Published online Feb 19, 2022. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.368
Peer-review started: May 2, 2021
First decision: June 17, 2021
Revised: July 5, 2021
Accepted: January 20, 2022
Article in press: January 20, 2022
Published online: February 19, 2022
Processing time: 290 Days and 14.3 Hours
Burnout amongst radiologists is common in many different institutions and is increasing day by day. To battle burnout, we have to address the root causes already recognized in published literature. Therefore, it is crucial to examine and discern important publications.
To provide evidence-based data and trends related to burnout in radiologists so that researchers can work on it further and develop preventive strategies to overcome this problem.
Bibliometric analysis conducted by two independent reviewers separately used Scopus Library for data extraction by using medical subject heading and International Classification of Diseases keywords. Forty-nine articles were selected for analysis after an extensive scrutiny. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences version 20 was used for analysis. Pearson correlation coefficient, Kruskal Wallis test, and Mann-Whitney U test were applied.
The most productive period with regards to the number of publications was between 2017 and 2019. A total of 160 authors contributed to the topic burnout among radiologists, with an average of 3.26 authors per paper. About 41.68% of the authors were female, whilst 35% of them were first authors. The co-citation analysis by author involved 188 cited authors, 13 of whom were cited at least 70 times. Only six out of forty-nine studies were funded by various government institutions and non-governmental organizations.
Current analysis casts a spotlight on important trends being witnessed in regard to the mental health of radiologists, including lack of funding for mental health research, narrowing of female vs male citation gap, as well as authorship and citation trends.
Core Tip: Our analysis casts a spotlight on important trends being witnessed in regard to the mental health of radiologists. These include lack of funding for mental health research, narrowing of female vs male citation gap, as well as authorship and citation trends. By studying these patterns, we can understand key areas lacking in the current bulk of radiological research and subsequently address them to improve the long-term yield, variety, and impact of radiological studies.
- Citation: Qureshi MFH, Mohammad D, Shah SMA, Lakhani M, Shah M, Ayub MH, Sadiq S. Burnout amongst radiologists: A bibliometric study from 1993 to 2020. World J Psychiatry 2022; 12(2): 368-378
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v12/i2/368.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v12.i2.368
Burnout is a syndrome described in International Classification of Diseases 11th edition as a result of chronic workplace stress that has not been successfully managed. It is characterized by feelings of exhaustion, negativism, and reduced professional efficacy[1,2]. Burnout is a major problem that is affecting multiple specialties[3]. The Medscape National Physician Burnout and Depression Report of 2018 conducted a survey that involved 15000 physicians from different specialties. It revealed that 42% of physicians were burned out, 12% were feeling depressed, and 3% were clinically depressed[4]. According to National Physician Burnout and Suicide Report 2020, radiologists rank among the top five specialties most burned out. Diagnostic radiologists have a higher rate of burnout than the average for all physicians[5]. Several studies have shown burnout in both radiology physicians and radiology trainees[6,7].
Burnout amongst radiologists is common in many different institutions and is increasing day by day. Shanafelt et al[8] stated the prevalence of burnout among radiologists in the United States to be 61.4% (n = 261) in 2014; a statistically significant increase from 47.7% (n = 216) in 2011[8]. Burnout in radiologists is also common in Canada because of increased workload and employment constraints[9]. A study conducted in Saudi Arabia concluded that one-fourth of radiology residents have high burnout rates[10]. These high rates of burnout not only affect the physicians’ well-being but also their patients and the healthcare system as a whole. It is associated with medical errors, lapses in patient safety, disruptive workplace behaviors, depression, and substance abuse[11]. People suffering from burnout are also at an increased risk of cardiovascular-related events, metabolic syndrome, systemic inflammation, and impaired immunity[12].
Essentially, bibliometric is the application of quantitative analysis and statistics to publications such as journal articles and their accompanying citation counts[13]. Analysis of the citation counts can reveal the most productive authors, countries, institutions, and journals within a particular research area[14]. The procedure is transparent, and results can be reproduced using the same method and are scalable. It serves the purpose of guiding limited resources to important research areas[14]. This research will provide evidence based data and trends related to burnout in radiologists so that researchers can work on it further and develop preventive strategies to overcome this problem.
Scopus Library was selected as the preferred library for data extraction because of its extensive coverage of articles from all over the globe, it is faster and operator friendly, and citation analysis is faster as compared with Web of Science, Google Scholar, and PubMed[15].
Only original articles were included in research to maintain authenticity of the paper. Reviews, editorials, reports, guidelines, and commentary were excluded. Articles written in English language were only included in the study. Only articles related to consultant radiologist and radiology trainees/postgraduates were selected for analysis. Articles related to radiology nurses, radiology technicians, and other helping staff were excluded in order to get an authentic estimation of burnout among radiology doctors. There was no limitation on the basis of time of publication of article.
