Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Rheumatol. Nov 12, 2013; 3(3): 25-31
Published online Nov 12, 2013. doi: 10.5499/wjr.v3.i3.25
Published online Nov 12, 2013. doi: 10.5499/wjr.v3.i3.25
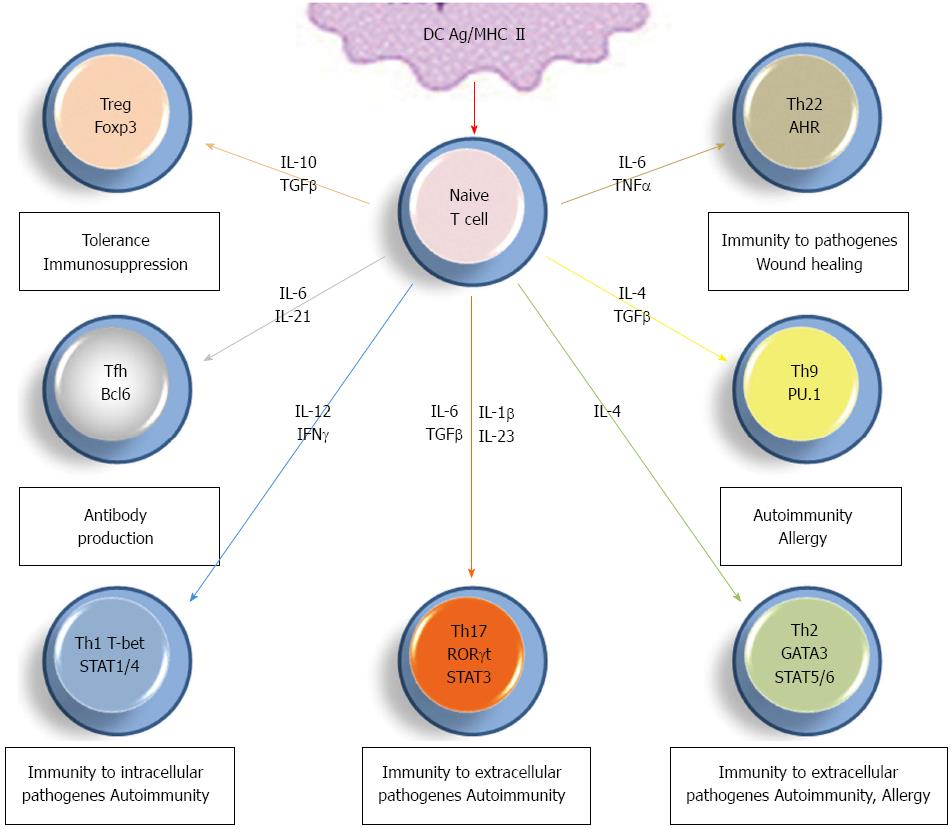
Figure 1 Diversity of CD4+ T helper cell subsets.
STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; HIF1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
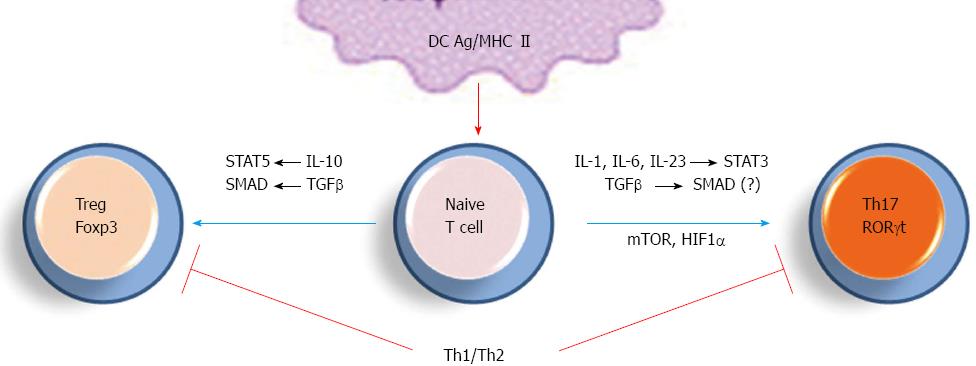
Figure 2 Differentiation of T helper 17/Treg cell subsets.
STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; HIF1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
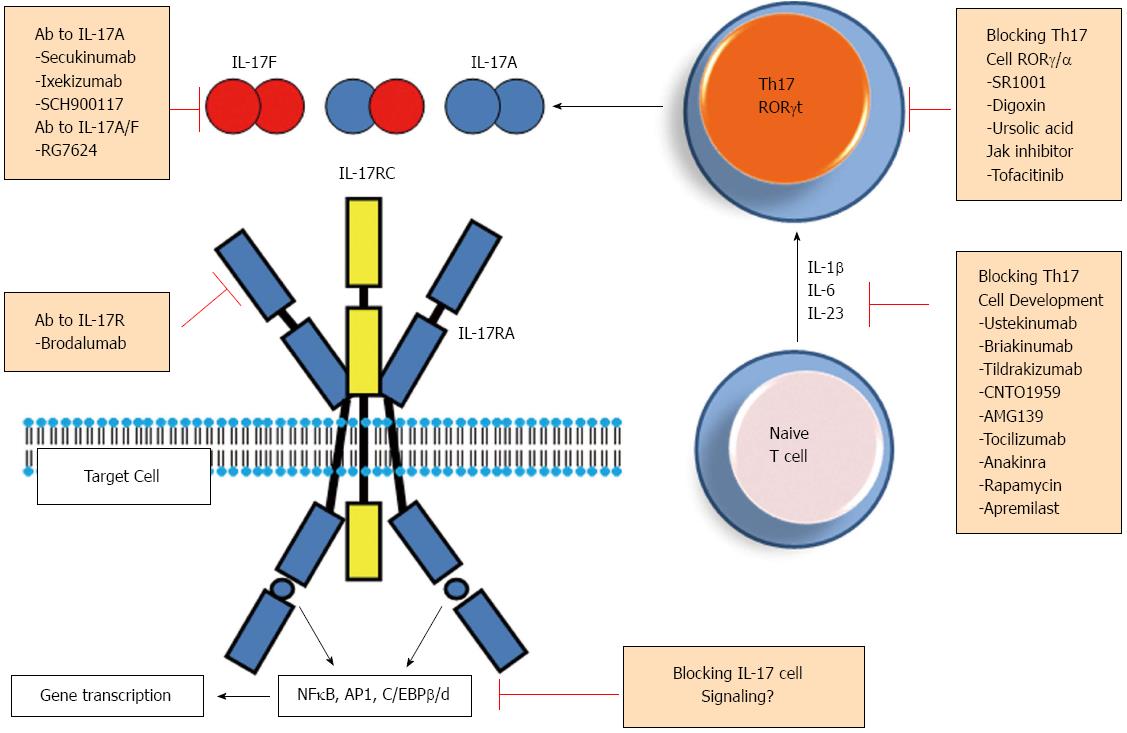
Figure 3 Strategies targeting the T helper 17 pathway.
STAT: Signal transducer and activator of transcription; IL: Interleukin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; HIF1: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1.
- Citation: Boniface K, Moynet D, Mossalayi MD. Role of Th17 cells in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. World J Rheumatol 2013; 3(3): 25-31
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3214/full/v3/i3/25.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5499/wjr.v3.i3.25