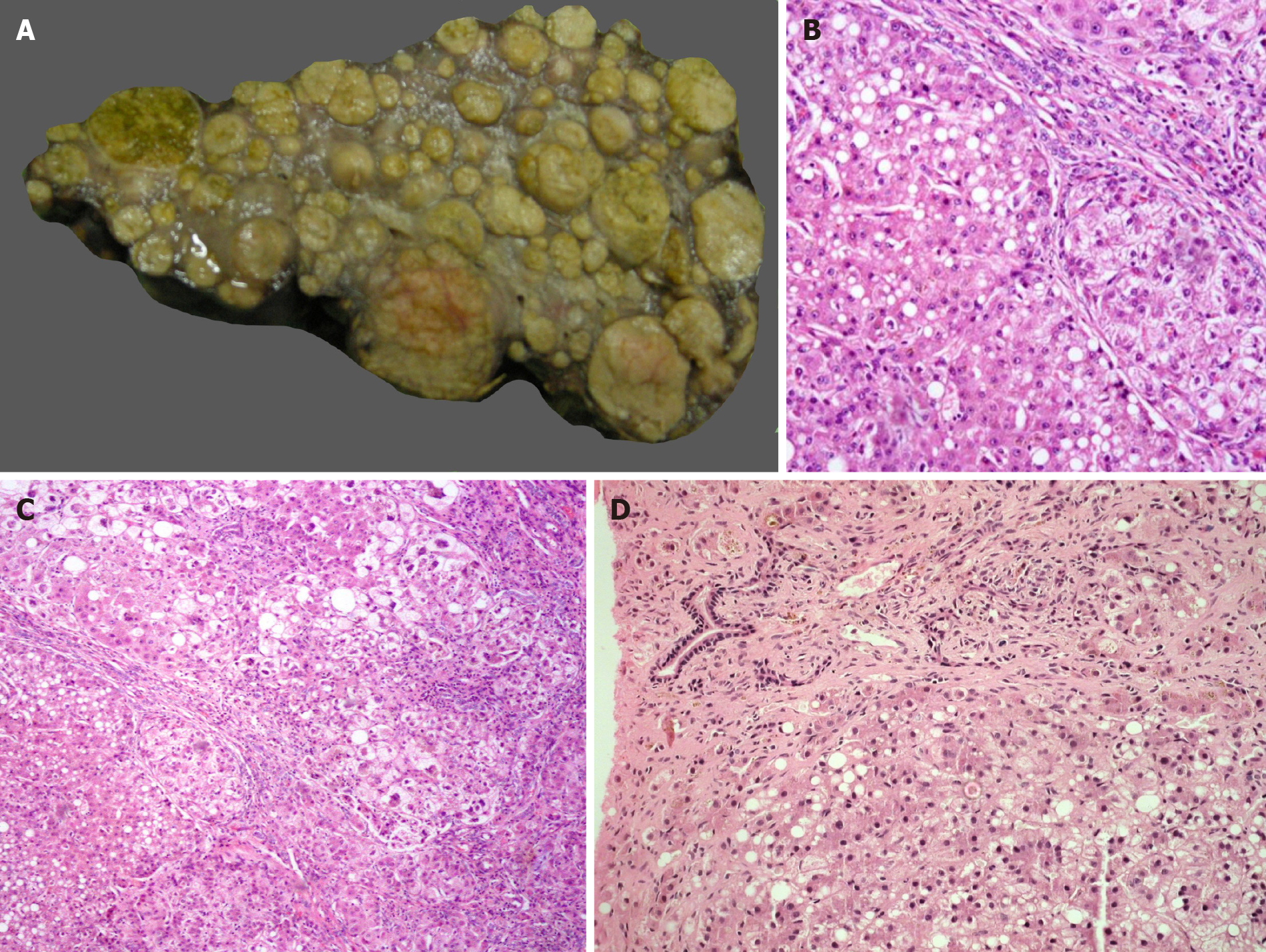
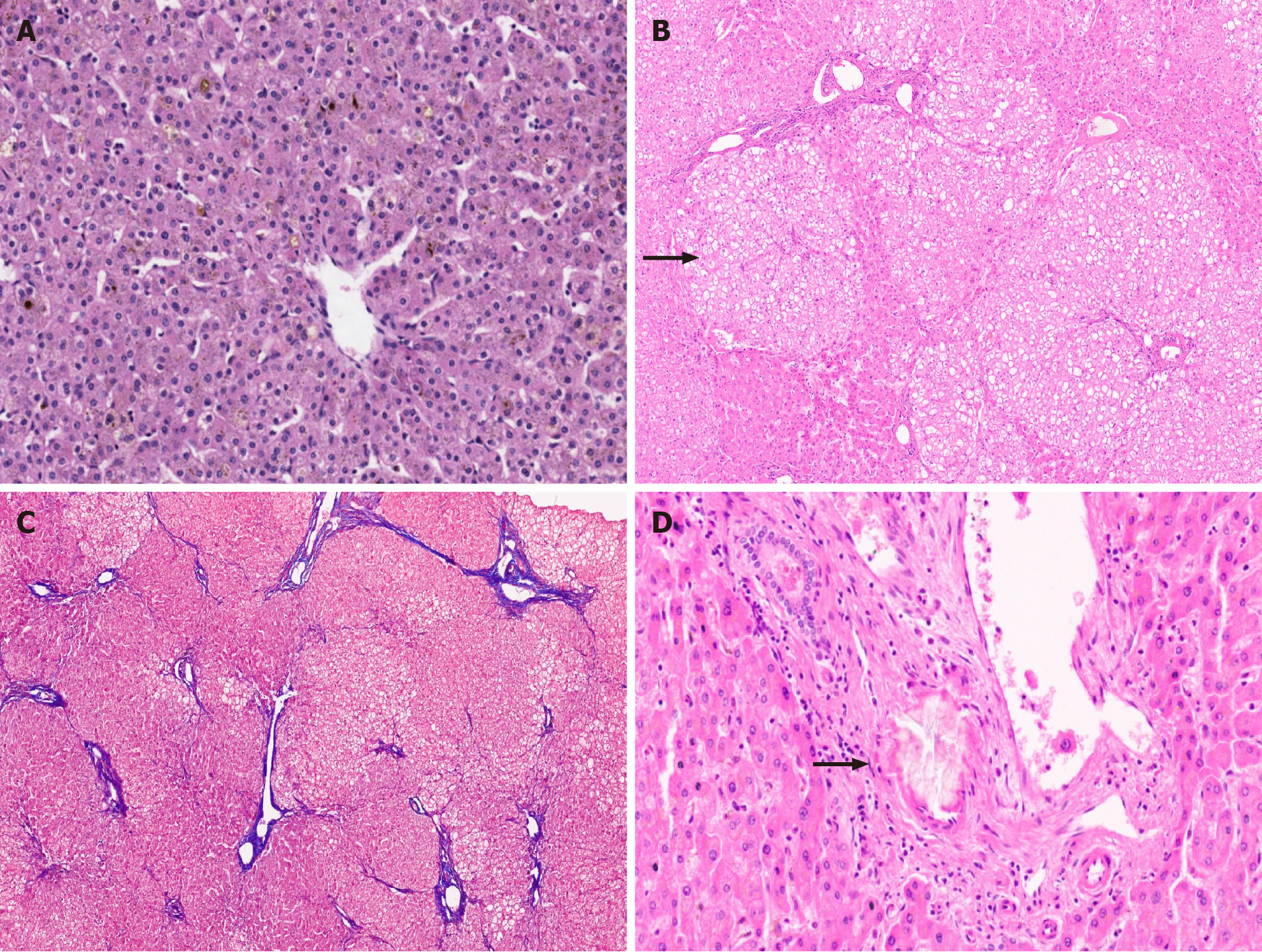
Figure 1 Metabolic liver disease.
A: Explant liver specimen of a case of tyrosinemia with nodules of varying sizes; B: Tyrosinemia liver with steatosis [hematoxylin and eosin (HE staining)]; C: Tyrosinemia liver with cirrhosis, hepatocellular ballooning, and fatty change (HE staining); D: Galactosemia with bridging fibrosis, bile ductular reaction, fatty change and rosetting (HE staining).
