Published online Aug 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i8.543
Peer-review started: May 11, 2023
First decision: May 31, 2023
Revised: June 28, 2023
Accepted: July 14, 2023
Article in press: July 14, 2023
Published online: August 19, 2023
Processing time: 98 Days and 6 Hours
Primiparas are usually at high risk of experiencing perinatal depression, which may cause prolonged labor, increased blood loss, and intensified pain, affecting maternal and fetal outcomes. Therefore, interventions are necessary to improve maternal and fetal outcomes and alleviate primiparas’ negative emotions (NEs).
To discusses the impact of nursing responsibility in midwifery and postural and psychological interventions on maternal and fetal outcomes as well as primiparas’ NEs.
As participants, 115 primiparas admitted to Quanzhou Maternity and Child Healthcare Hospital between May 2020 and May 2022 were selected. Among them, 56 primiparas (control group, Con) were subjected to conventional midwifery and routine nursing. The remaining 59 (research group, Res) were subjected to the nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions. Both groups were comparatively analyzed from the perspectives of delivery mode (cesarean, natural, or forceps-assisted), maternal and fetal outcomes (uterine inertia, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, neonatal pulmonary injury, and neonatal asphyxia), NEs (Hamilton Anxiety/Depression-rating Scale, HAMA/HAMD), labor duration, and nursing satisfaction.
The Res exhibited a markedly higher natural delivery rate and nursing satisfaction than the Con. Additionally, the Res indicated a lower incidence of adverse events (e.g., uterine inertia, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, neonatal lung injury, and neonatal asphyxia) and shortened duration of various stages of labor. It also showed statistically lower post-interventional HAMA and HAMD scores than the Con and pre-interventional values.
The nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions increase the natural delivery rate and reduce the duration of each labor stage. These are also conducive to improving maternal and fetal outcomes and mitigating primiparas’ NEs and thus deserve popularity in clinical practice.
Core Tip: Primiparas are at high risk for depression during the perinatal period, which can lead to prolonged labor, increased blood loss, and intensified pain that can affect maternal and fetal outcomes. Therefore, it is necessary to give relevant interventions to improve maternal and fetal outcomes and alleviate negative emotions in primiparas.
- Citation: Gao P, Guo CQ, Chen MY, Zhuang HP. Nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions: Impact on maternal and fetal outcomes and negative emotions of primiparas. World J Psychiatry 2023; 13(8): 543-550
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v13/i8/543.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v13.i8.543
Primiparas and multiparas are often at a high risk of experiencing perinatal depression because of the significant physical and psychological burdens they encounter[1]. As reported, the incidence of depression is higher among primiparas than multiparas[2,3]. Clinically, primiparas often develop negative emotions (NEs), such as fear and anxiety, due to severe labor pain caused by inexperience during delivery[4]. Owing to this, mothers may suffer from a lack of strength or improper exertion, leading to prolonged labor, increased blood loss, and intensified pain[5,6]. The type of delivery can also affect maternal and fetal outcomes, with mothers undergoing cesarean section (CS) facing a higher risk of complications[7]. Thus, this study intends to mitigate the NEs of primiparas and improve maternal and fetal outcomes by combining the appropriate nursing model with certain interventions. This study also contributes toward the prevention of maternal complications as well as management optimization during clinical application.
Although routine midwifery and nursing aid primiparas, the quality across medical institutions may vary[8]. There is a need to improve the regulatory effect of routine nursing on maternal NEs[9]. Therefore, our research team adopted the care model of midwifery, a novel model of midwifery nurse practice that prioritizes the psychological and emotional state of mothers and is more humanized[10,11]. In the study on maternal care by Beecher et al[12], the improvement of maternal psychological quality under the midwifery responsibility system was demonstrated and its positive effect was affirmed. Besides, Wu et al[13] reported on the intervention of primary maternal care, pointing out that combining postural and breathing training under the original nursing model can effectively smoothen the delivery process and improve the outcomes of primiparas.