The International Classification of Diseases 11th edition, medical subject heading, and review articles from various sources were used to form a final list of keywords. They were searched in abstract, article title, and keywords section of articles. Keywords include “burnout”, “burnout syndrome”, “stress”, “mental stress”, “strain”, “mental strain”, “overload”, “exhaustion”, “mental distress”, “depersonalization”, “companion fatigue”, “emotional wellbeing”, “job satisfaction”, “radiologist”, “radiology resident”, “radiology trainee”, “radiology postgraduate”, “radiology post-graduate”, “consultant radiologist”, “radiology department”, and “radiology fellow”.
Data were extracted in the month of March 2020 by two authors (MFHQ and MHA) separately and a final list of articles was prepared. A difference of 7.4% was identified between both the lists, which was resolved by consulting a third reviewer (DM). The final list of articles was composed by extensive vetting of articles through complete text reading of articles and determining its characters based on inclusion criteria. Forty-nine articles were selected for analysis. Data were extracted to Microsoft Excel from Scopus consisting of name of article, year of publication, number of citations, digital object identifier, affiliation of authors, country of origin of authors, journals, H-factor, and funding of study. Gender of authors was determined by searching for their profiles on official institutions sites. Impact factor was determined by Journal Citation Report 2019.
Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS), version 20 (Armonk, NY, United States) was used for analysis. In order to determine association between impact factor of journals and citations, the Pearson correlation coefficient test was used. In order to determine impact of funding and citations, Kruskal Wallis test was applied. For association of gender with citations, Mann-Whitney U test was applied. P < 0.05 was considered as significant. Co-citation analysis was performed using Vos Viewer version 1.6.14.
All the articles on burnout among radiologists with their total citation and digital object identifier are given Table 1 in descending order in reference to their year of publication. The mean number of citations for the article in Table 1 was 27, while the median was 10 (interquartile range = 18). When citations of all the articles were summed up, the sum was found to be 1328, of which 5.9% (n = 76) were self-citation. The number of citations per year ranged from one to 12 (Table 1).
| No | Article title | DOI | Number of citations |
| 1 | Burnout among Interventional Radiologists | 10.1016/j.jvir.2019.06.002 | 1 |
| 2 | Burnout in Canadian Radiology Residency: A National Assessment of Prevalence and Underlying Contributory Factors | 10.1177/0846537119885672 | 1 |
| 3 | Burnout in Academic Radiologists in the United States | 10.1016/j.acra.2019.12.029 | 1 |
| 4 | Radiologist Burnout According to Surveyed Radiology Practice Leaders | 10.1016/j.jacr.2019.07.008 | 5 |
| 5 | Burnout in Chairs of Academic Radiology Departments in the United States | 10.1016/j.acra.2018.12.006 | 3 |
| 6 | Association of Racial Bias with Burnout among Resident Physicians | 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.7457 | 6 |