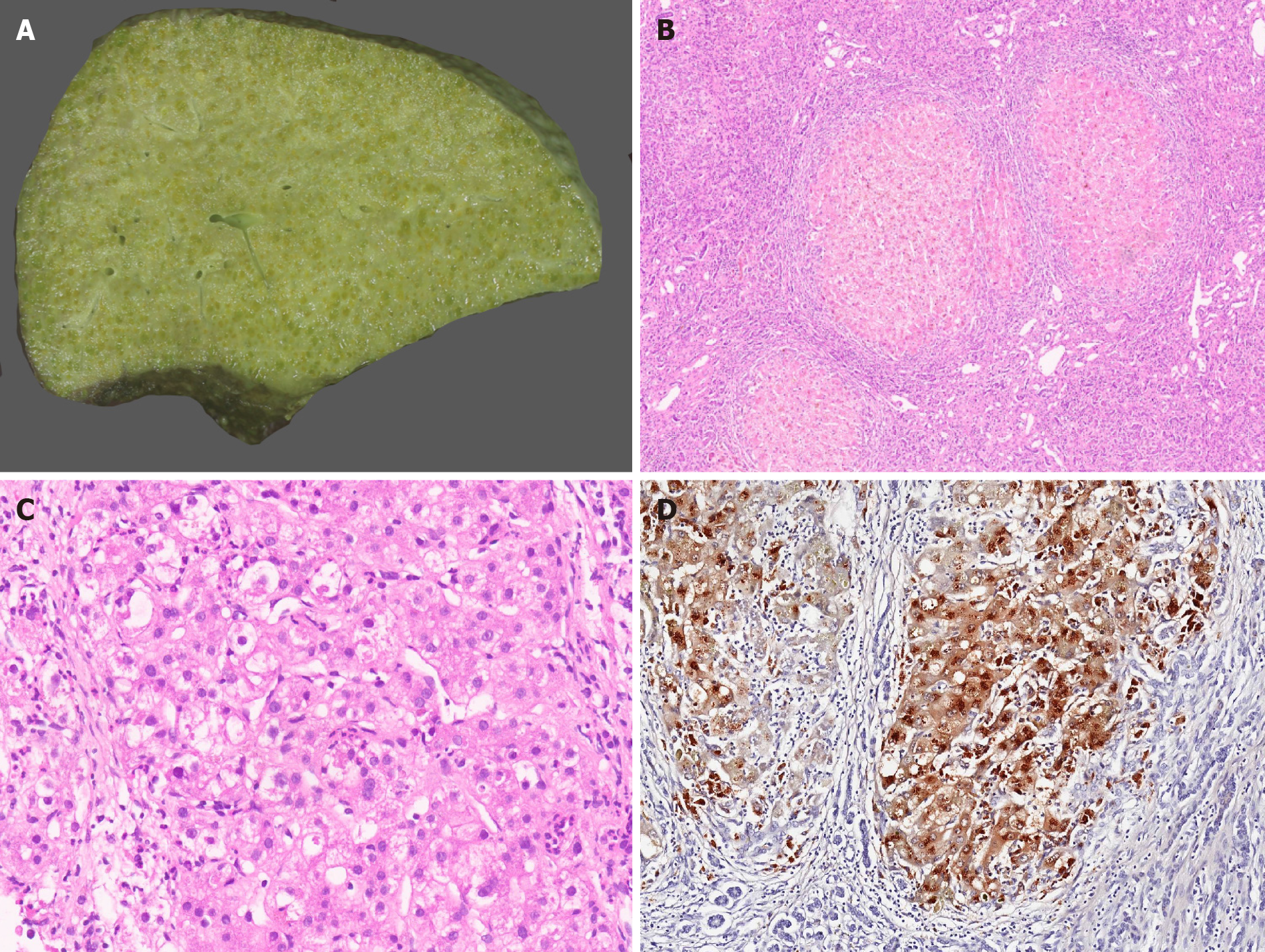
Figure 2 Wilson disease.
A: Explant hepatectomy specimen in a case of Wilson disease (WD) with marked cholestasis; B: Micronodular cirrhosis in a case of WD [hematoxylin and eosin (HE staining)]; C: WD with hepatocellular ballooning, Mallory Denk bodies, fatty change and neutrophilic satellitosis (HE staining); and D: WD with marked copper deposition in hepatocytes and macrophages (Rhodanine staining).