Currently, there are insufficient studies on the clinical application of the care model of midwifery as well as postural and psychological interventions in primipara nursing management, which is this study’s focus. It explores and analyzes the same from the perspectives of delivery mode, maternal and fetal outcomes, NEs, labor duration, and nursing satisfaction. Its ultimate goal is to provide an effective clinical basis for the nursing management of primiparas and improve their delivery experience.
The study participants were 115 primiparas who visited the Quanzhou Maternity and Child Healthcare Hospital between May 2020 and May 2022. The control group (Con; n = 56) was subjected to conventional midwifery and routine nursing; the research group (Res; n = 59) was subjected to the nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions. Both groups had similar baseline (P > 0.05) and clinical comparability. The inclusion criteria were as follows: Primiparas with full-term pregnancy and normal pelvic diameter after measurement; single pregnancy, normal fetal presentation, and priority for a vaginal birth; no high-risk maternal complications during pregnancy or pregnancy complications; and normal mental state and verbal communication ability. The exclusion criteria were as follows: Malignancies or organ dysfunction; conditions like nuchal cord, premature rupture of membranes, and amniotic fluid volume abnormality; history of uterine surgery; premature birth or post-term pregnancy; abnormal coagulation function; and autoimmune deficiency.
The Con was subjected to conventional midwifery and routine nursing. After admission, the midwives on duty provided services, such as routine fetal heart monitoring, maternal skin cleaning, labor process observation, and health guidance. There was no postural intervention during the labor period. The parturient was allowed to choose a comfortable posture, and the midwife delivered the baby after the cervix was fully dilated. Routine nursing measures were also provided.
The Res was subjected to the nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions. First, one-to-one nursing was provided to each primipara, and a private midwife was there to provide care and management throughout the process of labor preparation and delivery. This not only promoted mutual communication but also facilitated the collection of the primipara's information and the formulation and implementation of nursing strategies, thus improving the efficiency and experience of nursing. The main nursing and management provided by midwives included the following aspects: (1) Prenatal education: Midwives introduced perinatal knowledge to the parturients and informed them of the symptoms they may encounter during the perinatal period and the physiological process of delivery. Through videos and clinical demonstrations, mothers were instructed on pain relief in the first stage of labor through deep breathing, and proper force exertion in the second stage of labor to shorten the labor duration. Addi-tionally, exchanges between multiparas and primiparas were arranged to impart childbirth experience to first-time mothers in order to strengthen their confidence; (2) Psychological intervention: By communicating with the parturients, the midwives evaluated the mothers’ potential concerns, depression, fear, and other NEs; they encouraged the mothers to express their worries and provided one-on-one psychological counseling based on the mothers’ personality traits and educational level. Furthermore, by enumerating the successful childbirth experiences of other parturients, the midwives enhanced the mothers’ confidence in childbirth and relieved their unhealthy psychology; (3) Postural intervention: During the first stage of labor, the parturients were guided to take a free position, with their attention diverted. For mothers with half engagement of non-engagement of fetal presenting part, they were suggested to walk while supporting the belly to speed up the delivery. If the uterine orifice opening was 1-2 cm and the fetus was found to be in an occipital posterior position, the mother was instructed to assume the contralateral prone position during pregnancy, depending on the specific fixed position during pregnancy. During the second stage of labor when the fetal head descended slowly, the mother was instructed to squat according to the maternal situation; (4) Nursing during labor: During labor, the midwife paid close attention to the physical and mental condition of the mother and relieved contraction-induced pain by helping her wipe sweat, massaging the lower abdomen, and expressing encouragement. At the same time, the progress of labor was closely observed. In the case of increased maternal blood loss, uterine contraction weakness, prolonged second labor, fetal distress, and other conditions, the doctor was immediately reported to take timely corresponding measures; and (5) Postpartum care: After the fetus was delivered and processed, it was sent to the mother in time to guide and help early suckling. The newborn was observed in the infant room for two hours and was timely sent back to its mother if there was no abnormality. The midwives also closely observed the vital signs, uterine contraction, and mental state of the postpartum women, especially the amount of postpartum vaginal bleeding, and offered timely interventions when necessary.