| 7 | Stressors contributing to burnout amongst paediatric radiologists: Results from a survey of the Society for Paediatric Radiology | 10.1007/s00247-019-04370-z | 3 |
| 8 | Prevalence of Burnout Among Paediatric Radiologists | 10.1016/j.jacr.2018.08.016 | 10 |
| 9 | Impact of work hours and sleep on well-being and burnout for physicians-in-training: The Resident Activity Tracker Evaluation Study | 10.1111/medu.13757 | 4 |
| 10 | Using Wellness Days to Mitigate Resident Burnout | 10.1016/j.jacr.2018.09.005 | 1 |
| 11 | Burnout Phenomenon and Its Predictors in Radiology Residents | 10.1016/j.acra.2019.09.024 | 0 |
| 12 | Non-radiation occupational hazards and health issues faced by radiologists-A cross-sectional study of Indian radiologists | 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_403_18 | 1 |
| 13 | Prevalence of Burnout Among Canadian Radiologists and Radiology Trainees | 10.1016/j.carj.2018.05.005 | 5 |
| 14 | Burnout: Job Resources and Job Demands Associated with Low Personal Accomplishment in United States Radiology Residents | 10.1016/j.acra.2017.12.002 | 14 |
| 15 | Burnout: Prevalence and associated factors among radiology residents in New England with comparison against United States resident physicians in other specialties | 10.2214/AJR.16.17541 | 30 |
| 16 | Emotional Wellness of Current Musculoskeletal Radiology Fellows | 10.1016/j.acra.2016.12.024 | 8 |
| 17 | Occupational burnout among radiographers, sonographers and radiologists in Australia and New Zealand: Findings from a national survey | 10.1111/1754-9485.12547 | 6 |
| 18 | Reading efficiency can be improved by minor modification of assigned duties; a pilot study on a small team of general radiologists | 10.1007/s11604-017-0629-8 | 4 |
| 19 | Prevalence of burnout among musculoskeletal radiologists | 10.1007/s00256-017-2578-9 | 22 |
| 20 | Burnout, stress and satisfaction among Australian and New Zealand radiation oncology trainees | 10.1111/1754-9485.12541 | 14 |
| 21 | ‘You can’t be a person and a doctor’: The work-life balance of doctors in training – A qualitative study | 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013897 | 26 |
| 22 | Factors associated with burnout among residents in a developing country | 10.1016/j.amsu.2016.01.090 | 17 |
| 23 | Evaluation of the effect of a 1-day interventional workshop on recovery from job stress for radiation therapists and oncology nurses: A randomised trial | 10.1111/1754-9485.12322 | 15 |
| 24 | Quality care, public perception and quick-fix service management: A Delphi study on stressors of hospital doctors in Ireland | 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-009564 | 8 |
| 25 | A study on the relationship between stress and fatigue and the musculoskeletal symptoms experienced by Korean radiation workers | 10.1589/jpts.27.427 | 4 |
| 26 | Stress, satisfaction and burnout amongst Australian and New Zealand radiation oncologists | 10.1111/1754-9485.12217 | 35 |
| 27 | Work-related stress, musculoskeletal disorder complaints, and stress symptoms among radiographers in the northern part of Jordan | 10.1016/j.jmir.2014.04.002 | 0 |
| 28 | Audit of the job satisfaction levels of the UK radiography and physics workforce in UK radiotherapy centres 2012 | 10.1259/bjr.20130742 | 12 |
