Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Rheumatol. Nov 12, 2014; 4(3): 44-53
Published online Nov 12, 2014. doi: 10.5499/wjr.v4.i3.44
Published online Nov 12, 2014. doi: 10.5499/wjr.v4.i3.44
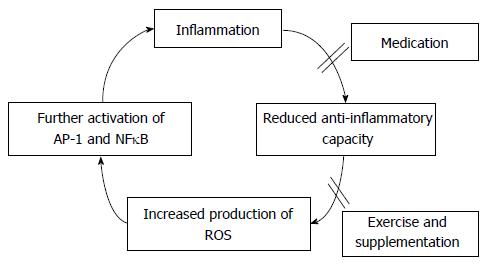
Figure 1 Hypothesis: Inflammation reduces anti-oxidant capacity which increases reactive oxygen species concentration, further activating pro-inflammatory pathways, entering the body into a vicious circle.
Control of inflammation via medication might increase anti-inflammatory capacity of the body while exercise and supplementation may lead to increased anti-oxidant capacity both resulting in reduced oxidative stress and preserve muscle mass. ROS: Reactive oxygen species. AP: Activator protein; NFκB: Nuclear factor kappa β.
- Citation: Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Deli C, Kitas GD, Jamurtas AZ. Muscle wasting in rheumatoid arthritis: The role of oxidative stress. World J Rheumatol 2014; 4(3): 44-53
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3214/full/v4/i3/44.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5499/wjr.v4.i3.44