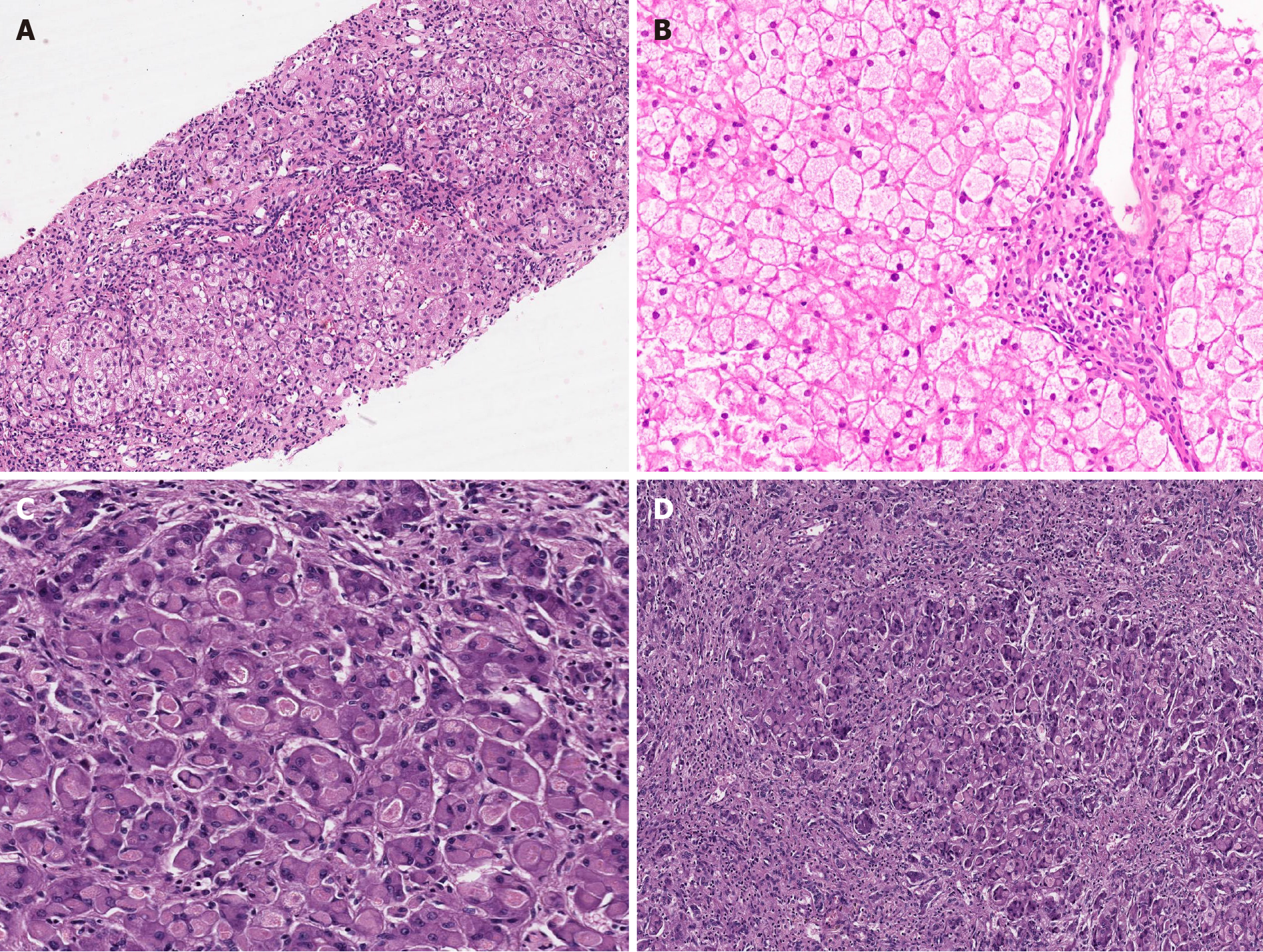
Figure 3 Metabolic liver disease.
A: Hereditary Fructosemia with bridging fibrosis [hematoxylin and eosin (HE staining)]; B: Glycogen storage disorder (GSD) type III displaying pale enlarged hepatocytes with thickened borders and portal fibrosis (HE); C: GSD type IV liver eosinophilic ground glass cytoplasmic inclusions (HE); D: Explant liver in case of GSD type IV with extensive fibrosis (HE).