(1) Mode of delivery. The delivery modes of both groups, including CS, natural delivery, and forceps-assisted delivery (FAD), were observed and recorded; (2) Maternal and fetal outcomes. The maternal and fetal outcomes were compared, including uterine inertia, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, neonatal lung injury, and neonatal asphyxia; (3) NEs. Maternal NEs were evaluated using the Hamilton Anxiety/Depression-rating Scale (HAMA/HAMD)[14]. HAMA has 14 assessment items, and HAMD has 24 assessment items; each item of both is graded from 0 to 4, with higher scores indicating more serious anxiety or depression symptoms; (4) Duration of labor. The duration of each stage of labor was recorded for comparative analysis; and (5) Nursing satisfaction. Patients were asked to fill in the self-made nursing satisfaction questionnaire of our hospital (0-100 points) to understand their satisfaction with the nursing services. Higher scores are indicative of better satisfaction, with a score of > 80 points, 60-80 points, and < 60 points representing satisfactory, basically satisfactory, and unsatisfactory, respectively.
The number of cases/percentage (n, %) and the mean ± SEM were used to represent categorical and continuous variables, respectively. Among these, the χ2 test was used to compare categorical data, and the independent sample t-test compared the continuous variables between the groups. In this study, the SPSS18.0 software package was used for statistical analysis, and a minimum significance level of P < 0.05 was used throughout.
Both study groups were comparable in terms of age, gestational age, body mass index, smoking history, drinking history, educational level, and other general data (P > 0.05) (Table 1).
| Factors | Control group (n = 56) | Research group (n = 59) | χ2/t | P value |
| Age (years) | 26.80 ± 7.23 | 28.46 ± 7.20 | 1.233 | 0.220 |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 37.71 ± 1.58 | 37.90 ± 1.77 | 0.606 | 0.546 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.85 ± 2.95 | 22.70 ± 3.21 | 0.261 | 0.795 |
| History of smoking (yes/no) | 14/42 | 11/48 | 0.682 | 0.409 |
| History of alcoholism (yes/no) | 10/46 | 16/43 | 1.408 | 0.235 |
| Educational level (primary school or junior high school/senior high school/junior college and above) | 17/26/13 | 18/30/11 | 0.403 | 0.818 |
According to the comparative analysis of the delivery modes (CS, natural delivery, and FAD), the Res had a higher natural delivery rate (P < 0.05), a lower CS rate (P < 0.05), and a comparable FAD rate than the Con (P > 0.05) (Table 2).
| Categories | Control group (n = 56) | Research group (n = 59) | χ2 value | P value |
| Cesarean section | 28 (50.00) | 4 (6.78) | 26.723 | < 0.001 |
| Natural delivery | 24 (42.86) | 53 (89.83) | 28.653 | < 0.001 |
| Forceps-assisted delivery | 4 (7.14) | 2 (3.39) | 0.818 | 0.366 |
Evaluating and comparing the maternal and fetal outcomes, such as uterine inertia, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, neonatal lung injury, and neonatal asphyxia indicated that the incidence of adverse maternal and fetal outcomes described above was statistically lower in the Res (P < 0.05) (Table 3).
| Categories | Control group (n = 56) | Research group (n = 59) | χ2 value | P value |
| Uterine inertia | 17 (30.36) | 7 (11.86) | 5.950 | 0.015 |
| Postpartum hemorrhage | 6 (10.71) | 1 (1.69) | 4.089 | 0.043 |
| Placental abruption | 5 (8.93) | 0 (0.00) | 5.507 | 0.019 |
| Neonatal lung injury | 6 (10.71) | 1 (1.69) | 4.089 | 0.043 |
| Neonatal asphyxia | 4 (7.14) | 0 (0.00) | 4.366 | 0.037 |
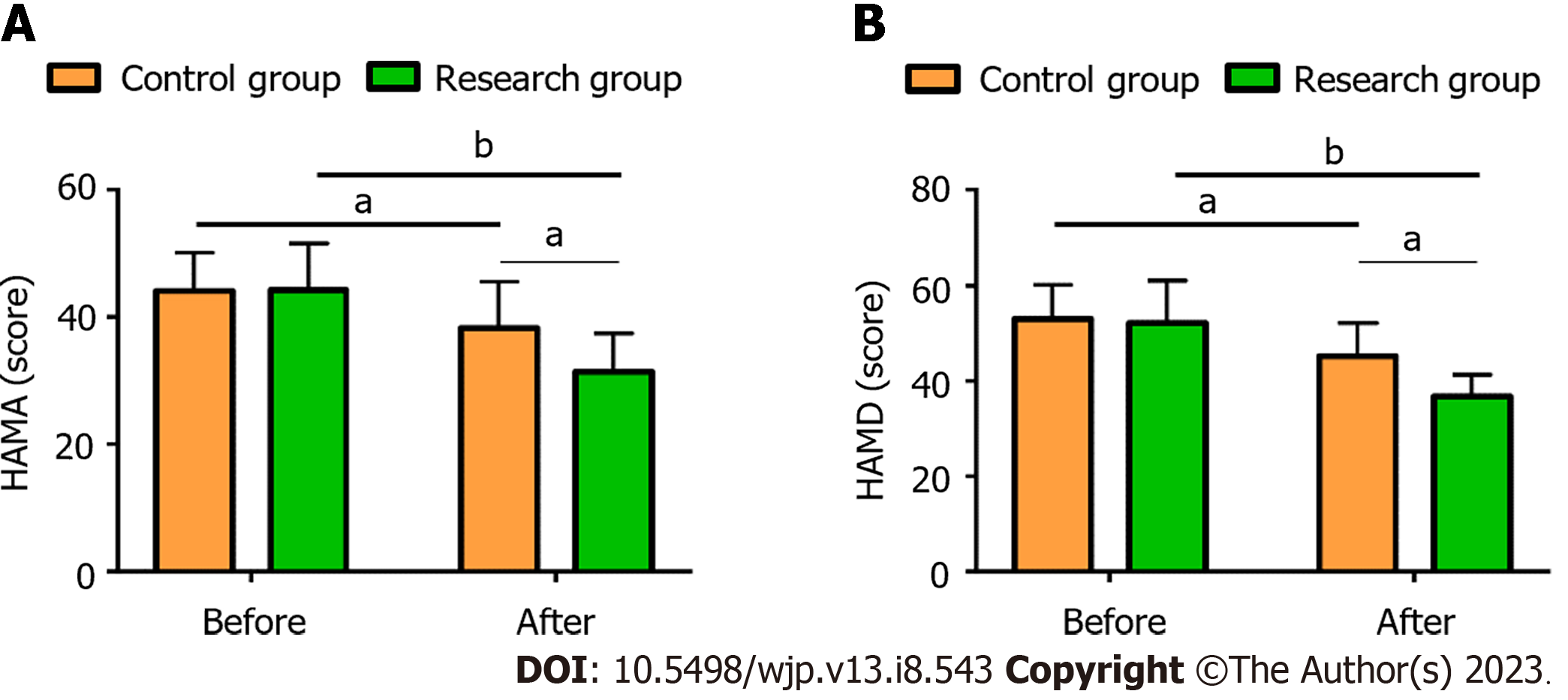
The assessment of maternal anxiety and depression using the HAMA and HAMD revealed that both scale scores were similar in the two groups before the interventions, but they significantly declined after corresponding interventions (P < 0.05), with even lower scores in the Res compared to the Con (P < 0.05) (Figure 1).
