Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Psychiatr. Sep 22, 2016; 6(3): 283-293
Published online Sep 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i3.283
Published online Sep 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i3.283
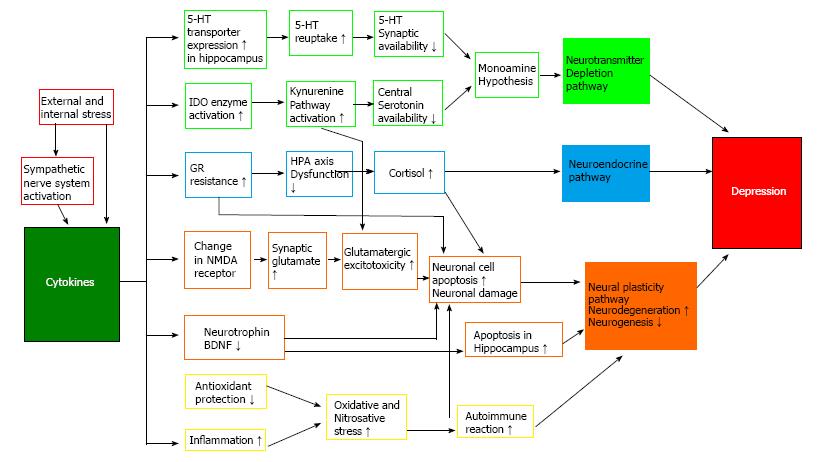
Figure 2 Schematic representation of neuroinflammatory pathways in the pathogenesis of depression.
Cytokine production is initially activated by stress and sympathetic nerve system activation. In turn, cytokines have an important role by acting via neurotransmitter depletion pathway, neuroendocrine pathway, and neural plasticity pathway. There are multiple interactions between these pathways suggesting existence of a complex model for pathogenesis of depression. 5-HT: Serotonin; BDNF: Brain derived neurotrophic factor; GR: Glucocorticoid receptor; HPA: Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal; IDO: Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartate.
- Citation: Jeon SW, Kim YK. Neuroinflammation and cytokine abnormality in major depression: Cause or consequence in that illness? World J Psychiatr 2016; 6(3): 283-293
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v6/i3/283.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v6.i3.283