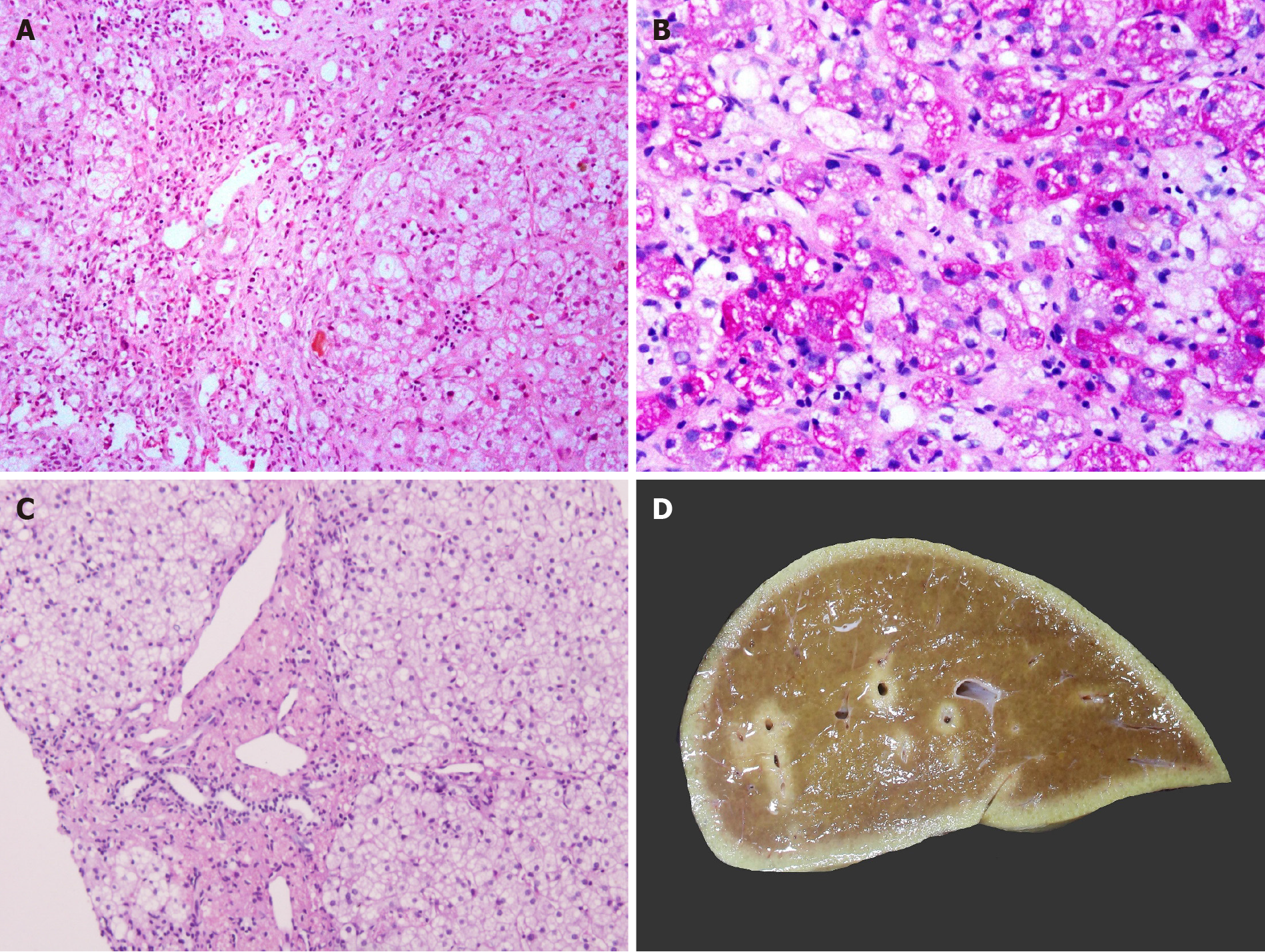
Figure 4 Metabolic liver disease.
A: Niemann Pick disease with marked fibrosis [hematoxylin and eosin (HE staining)]; B: Pale-staining storage cell clusters as compared to deeply stained glycogen containing hepatocytes [Periodic acid Schiff (PAS) staining]; C: Cholesteryl ester storage disease liver with granular microphages in portal tract and finely vacuolated hepatocytes (HE staining); and D: Largely unremarkable explant liver in a patient with urea cycle defect.