| 29 | Association of work-related stress with depression and anxiety in radiologists | 10.1007/s11547-013-0355-y | 12 |
| 30 | Work stress and metabolic syndrome in radiologists: First evidence | 10.1007/s11547-013-0329-0 | 23 |
| 31 | Results of a Canadian study examining the prevalence and potential for developing compassion fatigue and burnout in radiation therapists | 10.1017/S1460396914000144 | 5 |
| 32 | Is there a gender gap in Italian radiology? A cross-sectional study | 10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.04.007 | 11 |
| 33 | The emotional wellness of radiology trainees: Prevalence and predictors of burnout | 10.1016/j.acra.2012.12.018 | 29 |
| 34 | The incidence of burnout or compassion fatigue in medical dosimetrists as a function of various stress and psychologic factors | 10.1016/j.meddos.2012.07.006 | 4 |
| 35 | Burnout in therapy radiographers in the UK | 10.1259/bjr/16840236 | 25 |
| 36 | Anxiety and depression in doctors undergoing postgraduate training courses at Armed Forces Postgraduate Medical Institute Rawalpindi | Not Available | 0 |
| 37 | The relevance of psychological support to medical resident and specializing in radiology and imaging diagnosis | 10.1590/S0100-39842011000200006 | 1 |
| 38 | An investigation into work related stressors on diagnostic radiographers in a local district hospital | 10.1016/j.radi.2009.09.005 | 11 |
| 39 | Satisfaction at work among radiologists | 10.1007/s11547-009-0461-z | 14 |
| 40 | Work stress, satisfaction and burnout in New Zealand radiologists: Comparison of public hospital and private practice in New Zealand: Radiology-Original article | 10.1111/j.1754-9485.2009.02063.x | 19 |
| 41 | Job stress and job satisfaction of physicians, radiographers, nurses and physicists working in radiotherapy: A multi-centre analysis by the DEGRO Quality of Life Work Group | 10.1186/1748-717X-4-6 | 71 |
| 42 | Occupational stress and its predictors in radiographers | 10.1016/j.radi.2006.09.008 | 14 |
| 43 | Work stress in radiologists. A pilot study | 10.1007/s11547-008-0259-4 | 35 |
| 44 | Repetitive Stress Symptoms in Radiology: Prevalence and Response to Ergonomic Interventions | 10.1016/j.jacr.2008.01.014 | 31 |
| 45 | The informational roles and psychological health of members of 10 oncology multidisciplinary teams in the UK | 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602816 | 66 |
| 46 | Satisfaction and stress factors in the radiologist’s profession | Not Available | 5 |
| 47 | Job stress and satisfaction among clinical radiologists | 10.1053/crad.1999.0379 | 62 |
| 48 | Mental health of hospital consultants: The effects of stress and satisfaction at work | 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)90077-X | 628 |
| 49 | Job satisfaction in the medical imaging profession: alleviating the shortage of personnel | Not Available | 6 |
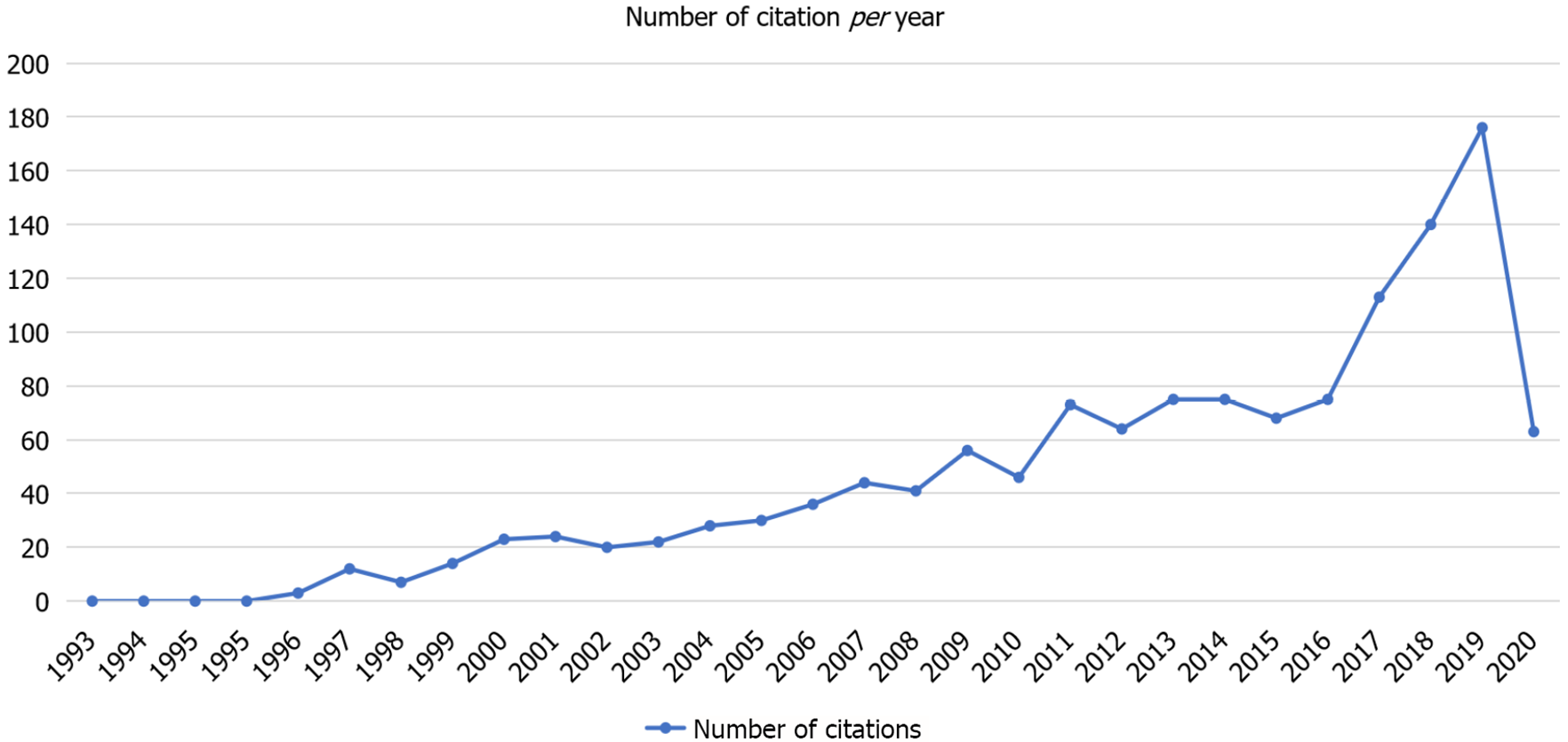
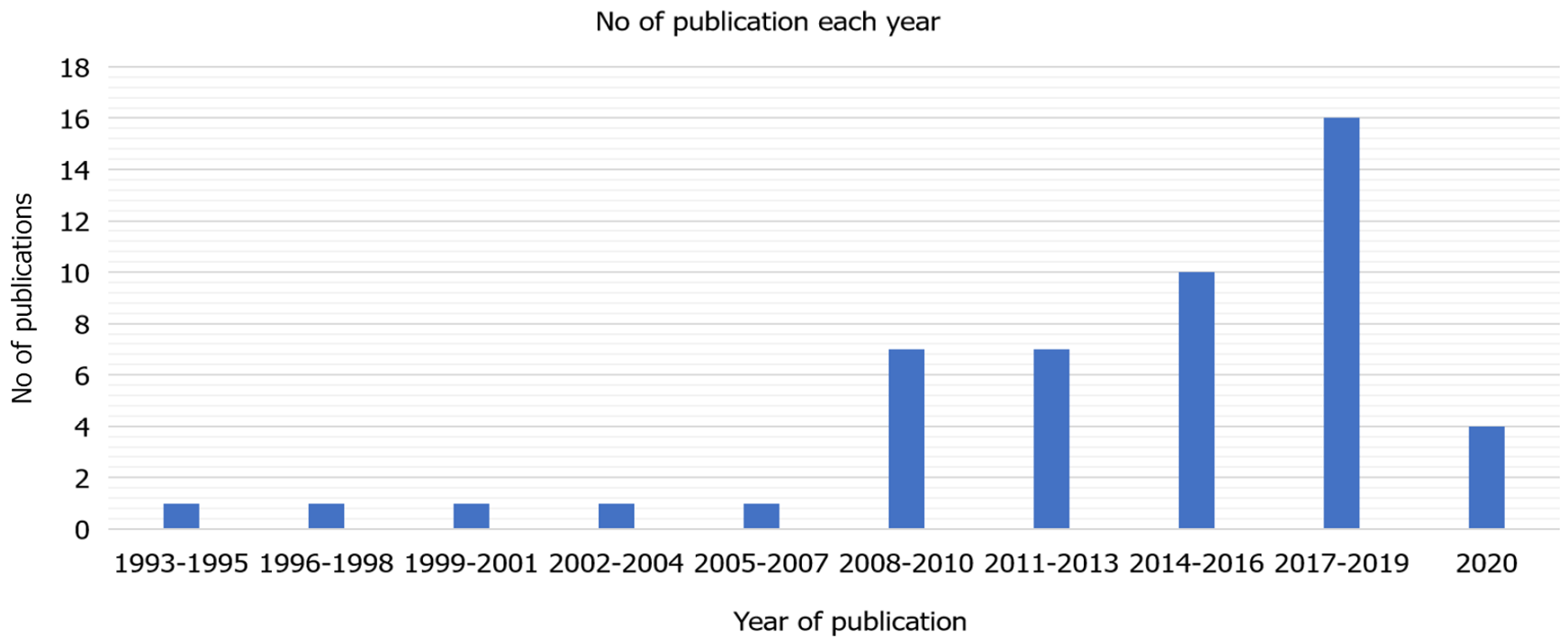
Figure 1 shows the total number of citations per year, with the graph increasing rapidly after 2016. The most productive time period with regards to number of publications was between 2017 and 2019, in which 16 articles were published out of 49, as shown in Figure 2, while the least productive time period was before 1993, during which not a single article was published on burnout among radiologists.