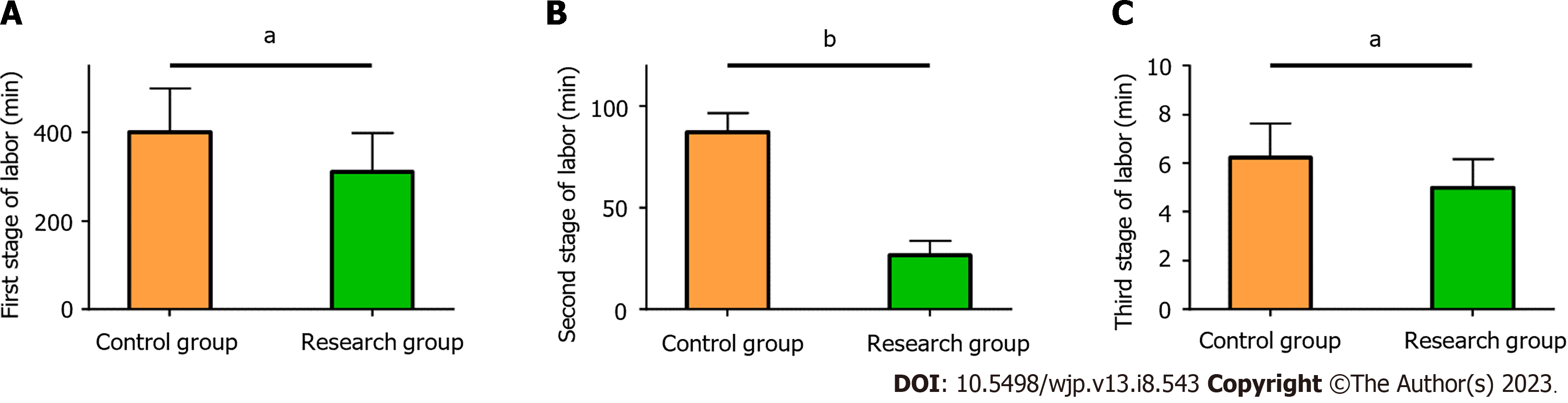
The time spent in the first, second, and third stages of labor was markedly shorter in the Res than the Con (P < 0.05) (Figure 2).
Patient satisfaction with the care services was assessed using a self-developed nursing satisfaction questionnaire. The satisfaction of the Res was statistically higher compared to the Con (96.61% vs 82.14%, P < 0.05) (Table 4).
| Categories | Control group (n = 56) | Research group (n = 59) | χ2 value | P value |
| Satisfactory | 17 (30.36) | 36 (61.02) | - | - |
| Basically satisfactory | 29 (51.79) | 21 (35.59) | - | - |
| Unsatisfactory | 10 (17.86) | 2 (3.39) | - | - |
| Satisfaction | 46 (82.14) | 57 (96.61) | 6.434 | 0.011 |
Labor is a physiological process a mother undergoes to deliver an infant, which is accompanied by pain and pressure[15]. Providing scientific and reasonable care management for primiparas is therefore of great value to improve their birthing experience and delivery outcomes. The mode of delivery affects not only maternal and infant health, but also the success rate of breastfeeding[16]. Specifically, although CS is devoid of childbirth pain, it is riskier for maternal and infant health compared to normal delivery; it is associated with a higher risk of maternal mortality and postoperative complications[17,18]. The analysis of delivery modes in this study revealed that the Res had a markedly higher natural delivery rate, a lower CS rate, and a comparable FAD rate than the Con, suggesting that the adoption of the nursing model of midwifery along with postural and psychological interventions can significantly improve the natural delivery rate in primiparas. This may be attributed to the postural guidance provided to the Res, which reduced the oppression of the uterus and the friction caused by the rotation of the carcass, thus ensuring natural delivery[19]. Furthermore, the statistics of maternal and fetal outcomes showed that the incidence of adverse events, such as uterine inertia, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, neonatal lung injury, and neonatal asphyxia, was markedly lower in the Res than in the Con. Thus, the nursing model of midwifery along with postural and psychological interventions is conducive to reducing adverse maternal and fetal outcomes. Considering the potential occurrence of the aforementioned adverse events, this novel nursing model pays close attention to these events and entails timely treatment of such conditions throughout the labor process and postpartum care; this explains the low incidence of adverse events in the Res[20]. In the research of Zhang et al[21], continuous midwifery services, which also integrate health education, psychological interventions, and labor and postpartum care, not only elevate the natural delivery rate of primiparas but also significantly improve maternal and fetal outcomes, similar to our findings.