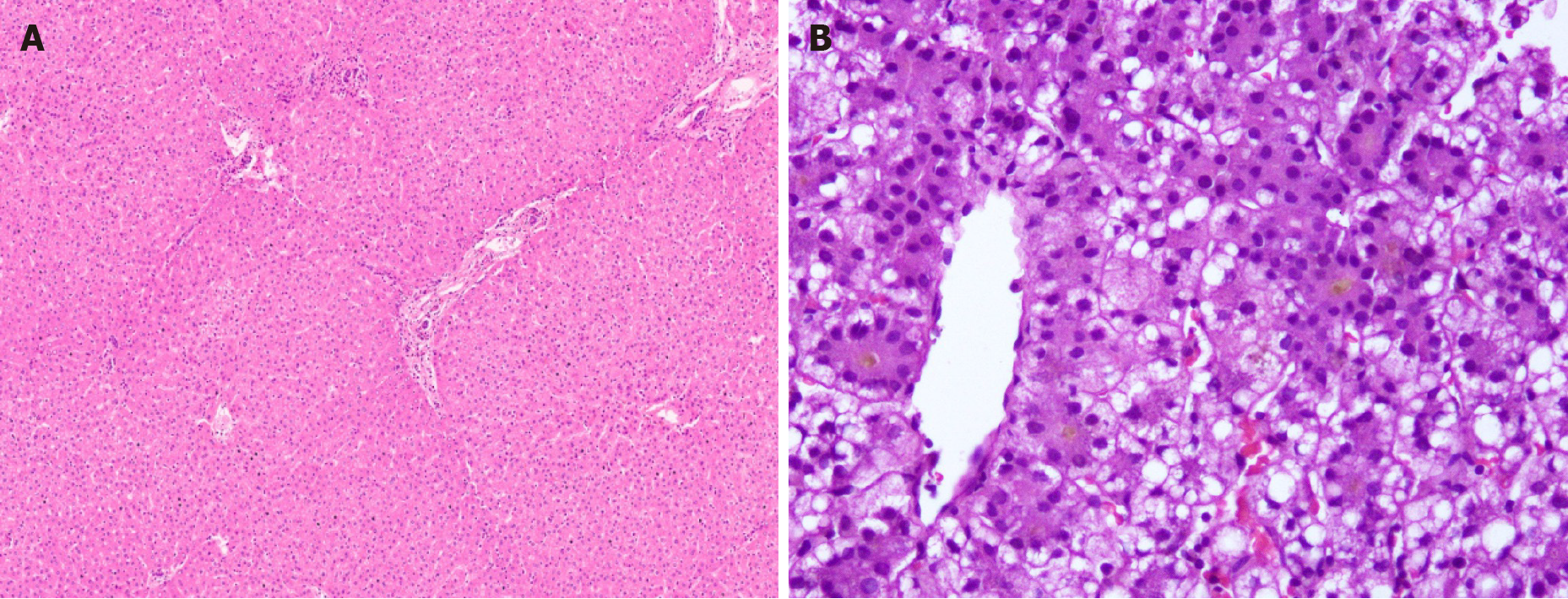
Figure 5 Metabolic liver disease.
A: Canalicular bilirubinostasis in case with urea cycle defect [hematoxylin and eosin (HE staining)]; B: Explanted liver in Arginase-1 (ARG-1) deficiency displaying nodules of pale enlarged hepatocytes (arrow, HE staining, B); C: Focal bridging fibrosis in a case of ARG-1 deficiency [Masson trichrome staining]; D: Portal vessel with oxalate crystals in primary hyperoxaluria type 1 (arrow, HE staining).
Figure 6 Metabolic liver disease.
A: Crigler Najjar explant liver with no significant morphological findings [Hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining]; B: Mitochondrial hepatopathy with mixed steatosis and bilirubinostasis HE staining).
- Citation: Menon J, Vij M, Sachan D, Rammohan A, Shanmugam N, Kaliamoorthy I, Rela M. Pediatric metabolic liver diseases: Evolving role of liver transplantation. World J Transplant 2021; 11(6): 161-179
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3230/full/v11/i6/161.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5500/wjt.v11.i6.161