All 49 articles were published in 29 journals belonging to different parts of the world; journals were ranked according to the greatest number of publications, which are shown in Table 2, along with their citations and impact factors. Impact factors of journals ranged from 0.32-15. Statistically significant association was found between number of publications and journal impact factor, with P value of < 0.01, while journal impact factor and number of citations was also significant, with P value of 0.02.
| No. | Journals | No of document | Citation | Impact factor |
| 1 | Academic Radiology | 6 | 55 | 2.0 |
| 2 | Journal of Medical imaging and Radiation Oncology | 5 | 89 | 1.2 |
| 3 | Journal of the American College of Radiology | 4 | 47 | 1.6 |
| 4 | Radiologia Medica | 4 | 84 | 1.8 |
| 5 | BMJ Open | 2 | 34 | 2.6 |
| 6 | British Journal of Radiology | 2 | 37 | 2.1 |
| 7 | Canadian Association of Radiologist Journal | 2 | 06 | 0.9 |
| 8 | Radiography | 2 | 25 | 0.7 |
Harvard Medical School and Università Cattolica Del Sacro Cuore, Rome were the leading institutions, with more than five publications, respectively, followed by University of Washington, Seattle (four publications) and University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Centre (three publications) (Supplementary Table 1).
A total of 160 authors contributed to the topic burnout among radiologists, with an average of 3.26 authors per paper. Author per article ranged from 1 to 12. Nineteen out of 160 worked on more than one article, as shown in Table 3 along with their H-index and gender. In total, 41.68% of the authors were female, while 35% of them were first authors. Statistically significant association was found between female as first author and number of citations, with a P value of 0.03.
| Author | Gender | Number of articles | H-index |
| Magnavita N | Female | 5 | 25 |
| Fileni A | Male | 4 | 13 |
| Mulcahy MJ | Male | 4 | 6 |
| Chew FS | Male | 3 | 26 |
| Ahmed FS | Male | 2 | 10 |
| Ayyala RS | Female | 2 | 04 |
| Bergamaschi A | Male | 2 | 31 |
| Ganeshan D | Male | 2 | 16 |
| Graham J | Female | 2 | 12 |
| Guenette JP | Male | 2 | 7 |
| Leung J | Male | 2 | 8 |
| Probst H | Female | 2 | 8 |
| Ramirez AJ | Female | 2 | 45 |
| Relyea-Chew A | Female | 2 | 13 |
| Richards MA | Male | 2 | 64 |
| Rioseco P | Female | 2 | 4 |
| Ruzal-Shapiro C | Female | 2 | 20 |
| Smith SE | Female | 2 | 14 |
| Taylor GA | Male | 2 | 48 |
Authors belonged to 20 different countries of the world (Supplementary Table 2). United States was the leading country, with the greatest number of researchers, followed by United Kingdom, Italy, Australia, Canada and South Korea as shown in Table 4.
| Country/Territory | Number of author |
| United States | 18 |
| United Kingdom | 8 |
| Italy | 5 |
| Australia | 4 |
| Canada | 4 |
| South Korea | 2 |
Co-citation analysis is important to understand if there is a subject similarity between two documents. Co-citation analysis by author shows the intellectual structure of scientific disciplines. When two authors are cited together in a third document, they are said to be co-cited. If two authors are cited together in more papers, the stronger the relationship, hence greater the co-citation strength and therefore, higher will be their probability to be logistically related in terms of substance and linguistics.
The co-citation analysis by author involved 188 cited authors, 13 of whom were cited at least 70 times. The authors that were most cited included Schulze W, followed by Schlen S and Dormin C. Supplementary Figures 1 and 2 depict the network; the names of authors are shown by a circle. The importance of an author is indicated by the size of the circle, the distance between the labels signifies the relevance, the connection represents collaboration, and the same color indicates belonging to the same cluster.
Only six out of forty-nine studies were funded by various government institutions and non-governmental organizations. Five of them yielded a positive result as compared to hypothesis. There was no significant relationship between funding and number of citations (P = 0.69). Funding organization is shown in Table 5.
| Funding organization | Frequency |
| National Institutes of Health | 2 |
| Mayo Clinic | 1 |
| National Cancer Institute | 1 |
| National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute | 1 |
| University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Centre | 1 |
Articles for most notable work burnout towards the field of radiology are listed in Table 1. The top cited source ‘Mental health of hospital consultants: The effects of stress and satisfaction at work’ was cited in 1996. The second most cited source ‘Job stress and job satisfaction of physicians, radiographers, nurses and physicists working in radiotherapy: A multi-centre analysis by the DEGRO Quality of Life Work Group’ was cited in 2009. The third most cited source was ‘The informational roles and psychological health of members of 10 oncology multidisciplinary teams in the UK’ was cited in 2005. This shows that there does not seem to be a particular trend amongst the most cited sources. They range from 1996-2009. However, what can be noted is that the top cited sources show a more general picture in the trend of burnout. In other words, the top cited sources involve multiple disciplines and healthcare workers such as consultants in different fields and different health care workers in the field of radiology. This allows the articles to be cited by multiple authors in different fields. If radiology-specific studies are seen then the trend shows that the top cited articles, which include ‘Stress, satisfaction and burnout amongst Australian and New Zealand radiation oncologists’ and ‘Burnout: Prevalence and associated factors among radiology residents in New England with comparison against United States resident physicians in other specialties’, are sited in the year 2017.
As far as the trend, in the field of radiology, most of the citations in radiology peaked after 1979[16]. Furthermore, the trend of psychiatric disorders and neuroimaging increased after 1989, with most neuroimaging studies produced in 2007[17]. However, there are no particular bibliometric analyses produced for depression and burnout amongst healthcare workers. The trend in this particular research shows that studies on burnout started in 1993, but the bulk of studies involving burnout in radiologists were seen between 2017-2019.
Table 2 shows that the top number of citations, which were (n = 89) and (n = 84), were seen in the journals the Journal of Medical imaging and Radiation Oncology and Radiologia Medica. These journals have lower impact factors compared to other journals such as BMJ Open. This refutes Bradford's law that states that most authors prefer publishing in core journals because straying from main articles reduces the impact of an article[18]. In other words, journals with more citations do not correlate with journals that have higher impact factors, specifically for the topic of burnout.
The impact of each author and their work is shown in Table 3. An observation to be made is that the number of articles does not correlate with an increased H-index. In fact, the authors with the highest H-index only have two articles published, whereas the author with five articles has a lower H-index than the top authors. The highest H-index was seen by author, Richard MA, with an H-index of 64. He has only published two articles. The author, Magnavita N has five articles published but has an H-index of 25. This is supported by an article that states that H-index is loosely related to the number of articles[19]. Rather, H-index is more closely associated with academic rank in certain fields[20]. Therefore, more articles do not correlate with high H-indexes in the topic of burnout in radiology.
The study shows that the majority of papers were published in the United States with a number of 18 authors. This trend seems to be the basic trend in many current and older studies in multiple fields[21]. A study by Tran et al[22] about depression and artificial intelligence showed the same trend that more papers were produced from the United States[22]. This trend happens because, according to an article on reviewer analysis, it seems that papers from the United States are reviewed and considered more highly than other papers from different countries[23].
Overall, 58.3% of the authors were males and 41.7% were female, and the proportion of female first authors (84.0%) was larger than the proportion of male first authors (82.3%). The differences in total authors could be attributed to the fact that, according to the World Health Organization, the number of male physicians on average worldwide generally outweighs their female counterparts[24]. However, the slightly higher proportion of female first authors indicates women are better at collaborating with their peers for research purposes. This could be due to their more egalitarian nature[25] and hence a more collaborative approach in the workforce. Our analysis found a significant association (P = 0.03) between female first authors and number of citations, indicating that female first authors tended to be cited more than their male counterparts. This is in contrast to a prior study that reported low citations in primary female authors[26], which could indicate a possible narrowing of prior lack of female representation.
All of the articles in our top-cited list focused on the prevalence, causes, and prevention aspect of burnout. This was also demonstrated by the co-citation analysis by author. Co-citation creates clusters of research for the articles that are cited together. These clusters reveal which researchers all over the world are working on burnout among radiologists, and this research will have a substantial effect on the betterment of working environment and preventive strategies. Interestingly, the conclusions of these studies were consistent and help the reader to determine the burden of disease and its importance.
Only 6 out of 49 studies were funded by various government institutions and non-governmental organizations. Five of them yielded a positive result as compared to the hypothesis. Our analysis shows that most research was privately funded/funded by non-government agencies, hence raising the ethical concerns about a possible conflict of interest in regards to reporting of results[27]. Moreover, we found no significant relationship between funding and the number of citations (P = 0.69), which is in contrast to prior research that claimed grant sponsored articles to receive generally more citations and be published in higher quality journals[28].
It could also be concluded that government emphasis and subsequent funding on mental health research regarding radiologists remain small-scale despite adequate data showing significant burnout being noted in one-fourth of all radiologists[29], while another study noting only 19% of radiologists having mechanisms to address burnout[30].
Inherent limitations of bibliometric analysis should be considered, the first being technical problems: Spelling and name changes, progressive changes in the database, language biases, and problems with journal impact factor[31]. These limitations apply to our study as well; nevertheless we tried to alleviate their impact by choosing articles only from the Scopus database to ensure some degree of uniformity in method and use of citations. However, using solely Scopus predisposes us to the exclusion of influential studies present in other databases and the exclusion of any studies before 1996 due to the lack of complete citation information in the database before that year[32,33].
Our analysis casts a spotlight on important trends being witnessed in regards to the mental health of radiologists. These include lack of funding for mental health research, narrowing of female vs male citation gap, as well as authorship and citation trends. By studying these patterns, we can understand key areas lacking in the current bulk of radiological research and subsequently address them to improve the long-term yield, variety, and impact of radiological studies.
Burnout is an important topic in today’s era, with many articles trying to figure out the causes and stressors in the medical field. As a health community, we need to collect all the data for burnout to first understand the prevalence in each area and then the causes for each area. Burnout among radiologists is common in many different institutions and is increasing.
To battle burnout, we have to address the root causes already recognized in published literature. It is crucial to examine and discern important publications. This analysis will allow us to see which areas have collected data on the prevalence and causes of burnout. This analysis will also allow us to determine the missing areas from where we need data.
The current study will provide evidence-based data and trends related to burnout in radiologists so that researchers can work on it further and develop preventive strategies to overcome this problem.
Bibliometric analysis was conducted using Scopus Library for data extraction by using Medical subject heading and International Classification of Diseases keywords. Forty-nine articles were selected for analysis after extensive scrutiny. Statistical Package for the Social Sciences, version 20 was used for analysis. Pearson correlation coefficient, Kruskal Wallis test, and Mann-Whitney U test were applied.
The most productive time period with regards to the number of publications was between 2017 and 2019. A total of 160 authors contributed to the topic burnout among radiologists, with an average of 3.26 authors per paper. About 41.68% of the authors were female, while 35% of them were first authors. The co-citation analysis by the author involved 188 cited authors, 13 of whom were cited at least 70-times. Only six out of 49 studies were funded by government institutions and non-governmental organizations.
The current analysis casts a spotlight on important trends being witnessed in regards to the mental health of radiologists, including lack of funding for mental health research, narrowing of female vs male citation gap, as well as authorship and citation trends.
This analysis provides high yield information that will allow for the identification of additional areas of interest that need to be addressed and what information has high value. This information can be used in the long run to produce higher-quality papers.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Psychiatry
Country/Territory of origin: Pakistan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Gunlu A S-Editor: Fan JR L-Editor: Filipodia P-Editor: Fan JR
| 1. | WHO. Burn-out an "occupational phenomenon": International Classification of Diseases. 2019. [cited 10 April 2021]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/28-05-2019-burn-out-an-occupational-phenomenon-international-classification-of-diseases. |
| 2. | Maslach C, Leiter M. Burnout. Stress and Quality of Working Life: Current Perspectives in Occupational Health 2006; 37: 42-49. |
| 3. | Chetlen AL, Chan TL, Ballard DH, Frigini LA, Hildebrand A, Kim S, Brian JM, Krupinski EA, Ganeshan D. Addressing Burnout in Radiologists. Acad Radiol. 2019;26:526-533. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 130] [Cited by in RCA: 118] [Article Influence: 19.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Peckham C. Medscape national physician burnout & depression report 2018. Medscape, New York. [cited 10 April 2021]. Available from: https://www.medscape com/slideshow/2018-lifestyle-burnout-depression-6009235#17. |
| 5. | Harolds JA, Parikh JR, Bluth EI, Dutton SC, Recht MP. Burnout of Radiologists: Frequency, Risk Factors, and Remedies: A Report of the ACR Commission on Human Resources. J Am Coll Radiol. 2016;13:411-416. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 162] [Cited by in RCA: 201] [Article Influence: 22.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Porrino J, Mulcahy MJ, Mulcahy H, Relyea-Chew A, Chew FS. Emotional Wellness of Current Musculoskeletal Radiology Fellows. Acad Radiol. 2017;24:682-693. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Guenette JP, Smith SE. Burnout: Prevalence and Associated Factors Among Radiology Residents in New England With Comparison Against United States Resident Physicians in Other Specialties. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2017;209:136-141. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 58] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 8.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Shanafelt TD, Hasan O, Dyrbye LN, Sinsky C, Satele D, Sloan J, West CP. Changes in Burnout and Satisfaction With Work-Life Balance in Physicians and the General US Working Population Between 2011 and 2014. Mayo Clin Proc. 2015;90:1600-1613. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1478] [Cited by in RCA: 1588] [Article Influence: 158.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Zha N, Patlas MN, Neuheimer N, Duszak R Jr. Prevalence of Burnout Among Canadian Radiologists and Radiology Trainees. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2018;69:367-372. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 36] [Article Influence: 5.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Dahmash AB, Alorfi FK, Alharbi A, Aldayel A, Kamel AM, Almoaiqel M. Burnout Phenomenon and Its Predictors in Radiology Residents. Academic radiology. 2019;. |