Primiparas are prone to anxiety, fear, and other NEs due to their lack of experience in childbirth; this can affect the progress of labor and the smooth delivery, making psychological interventions crucial[22]. In this study, the Res showed lower HAMA and HAMD scores than the Con after the interventions, indicating that the nursing model of midwifery along with postural and psychological interventions can significantly relieve anxiety, depression, and other NEs in primiparas. This may be related to the fact that the nursing model experienced by the Res included psychological interventions and the timely channelization of maternal NEs[23]. In terms of the labor process, the Con spent more time in the first, second, and third stages of labor than the Res, indicating that the labor process of primiparas is smoother when the nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions are adopted. In this study, the prenatal education in the nursing management model used in the Res provided primiparas with guidance on the possible problems and coping approaches during the labor process, which helps accelerate the progress of labor[24,25]. Finally, the evaluation of the nursing satisfaction questionnaire showed a satisfaction degree as high as 96.61% in the Res, demonstrating that the nursing model along with the interventions is more popular among first-time mothers and advantageous over the conventional model in clinical practice. Based on the one-to-one nursing model, this novel nursing model provides services, such as prenatal education, psychological and postural interventions, labor care, and postpartum care for primiparas to improve their delivery experience, thus enhancing care quality and nursing satisfaction.
For primiparas, the nursing model of midwifery and postural and psychological interventions effectively improves maternal and fetal outcomes. Consequently, maternal anxiety and depression are alleviated, the natural delivery rate and nursing satisfaction increased, and the progress of labor is promoted. Therefore, this technique deserves clinical promotion.
Parturients are physically and psychologically burdened during the perinatal period, so both primiparas and multiparas are at higher risk of depression. In addition, the mode of delivery of primiparas has an impact on maternal and infant outcomes, and those given birth by cesarean section (CS) are at a higher risk of complications.
To increase people’s awareness of perinatal maternal management and provide reference for clinical care optimization of parturients during the perinatal period.
This study aims to analyze the effects of midwifery responsibility nursing plus postural interventions on maternal and fetal outcomes and negative emotions (NEs) of primiparas.
In this study, 59 primiparas in the research group were treated by midwifery responsibility nursing plus posture interventions, and 56 primiparas in the control group were given conventional midwifery and routine nursing. The two groups were comparatively analyzed in terms of the mode of delivery, maternal and infant outcomes, NEs (Hamilton Anxiety/Depression-rating Scale, HAMA/HAMD), duration of labor, and nursing satisfaction.
Significantly higher natural delivery rate and nursing satisfaction, as well markedly lower CS and forceps delivery rates were determined in the research group compared with the control group; the research group also showed obviously lower incidence of uterine inertia, postpartum hemorrhage, placental abruption, neonatal lung injury, neonatal asphyxia and other events and shorter duration of each stage of labor than the control group; moreover, the HAMA and HAMD scores of the research group after intervention were significantly lower than those before treatment and in the control group.
Midwifery responsibility nursing plus postural interventions is beneficial to improve maternal and infant outcomes, relieve maternal NEs, increase the rate of spontaneous labor, and shorten the duration of natural labor.
This study mainly analyzes the application value of midwifery responsibility nursing plus postural intervention program in the care management of primiparas, focusing on the exploration and analysis of maternal and infant outcomes and NEs, in an attempt to provide an effective clinical basis for the care management of primiparas and contribute to improving their childbirth experience.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Psychiatry
Country/Territory of origin: China
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kathirvel N, Singapore; Newson JJ, United States S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: A P-Editor: Chen YX
| 1. | Nakamura Y, Okada T, Morikawa M, Yamauchi A, Sato M, Ando M, Ozaki N. Perinatal depression and anxiety of primipara is higher than that of multipara in Japanese women. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17060. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Barnes J, Theule J. Maternal depression and infant attachment security: A meta-analysis. Infant Ment Health J. 2019;40:817-834. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 33] [Cited by in RCA: 58] [Article Influence: 9.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Shi P, Ren H, Li H, Dai Q. Maternal depression and suicide at immediate prenatal and early postpartum periods and psychosocial risk factors. Psychiatry Res. 2018;261:298-306. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 63] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Whitley J, Wouk K, Bauer AE, Grewen K, Gottfredson NC, Meltzer-Brody S, Propper C, Mills-Koonce R, Pearson B, Stuebe A. Oxytocin during breastfeeding and maternal mood symptoms. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2020;113:104581. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 31] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Tabatabaeichehr M, Mortazavi H. The Effectiveness of Aromatherapy in the Management of Labor Pain and Anxiety: A Systematic Review. Ethiop J Health Sci. 2020;30:449-458. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Cavalcanti ACV, Henrique AJ, Brasil CM, Gabrielloni MC, Barbieri M. Complementary therapies in labor: randomized clinical trial. Rev Gaucha Enferm. 2019;40:e20190026. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Netsi E, Pearson RM, Murray L, Cooper P, Craske MG, Stein A. Association of Persistent and Severe Postnatal Depression With Child Outcomes. JAMA Psychiatry. 2018;75:247-253. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 342] [Cited by in RCA: 405] [Article Influence: 57.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Guzha BT, Magwali TL, Mateveke B, Chirehwa M, Nyandoro G, Munjanja SP. Assessment of quality of obstetric care in Zimbabwe using the standard primipara. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018;18:205. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Waldrop J, Baker M, Salomon R, Moreton E. Parenting Interventions and Secondary Outcomes Related to Maternal Mental Health: A Systematic Review. Matern Child Health J. 2021;25:870-880. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 7] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Brundell K, Vasilevski V, Sweet L. Australian maternity care, considering risk and supporting safety: A scoping review. Midwifery. 2022;112:103408. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Bernstein SL. Respectful Maternity Care. MCN Am J Matern Child Nurs. 2022;47:227. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Beecher C, Greene R, O'Dwyer L, Ryan E, White M, Beattie M, Devane D. Measuring women's experiences of maternity care: A systematic review of self-report survey instruments. Women Birth. 2021;34:231-241. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 16] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Wu C, Ge Y, Zhang X, Du Y, He S, Ji Z, Lang H. The combined effects of Lamaze breathing training and nursing intervention on the delivery in primipara: A PRISMA systematic review meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021;100:e23920. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Meng J, Du J, Diao X, Zou Y. Effects of an evidence-based nursing intervention on prevention of anxiety and depression in the postpartum period. Stress Health. 2022;38:435-442. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 4.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Oyarzabal EA, Seuferling B, Babbar S, Lawton-O'Boyle S. Mind-Body Techniques in Pregnancy and Postpartum. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2021;64:683-703. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 16. | Hobbs AJ, Mannion CA, McDonald SW, Brockway M, Tough SC. The impact of caesarean section on breastfeeding initiation, duration and difficulties in the first four months postpartum. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2016;16:90. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 219] [Cited by in RCA: 308] [Article Influence: 34.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Wang J, Lu X, Wang C, Li X. The effectiveness of delivery ball use versus conventional nursing care during delivery of primiparae. Pak J Med Sci. 2020;36:550-554. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Zandvakili F, Rezaie M, Shahoei R, Roshani D. Maternal Outcomes Associated with Caesarean versus Vaginal Delivery. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11:QC01-QC04. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 2] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Budin WC. Making a difference with evidence. J Perinat Educ. 2010;19:1-3. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Yang J, Armson BA, Attenborough R, Carson GD, da Silva O, Heaman M, Janssen P, Murphy PA, Pasquier JC, Sauve R, Von Dadelszen P, Walker M, Lee SK; Canadian Mode of Delivery Study Group. Survey of Mode of Delivery and Maternal and Perinatal Outcomes in Canada. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2022;44:960-971. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Zhang Y, Xu K, Gong L, Sun Y, Ren F. The effect of continuous midwifery services on the delivery mode, labor progress, and nursing satisfaction of primiparas during natural deliveries. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13:7249-7255. [PubMed] |
| 22. | Jepsen I, Juul S, Foureur MJ, Sørensen EE, Nohr EA. Labour outcomes in caseload midwifery and standard care: a register-based cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2018;18:481. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Fan W, Wang L, Zhang L, Liu X, Meng Z. Analysis of the Influence of Midwife Led Antenatal Clinic on the Delivery Outcomes of Primipara under the Evaluation of Medical Data. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022;2022:7454258. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Crowther S, MacIver E, Lau A. Policy, evidence and practice for post-birth care plans: a scoping review. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2019;19:137. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Simpson M, Catling C. Understanding psychological traumatic birth experiences: A literature review. Women Birth. 2016;29:203-207. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 88] [Cited by in RCA: 131] [Article Influence: 13.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |