Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2022; 12(3): 379-392
Published online Mar 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.379
Published online Mar 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.379
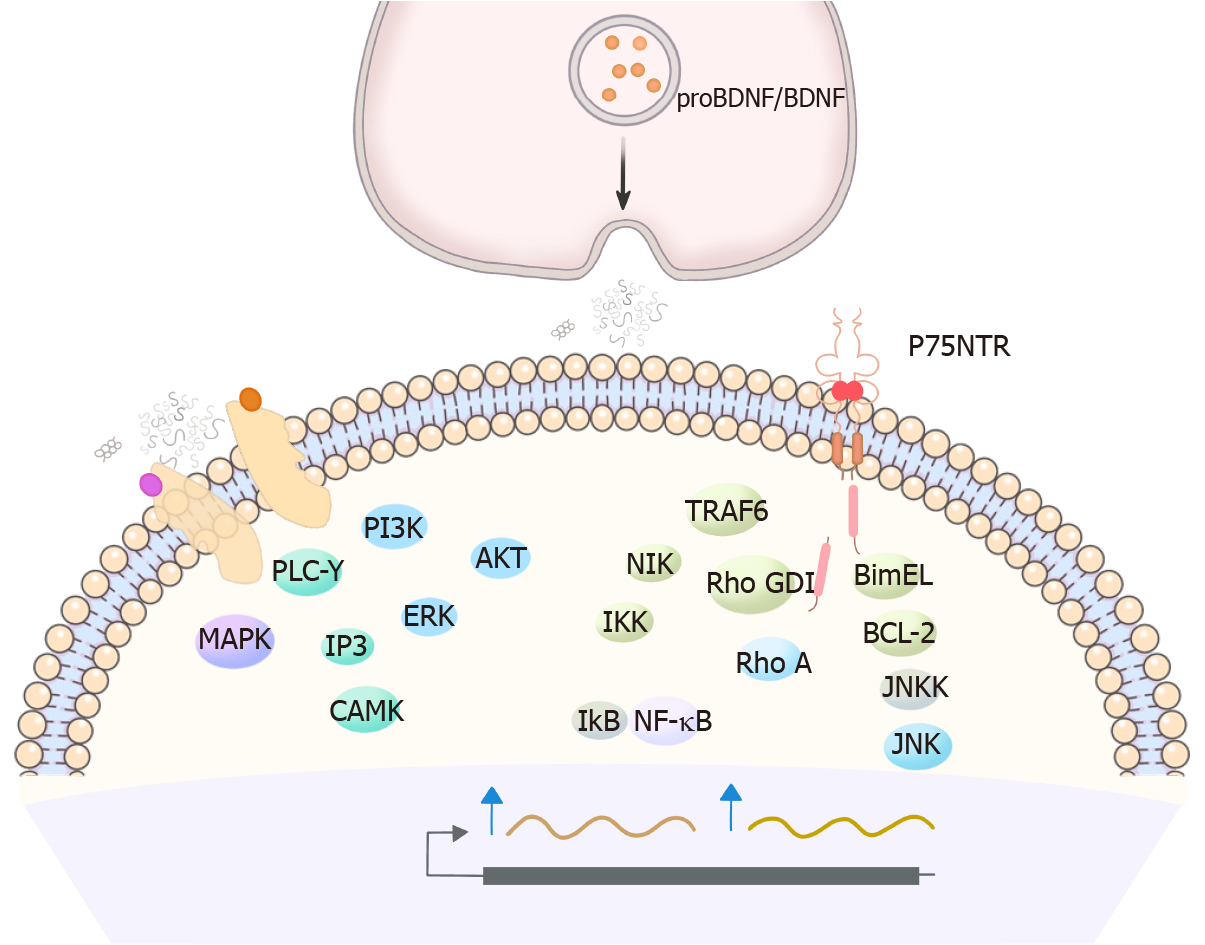
Figure 1 Role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and pro-BDNF in neuroimmune crosstalk in mood disorders.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) or pro-BDNF can be stored in the dense-core vesicles and released upon neuronal activity. The released BDNF and pro-BDNF mainly bind to their high affinity receptors, TrkB and p75NTR, respectively and mediate the downstream signaling pathways. BDNF-TrkB signaling leads to neuronal survival, development and long-term potentiation. In contrast, pro-BDNF-p75NTR signaling mediates neuronal apoptosis, axonal pruning and long-term depression. BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κB.
- Citation: Zhao XP, Li H, Dai RP. Neuroimmune crosstalk through brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its precursor pro-BDNF: New insights into mood disorders. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(3): 379-392
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i3/379.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i3.379