| 11. | Nicola R, McNeeley MF, Bhargava P. Burnout in Radiology. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2015;44:389-390. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 3.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Melamed S, Shirom A, Toker S, Berliner S, Shapira I. Burnout and risk of cardiovascular disease: evidence, possible causal paths, and promising research directions. Psychol Bull. 2006;132:327-353. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 479] [Cited by in RCA: 412] [Article Influence: 21.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Moed HF. New developments in the use of citation analysis in research evaluation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009;57:13-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 252] [Cited by in RCA: 280] [Article Influence: 17.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Mering M. Bibliometrics: Understanding Author-, Article- and Journal-Level Metrics. Serials Review. 2017;43:41-45. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 16] [Cited by in RCA: 10] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008;22:338-342. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1736] [Cited by in RCA: 1651] [Article Influence: 91.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Yoon DY, Yun EJ, Ku YJ, Baek S, Lim KJ, Seo YL, Yie M. Citation classics in radiology journals: the 100 top-cited articles, 1945-2012. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201:471-481. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 71] [Cited by in RCA: 82] [Article Influence: 6.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Gong B, Naveed S, Hafeez DM, Afzal KI, Majeed S, Abele J, Nicolaou S, Khosa F. Neuroimaging in Psychiatric Disorders: A Bibliometric Analysis of the 100 Most Highly Cited Articles. J Neuroimaging. 2019;29:14-33. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Brookes BC. Bradford's law and the bibliography of science. Nature. 1969;224:953-956. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 201] [Cited by in RCA: 211] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Bertoli-Barsotti L, Lando T. The h-index as an almost-exact function of some basic statistics. Scientometrics. 2017;113:1209-1228. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 22] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Ashfaq A, Kalagara R, Wasif N. H-index and academic rank in general surgery and surgical specialties in the United States. J Surg Res. 2018;229:108-113. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 40] [Cited by in RCA: 59] [Article Influence: 8.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Deng Z, Wang H, Chen Z, Wang T. Bibliometric Analysis of Dendritic Epidermal T Cell (DETC) Research From 1983 to 2019. Front Immunol. 2020;11:259. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 30] [Cited by in RCA: 47] [Article Influence: 9.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Tran BX, McIntyre RS, Latkin CA, Phan HT, Vu GT, Nguyen HLT, Gwee KK, Ho CSH, Ho RCM. The Current Research Landscape on the Artificial Intelligence Application in the Management of Depressive Disorders: A Bibliometric Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 7.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Link AM. US and non-US submissions: an analysis of reviewer bias. JAMA. 1998;280:246-247. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 221] [Cited by in RCA: 197] [Article Influence: 7.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Boniol MMM, Xu L, Wuliji T, Diallo K, Campbell J. Gender equity in the health workforce: Analysis of 104 countries, 2019. |
| 25. | Araújo EB, Araújo NAM, Moreira AA, Herrmann HJ, Andrade JS Jr. Gender differences in scientific collaborations: Women are more egalitarian than men. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0176791. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 5.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Huang M, Naser-Tavakolian K, Clifton M, Franceschi AM, Kim D, Zhang JZ, Schweitzer M. Gender Differences in Article Citations by Authors from American Institutions in Major Radiology Journals. Cureus. 2019;11:e5313. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 1.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Lexchin J, Bero LA, Djulbegovic B, Clark O. Pharmaceutical industry sponsorship and research outcome and quality: systematic review. BMJ. 2003;326:1167-1170. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1396] [Cited by in RCA: 1267] [Article Influence: 57.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Wang J, Shapira P. Is there a relationship between research sponsorship and publication impact? PLoS One. 2015;10:e0117727. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 52] [Article Influence: 5.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Bin Dahmash A, Alorfi FK, Alharbi A, Aldayel A, Kamel AM, Almoaiqel M. Burnout Phenomenon and Its Predictors in Radiology Residents. Acad Radiol. 2020;27:1033-1039. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 32] [Article Influence: 6.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Parikh JR, Wolfman D, Bender CE, Arleo E. Radiologist Burnout According to Surveyed Radiology Practice Leaders. J Am Coll Radiol. 2020;17:78-81. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 10.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Holden G, Rosenberg G, Barker K. Tracing thought through time and space: a selective review of bibliometrics in social work. Soc Work Health Care. 2005;41:1-34. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 56] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Jacso P. The h-index, h-core citation rate and the bibliometric profile of the Scopus database. Online Infor Rev. 2011;35:492-501. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 37] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Gajra A, Bapat B, Jeune-Smith Y, Nabhan C, Klink AJ, Liassou D, Mehta S, Feinberg B. Frequency and Causes of Burnout in US Community Oncologists in the Era of Electronic Health Records. JCO Oncol Pract. 2020;16:e357-e365. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |