Published online Dec 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i12.1288
Peer-review started: April 26, 2021
First decision: June 17, 2021
Revised: June 29, 2021
Accepted: November 5, 2021
Article in press: November 5, 2021
Published online: December 19, 2021
Processing time: 233 Days and 0.1 Hours
Displaced aggression occurs when a person encounters a provoking situation, is unable or unwilling to retaliate against the original provocateur, and sub
To develop a Dutch version of the DAQ and examine relationships between the DAQ and novel individual differences.
The Dutch version of the DAQ was created using a back-translation procedure. Undergraduate students (n = 413) participated in the current study. The questionnaires were administered online.
The results confirmed the original three-factor structure and showed good reliability and validity. We also found differential relationships between trait displaced aggression, social anxiety and cognitive distortions.
The results may indicate that distinct patterns exist in the development of the different dimensions of trait displaced aggression. This study adds to the growing cross-cultural literature showing the robustness of trait displaced aggression in several different cultures.
Core Tip: The current study confirmed the original three-factor structure of the Displaced Aggression Questionnaire in a Dutch sample. We also found differential relationships between trait displaced aggression, social anxiety and cognitive distortions. The results may indicate that distinct patterns exist in the development of the different dimensions of trait displaced aggression. This study adds to the growing cross-cultural literature showing the robustness of trait displaced aggression in several different cultures.
- Citation: Smeijers D, Denson TF, Bulten EH, Brazil IA. Validity and reliability of the Dutch version of the displaced aggression questionnaire. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(12): 1288-1300
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i12/1288.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i12.1288
Everyone experiences aggressive urges once in a while, but people are generally not very likely to “take these feelings out” on innocent others. Aggression is usually directed towards the source of provocation[1]. However, some factors can force us to displace our aggressive urges onto underserving others: When the source of frustration or the provocateur are not present and/or when someone is unable, unwilling or afraid to retaliate against the original provocateur[1-4]. Under any of these circumstances, aggression is redirected toward/displaced onto less powerful, easily available or seemingly innocent targets. The tendency to displace aggression is considered to be a stable trait that differs between individuals[5]. People with high inclinations towards displacing aggression seem more likely to aggress against undeserving others, such as coworkers, family members, or fellow drivers[5,6]. Also, individuals with the antisocial, borderline, and narcissistic personality disorder are thought to be more likely to exhibit trait displaced aggression, which highlights the clinical relevance of this phenomenon[7].
Trait displaced aggression consists of three dimensions: angry rumination (affective dimension), revenge planning (cognitive dimension) and behavioral displaced aggression (behavioral dimension)[5]. Angry rumination refers to perseverative thinking about a personally meaningful anger-inducing event[8]. Revenge planning is defined as engaging in thoughts about retaliation for a prior provocation[9]. Displaced aggression as a behavioral dimension is conceptualized as the tendency to act aggressively towards people other than the original source of a provocation[5]. It is thought that individuals high in trait displaced aggression use anger rumination to cope with life’s provocations. Furthermore, individuals who take it out on others may be more likely to ruminate about the initial provocation[7], and are more likely to focus on their angry mood and to plan retaliation. Therefore, it is thought that ruminative activity maintains aggression-related affect, cognition, and arousal, through which negative emotional reactions toward those they subsequently encounter increase[5].
To assess individual differences in trait displaced aggression, Denson et al[5] developed the Displaced Aggression Questionnaire (DAQ). The DAQ consists of 31-items sub-divided in three subscales: angry rumination (e.g., “I often find myself thinking over and over about things that have made me angry”), revenge planning (e.g., “if somebody harms me, I am not at peace until I can retaliate”) and behavioral displaced aggression (e.g., “when angry, I have taken it out on people close to me”). All items are rated on a 7-point scale (1 = extremely uncharacteristic of me, 7 = extremely characteristic of me). The DAQ has high levels of internal consistency (Angry rumination α = 0.92; Revenge planning α = 0.91; Behavioral displaced aggression α = 0.91; total scale α = 0.95), exhibits good test-retest reliability at an interval of 4-wk (ranging from 0.75-0.80) and 11-wk (ranging from 0.78-0.89), and has good discriminant (e.g., impulsivity, extroversion) and convergent validity (e.g., physical and verbal aggression, anger coping styles). Finally, the DAQ predicted displaced aggression in a laboratory paradigm, domestic abuse, and road rage[5].
The DAQ has previously been translated into Romanian and Spanish. Both these adaptations confirmed the three-factor structure of the original questionnaire and showed good psychometric properties[10,11]. Both translations also confirmed positive associations with criterion measures (e.g., trait anger, trait aggression, impulsivity, and big five personality traits), but did not explore any associations with other clinically relevant characteristics. For instance, Denson et al[5] suggested a potential association with fear or anxiety as their results showed an association between trait displaced aggression and behavioral inhibition. The authors reasoned that individuals high in trait displaced aggression are more likely to initially inhibit retaliatory responses when confronted with provocations. Subsequently, they withdraw from the provocation and continue to experience anger and conspire revenge. This association with behavioral inhibition and social withdrawal might also indicate that individuals high in trait displaced aggression experience elevated levels of withdrawal-related affect, such as anxiety and fear. Moreover, self-focused rumination is not only thought to generate and maintain anger, but also social anxiety (for review see[8,12]). It has also been suggested that anger rumination is associated with blame externalization and self-centeredness[8], also referred to as cognitive distortions. Cognitive distortions are defined as inaccurate thoughts, attitudes, or beliefs regarding own or others’ behavior[13]. Previous studies have shown a strong association between such cognitive distortions and aggressive behavior[14-17]. However, the association with rumination and displaced aggression remains understudied. Elucidating the association between trait displaced aggression, social anxiety, and cognitive distortions will further increase our understanding of the mechanism of trait displaced aggression.
The current study sought to create and examine the validity and reliability of a Dutch version of the DAQ. The original three-factor structure was verified, and the convergent and discriminant validity were examined by investigating the association between the Dutch version of the DAQ and state and trait anger, physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger disposition, hostility, impulsivity and extraversion. Additionally, the association with social anxiety and cognitive distortions was examined. It was hypothesized that impulsivity, hostility, anger, and aggression were positively associated with displaced aggression. A negative association with extra
413 undergraduate students (82.6% female; 17.4% male) from Radboud University, Nijmegen participated in the current study. The mean age of the participants was 20.04 years (SD = 3.18) and the majority were undergraduates enrolled in social sciences (n = 310; 75%).
DAQ: The DAQ[5] consists of 31-items which assess trait displaced aggression and consists of three facets: Angry rumination (e.g., “I keep thinking about events that angered me for a long time”), revenge planning (e.g., “When someone makes me angry, I can’t stop thinking about how to get back at this person”) and behavioral displaced aggression (e.g., ”I take my anger out on innocent others”). The Dutch version of the DAQ was created in the current study (see Supplementary material).
Aggression questionnaire: The aggression questionnaire (AQ)[18] is a self-report questionnaire to assess an overall trait of aggression. It consists of 29 items which are divided into four subscales: physical aggression, verbal aggression, anger and hostility. The items are scored on a 5-point Likert scale (1 = extremely unlike me to 5 = extremely like me). The Dutch translation has acceptable/good psychometric properties (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.51 to 0.86)[19]. In the present study, the internal consistency was acceptable to good (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.69 to 0.81).
How I think questionnaire: The How I think questionnaire (HIT)[13] is a 54-item self-report questionnaire to assess self-serving cognitive distortions. The items are divided into four cognitive distortion subscales (self-centered, blaming others, minimizing/ labeling, assuming the worst) and four behavioral referent categories (physical aggression, opposition-defiance, lying, stealing). The cognitive distortion subscales refer to the actual distortions, whereas the behavioral referent categories concern the types of cognitive distortions that are related to antisocial behavior. Items have to be answered on a 6-point Likert scale (1 = totally agree to 6 = totally disagree). The Dutch translation has good reliability (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.90 to 0.94) and validity (all R’s > 0.20)[20]. In the current study the internal consistency varied from acceptable to good (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.75 to 0.87).
State-Trait Anger Scale: The State-Trait Anger Scale (STAS)[21] has been designed to measure state and trait anger. It is a self-report questionnaire of 20 items subdivided into two subscales that capture state (10 items) and trait anger (10 items), respectively. State anger refers to an emotional condition of a patient, which is consciously experienced and fluctuates over time. Trait anger refers to the disposition to become angry, and is thought to be a stable personality quality and to differ greatly across individuals[22]. The Dutch translation has good reliability for trait anger (Cronbach’s α = 0.78)[23]. The internal consistency was excellent in the current study (Cronbach’s α for state anger = 0.91, trait anger = 0.87).
Novaco Anger Scale-Provocation Inventory: The Novaco Anger Scale-Provocation Inventory (NAS-PI)[24,25] consists of two parts: the NAS and the PI. The NAS assesses anger. It consists of 48 items that quantify things that people sometimes think, feel, and do. The items are subdivided in three subscales: Cognition, arousal and behavior, which are rated on a 3-point scale (1 = never true, 2 = sometimes true, 3 = always true). The PI consists of 25 items that refer to anger-eliciting situations that need to be rated on a 4-point scale (1 = not at all angry, 4 = very angry). The Dutch translation has excellent psychometric properties (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.92 to 0.95)[24]. The internal consistency was good in the current study (Cronbach’s α ranging from 0.75 to 0.89).
Barratt Impulsivity Scale: The Barratt Impulsivity Scale (BIS-11)[26] is a 30-item self-report questionnaire that assesses individual differences in impulsivity. The BIS-11 measures 3 types of impulsivity defined as attentional impulsiveness, motor impulsiveness and non-planning impulsiveness. Items are rated on a 4-point scale ranging from 1 (rarely/never) to 4 (almost always/always). The Dutch translation has good psychometric properties (Cronbach's α = 0.81)[27]. Because we employed the BIS-11 as a measure for overall impulsivity, only the total score was used. In the current study the internal consistency was good (Cronbach's α = 0.81).
Ten-Item Personality Inventory: The Ten-Item Personality Inventory (TIPI)[28] is a 10-item self-report questionnaire to assess Big-Five personality dimensions. The TIPI consists of five subscales: extraversion, openness to experiences, emotional stability, conscientiousness and agreeableness. Items are rated on a 7-point scale (1 = strongly disagree, 7 = strongly agree). The Dutch translation has good convergent and discriminant validity (all R’s > 0.20)[29]. In the current study, only the subscale extraversion showed good internal consistency (Cronbach’s α = 0.72) and was, therefore, the only subscale of the TIPI used for the validation. For the other subscales Cronbach’s α ranged from 0.28 to 0.59, indicating that these scales did not measure the target construct reliably.
Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale: The Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale (LSAS)[30,31] is a 24-item self-report questionnaire to assess social anxiety and avoidance. Each item is rated for level of fear (ranging from 0 = none to 3 = severe) and avoidance (ranging from 0 = none to 3 = almost always) it triggered in the past week. Both the original and the Dutch version have stable psychometric properties. In the current study the internal consistency was excellent (Cronbach’s α = anxiety: 0.93, avoidance: 0.89).
The Dutch version of the DAQ was created using a back-translation procedure. First, the original DAQ was translated to Dutch by Smeijers D and Brazil IA. Then, the first Dutch version was translated back to English by a native English speaker. Finally, the back-translation was evaluated by Denson TF, who developed the original DAQ[5]. No content edits were made to the DAQ during the translation process.
The current study had a cross-sectional design. The questionnaires were ad
First, the means, standard deviations, mean inter-item correlations, skewness and kurtosis statistics for the DAQ total and the individual subscale scores were calculated. Next, the internal reliability of the DAQ Dutch version in the current sample was investigated using Cronbach’s α. Subsequently, a confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was used to verify the three-factor model of the DAQ[5] and to test whether the three factors loaded on a general latent variable represented trait displaced aggression. The analysis was conducted with a WLSMV estimator in Mplus version 7[32]. The DAQ items are rated on a 7-point Likert scale, and thus yields ordinal data. Therefore, the WLSMV estimator was favored because it is specifically designed for categorical (e.g., binary or ordinal) observed data (e.g.,[33]). Each item was constrained to load on one factor (i.e., the original factor identified by Denson et al[5], 2006). Model fit was evaluated using absolute and conventional fit indices; the Chi-square statistic, the Tucker-Lewis index (TLI), and the comparative fit index (CFI), the root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA) model fit was considered to be good for CFI and TLI values greater than 0.90 and a non-significant Chi-square test (P > 0.05)[34-36]. For RSMEA, a value less than 0.06 was considered to be good, and a value between 0.05 and 0.10 was considered an acceptable fit[37]. A factor loading ≥ 0.4 was considered strong[38].
The convergent and discriminant validity were examined using correlation analyses. A bootstrapping procedure (5000 iterations) was used to determine 95%CI and to test the significance of the correlations. By bootstrapping, one is able to simulate the population distribution of the correlation and to provide confidence intervals for the correlation coefficients[39]. This approach yields more accurate estimates compared to estimates obtained without resampling, as would be the case in traditional parametric correlation analysis[40].
Finally, the relationships between the DAQ and social anxiety and cognitive distortions were explored in more detail. Specifically, unique patterns of social anxiety and cognitive distortions on anger rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression were examined. Bayesian path analyses were conducted using Mplus version 7[32]. Social anxiety and avoidance, and the cognitive distortions related to self-centeredness, blaming others, minimizing/mislabeling, and assuming the worst served as independent variables, while anger rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression served as dependent variables. Instead of the DAQ items, the DAQ subscales were now used. The subscales consisted of the mean of the corresponding items and were, therefore, on a continuous instead of an ordinal scale. In order to be able to compare the estimates, these variables were standardized by computing z-scores. All variables were treated as continuous, observed, variables. Path analysis was conducted with a Bayesian estimator (using the default Gibbs sampler PX1), 4 Markov Chain Monte Carlo chains and 100.000 iterations (of which the first 50.000 were used as burn-in trials) (see [16]). This analysis was exploratory in nature. Therefore, a Bayesian estimator was favored because it is data driven and, furthermore, avoids statistical assumptions about the distribution of the test statistics (e.g.,[41]).
In this study, a model was considered to show good fit if convergence was achieved with a proportional scale reduction ≤ 1.05[42]. Furthermore, the posterior predictive P value, a measure of similarity between observed and simulated data generated by the model being examined, should ideally be close to 0.5, which means that the model’s predictions are consistent with the observed data[43]. Finally, the Chi-Square test to conduct Posterior Predictive Checking (with a 95% credibility interval; 95%CI) should include the value 0[42]. Significance of the regression weights were determined based on the 95%CIs of the Bayesian posterior distribution. The 95%CIs of the regression weights that did not contain the value 0 were considered significant.
Descriptive statistics are displayed in Table 1. The internal consistency and mean inter-item correlations were found to vary from good to excellent for all subscales and the scale as a whole. Finally, all subscale scores correlated positively with each other (see Table 2).
| α | r | mean ± SD | Skewness | SE | Kurtosis | SE | |
| Anger rumination | 0.924 | 0.552 | 3.36 ± 1.32 | 0.474 | 0.12 | -0.437 | 0.24 |
| Behavioral displaced aggression | 0.925 | 0.558 | 2.43 ± 1.13 | 0.909 | 0.12 | 0.545 | 0.24 |
| Revenge planning | 0.921 | 0.556 | 1.89 ± 0.97 | 2.138 | 0.12 | 5.376 | 0.24 |
| Total | 0.95 | 0.392 | 2.56 ± 0.94 | 0.992 | 0.12 | 1.498 | 0.24 |
| Anger rumination | Behavioral displaced aggression | Revenge planning | |
| Anger rumination | - | r = 0.529c, 95%CI = 0.452-0.599 | r = 570c, 95%CI = 0.499-0.631 |
| Behavioral displaced aggression | r = 0.529c, 95%CI = 0.452-0.599 | - | r = 0.510c, 95%CI = 0.406-0.602 |
| Revenge planning | r = 0.570c, 95%CI = 0.499-0.631 | r = 0.510c, 95%CI = 0.406-0.602 | - |
| STAS state | r = 0.317c, 95%CI = 0.233-0.398 | r = 0.290c, 95%CI = 0.204-0.385 | r = 0.465b, 95%CI = 0.323-0.597 |
| STAS trait | r = 0.475c, 95%CI = 0.389-0.556 | r = 0.515c, 95%CI = 0.415-0.605 | r = 0.546b, 95%CI = 0.420-0.665 |
| LSAS anxiety | r = 0.320c, 95%CI = 0.230-0.408 | r = 0.267c, 95%CI = 0.159-0.371 | r = 0.253b, 95%CI = 0.123-0.381 |
| LSAS avoidance | r = 0.308c, 95%CI = 0.214-0.404 | r = 0.236c, 95%CI = 0.133-0.337 | r = 0.263b, 95%CI = 0.156-0.376 |
| BIS-11 total | r = 0.185c, 95%CI = 0.088-0.274 | r = 0.200c, 95%CI = 0.105-0.288 | r = 0.379c, 95%CI = 0.283-0.469 |
| TIPI extraversion | r = -0.099a, 95%CI = -0.181-0.000 | r = -0.034, 95%CI = -0.127-0.064 | r = -0.111a, 95%CI = -0.198--0.014 |
| AQ physical | r = 0.311c, 95%CI = 0.215-0.399 | r = 0.332c, 95%CI = 0.232-0.425 | r = 0.611b, 95%CI = 0.516-0.698 |
| AQ verbal | r = 0.250c, 95%CI = 0.161-0.346 | r = 0.259c, 95%CI = 0.173-0.351 | r = 0.321b, 95%CI = 0.236-0.409 |
| AQ anger | r = 0.511c, 95%CI = 0.429-0.587 | r = 0.581c, 95%CI = 0.491-0.664 | r = 0.497b, 95%CI = 0.382-0.597 |
| AQ hostility | r = 0.502c, 95%CI = 0.419-0.581 | r = 0.411c, 95%CI = 0.320-0.501 | r = 0.481b, 95%CI = 0.381-0.571 |
| HIT self-centered | r = 0.215c, 95%CI = 0.123-0.307 | r = 0.325c, 95%CI = 0.225-0.416 | r = 0.517b, 95%CI = 0.412-0.612 |
| HIT blaming others | r = 0.275c, 95%CI = 0.193-0.349 | r = 0.370c, 95%CI = 0.283-0.452 | r = 0.557b, 95%CI = 0.459-0.652 |
| HIT minimizing/mislabeling | r = 0.267c, 95%CI = 0.178-0.349 | r = 0.321c, 95%CI = 0.220-0.411 | r = 0.588b, 95%CI = 0.494-0.674 |
| HIT assuming the worst | r = 0.278c, 95%CI = 0.201-0.351 | r = 0.329c, 95%CI = 0.232-0.422 | r = 0.542b, 95%CI = 0.428-0.643 |
| HIT opposition defiance | r = 0.312c, 95%CI = 0.222-0.397 | r = 0.387c, 95%CI = 0.295-0.473 | r = 0.586b, 95%CI = 0.488-0.676 |
| HIT physical aggression | r = 0.286c, 95%CI = 0.200-0.364 | r = 0.360c, 95%CI = 0.272-0.445 | r = 0.617b, 95%CI = 0.518-0.705 |
| HIT lying | r = 0.278c, 95%CI = 0.186-0.368 | r = 0.298c, 95%CI = 0.218-0.388 | r = 0.461c, 95%CI = 0.369-0.554 |
| HIT stealing | r = 0.122a, 95%CI = 0.042-0.204 | r = 0.239c, 95%CI = 0.144-0.336 | r = 0.432c, 95%CI = 0.309-0.543 |
| NAS cognition | r = 0.572c, 95%CI = 0.487-0.649 | r = 0.441c, 95%CI = 0.336-0.530 | r = 0.539c, 95%CI = 0.420-0.635 |
| NAS arousal | r = 0.638c, 95%CI = 0.566-0.704 | r = 0.542c, 95%CI = 0.442-0.622 | r = 0.534c, 95%CI = 0.420-0.636 |
| NAS behavior | r = 0.417c, 95%CI = 0.329-0.501 | r = 0.504c, 95%CI = 0.411-0.588 | r = 0.640c, 95%CI = 0.528-0.734 |
| NAS PI | r = 0.417c, 95%CI = 0.325-0.505 | r = 0.434c, 95%CI = 0.347-0.516 | r = 0.412c, 95%CI = 0.329-0.503 |
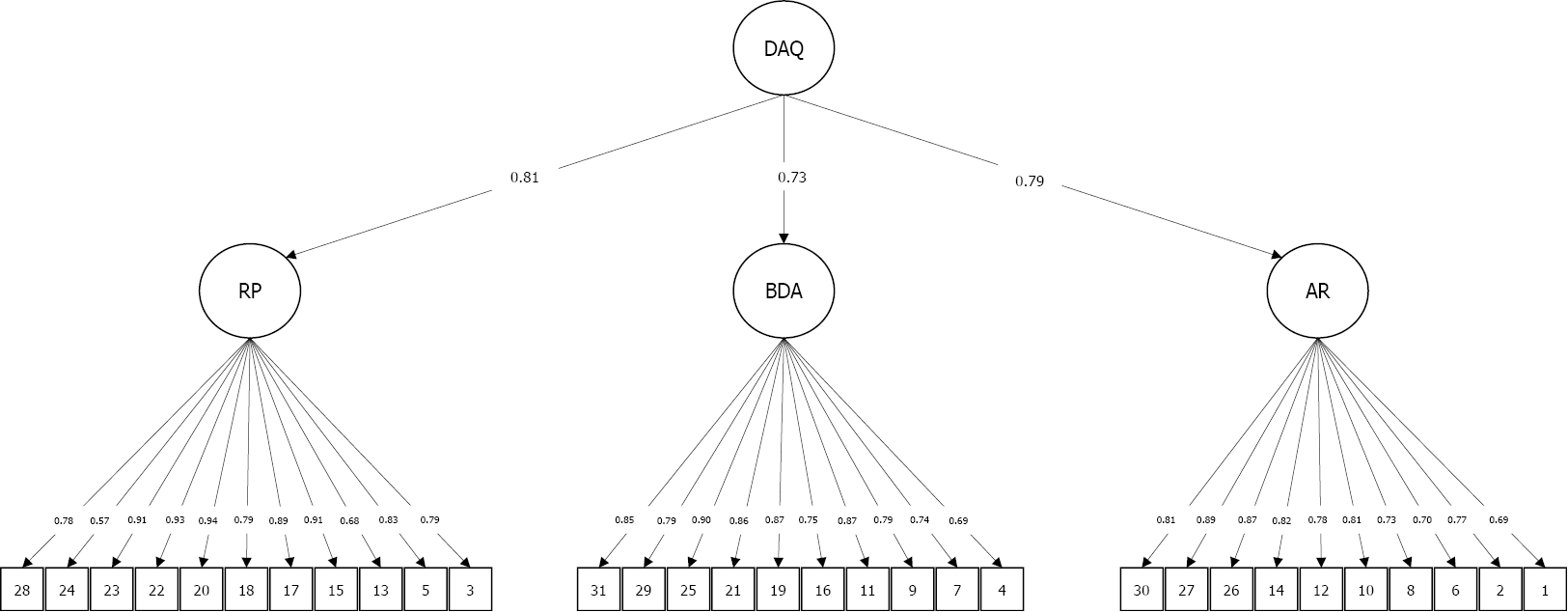
A CFA was conducted to verify the original three-factor solution of the DAQ. The CFA showed an acceptable fit: χ2 (431) = 2034.65, P < 0.001; CFI = 0.92; TLI = 0.91; and RMSEA = 0.09. The items demonstrated good factor loadings (see Supplementary material). Additionally, the three factors loaded significantly (all P’s < 0.001) on the superordinate latent variable for trait displaced aggression, and demonstrated high factor loadings (anger rumination = 0.792; revenge planning = 0.810; behavioral displaced aggression = 0.734), see Figure 1.
Anger rumination, revenge planning and behavioral displaced aggression were significantly positively correlated with the STAS state and trait anger, LSAS anxiety and avoidance, BIS-11, and all subscales of the AQ, HIT and the NAS and negatively with the TIPI extraversion subscale (see Table 2).
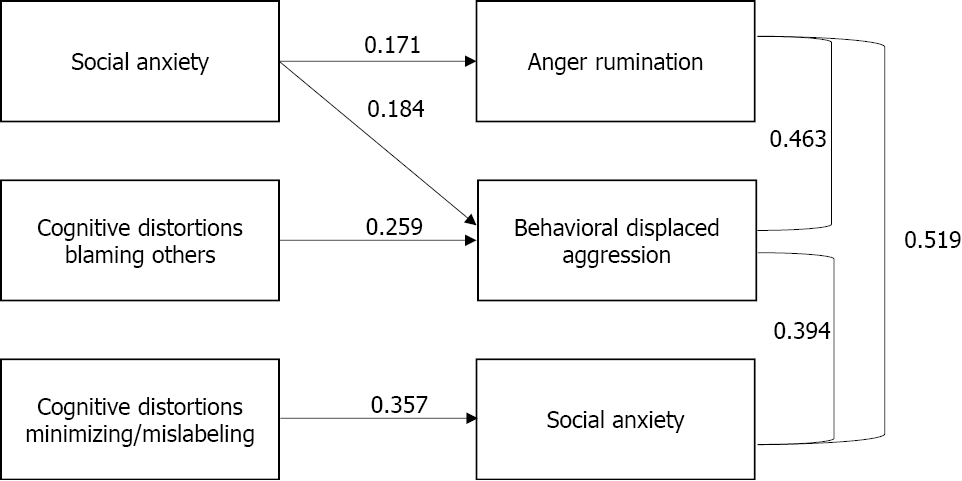
Social anxiety and avoidance, the four types of cognitive distortions, and anger rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression were included in the model. The path model is displayed in Figure 2, only significant results are displayed. The results revealed that social anxiety had a direct positive effect on anger rumination and behavioral displaced aggression (see Table 3). Cognitive distortions related to Blaming Others had a direct positive effect on behavioral displaced aggression, whereas cognitive distortions related to minimizing/mislabeling had a direct effect on revenge planning. The 95% credibility interval for the difference between the observed and the replicated Chi-square values is -20.76 to 21.43. Posterior predictive P value = 0.49, indicating an excellent model fit.
| Dependent variable | Parameter | Estimate (β) | 95%CI (lower 2.5%-upper 2.5%) |
| Anger rumination | Social anxiety | 0.171 | (0.003, 0.3351) |
| Social avoidance | 0.095 | (-0.072, 0.26) | |
| Cognitive distortions SC | -0.069 | (-0.237-0.102) | |
| Cognitive distortions BO | 0.05 | (-0.155, 0.253) | |
| Cognitive distortions MM | 0.091 | (-0.103, 0.283) | |
| Cognitive distortions AW | 0.132 | (-0.075, 0.335) | |
| Revenge planning | Social anxiety | 0.042 | (-0.103, 0.185) |
| Social avoidance | 0.048 | (-0.097, 0.192) | |
| Cognitive distortions SC | 0.037 | (-0.11, 0.183) | |
| Cognitive distortions BO | 0.157 | (-0.02, 0.331) | |
| Cognitive distortions MM | 0.357 | (0.189, 0.5191) | |
| Cognitive distortions AW | 0.042 | (-0.137, 0.219) | |
| Behavioral displaced aggression | Social anxiety | 0.184 | (0.017, 0.3461) |
| Social avoidance | -0.018 | (-0.183, 0.148) | |
| Cognitive distortions SC | 0.114 | (-0.055, 0.281) | |
| Cognitive distortions BO | 0.259 | (0.057, 0.4551) | |
| Cognitive distortions MM | -0.015 | (-0.207, 0.176) | |
| Cognitive distortions AW | -0.03 | (-0.232, 0.175) |
The current study examined the validity and reliability of the Dutch version of the DAQ. The results showed that the descriptive characteristics for the subscales of the Dutch DAQ were consistent with previous findings[5,11]. Furthermore, all subscales exhibited excellent reliability, and the inter-item correlations were good. Also, the original three-factor structure was confirmed in the current sample. However, the Chi-square value did not indicate a good fit, but this finding is in line with previous research[10,11]. It is important to note that this statistic is sensitive to sample size and often rejects the model when large samples are used[34]. In combination with the good values for CFI and TLI, the acceptable value for RMSEA, and the good factor loadings, the model showed acceptable fit. Finally, the three factors loaded significantly on a general latent variable. This finding provides support for the notion that anger rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression reflect dimensions of the general construct of trait displaced aggression. The current findings indicate that the proposed three-factor structure for the DAQ scales extends to the Dutch version and showed the robustness of trait displaced aggression cross-culturally.
Furthermore, all subscales correlated in the expected directions with the criterion measures; positive associations were found with hostility, impulsivity, and several forms of anger and aggression and a negative association was found with extraversion, which is in line with previous studies[5,10,11]. Additionally, a positive association was found with two other clinically relevant characteristics; social anxiety and several forms of cognitive distortions. Specifically, it was found that a high score on all three dimensions of trait displaced aggression were associated with high social anxiety and the tendency to avoid social situations. Denson et al[5] suggested a possible relation between trait displaced aggression and fear and anxiety. The current findings provide support for this notion. Based on the confidence intervals and effect sizes, it seemed that the association was the strongest with anger rumination. This may suggest that anxious individuals are more internally focused, which is also supported by the aforementioned negative association with extraversion.
Additionally, the results of the path analysis showed that social anxiety indeed had the strongest relation with anger rumination but also with behavioral displaced aggression. It can be speculated that anxious individuals may act out their anger less easily and withdraw from provoking situations. Consequently, they seem to be more likely to ruminate about anger-provoking events, which in turn could increase the risk of behavioral displaced aggression[5]. Social anxiety is characterized by the fear that your behavior/performance will be evaluated as humiliating or embarrassing[44]. This fear may inhibit any form of acting out towards the original (less familiar) provocateur. However, among close others, social anxious individuals may not experience this intense fear[45], because they probably have learned that close others will support them regardless of their performance. This may induce a sense of safety. When feeling safe, it might be easier to vent (suppressed) feelings. Individuals high in trait anger and aggression and with high levels of social anxiety may avoid acting out their anger in provoking situations, but displace aggression towards close others. This combination of characteristics might play a role in the mechanism behind, for instance, domestic violence.
Also, the correlations with cognitive distortions may provide some additional evidence for an internal focus in individuals high in trait displaced aggression. Specifically, when comparing the confidence intervals and effect sizes, it seemed that all cognitive distortions showed a stronger association with revenge planning, which was contrary to our hypothesis. The findings of the path analysis showed that cognitive distortions related to minimizing/mislabeling had the strongest relation with revenge planning. Cognitive distortions of this type refer to depicting antisocial behavior as being acceptable, causing no real harm, or referring to others with a dehumanizing label[13]. It may be that such cognitive distortions have a reinforcing effect on revenge planning by easily justifying antisocial behavior in general and possibly retaliation in specific.
Additionally, cognitive distortions related to Blaming Others were most strongly related to behavioral displaced aggression. Distortions of this type refer to the misattribution of blame to outside sources or misattributing misfortune to innocent others[13]. Such distortions might increase the risk of displaced aggression as believing that others are the ones to blame probably easily justifies acting out anger or aggression. Contrary to our hypothesis, the path analysis did not indicate an association between trait displaced aggression and cognitive distortions related to self-centeredness. Cognitive distortions of this type refer to acquiring status to one’s own needs, views, expectations, and desires to such a degree that the legitimate views of others are scarcely considered or even disregarded[13]. These types of distortions might play a role in the emergence of an aggressive conflict. However, it also may be suggested that due to such distortions the focus is too much on the self that it might even limit or distract from any angry feelings causing no rumination or displaced aggression. Also, a different view of another might not even induce anger as someone else’s opinion will be disregarded.
Generally, cognitive distortions are thought to be strongly related to externalizing behaviors (for a meta-analysis see[46]). Cognitive distortions might play a role in neutralizing feelings of blame and preserving a positive self-image. If the individual has learned that this can be achieved through inappropriate use of aggression and/or antisocial behavior, cognitive distortions may strengthen or maintain such malada
The present research allowed us to test aspects of the multiple system models of angry rumination[8]. According to the model, following a provocation, some people are more likely to ruminate than other people. Trait displaced aggression is one such individual difference that increases the likelihood of rumination following provocation. The influence of trait displaced aggression on actual aggressive behavior is subsequently moderated by the cognitive features of the rumination itself (called the “cognitive level” in the model). Because we know little of the cognitive content of the rumination associated with trait displaced aggression, in the present research, we assessed various aggression-related cognitive distortions. This allowed us to investigate the extent to which these cognitive distortions characterize individual differences in trait displaced aggression. Doing so may expand the multiple system models by providing novel information on the content of angry rumination among people high in trait displaced aggression.
Trait displaced aggression is thought to be an important contributor to the development of aggression. It is considered to be a personality characteristic, which means that through the repeated use of aggression individuals high in trait displaced aggression have developed aggressive schemas and knowledge structures[5]. Consequently, they have acquired strong associations between provocations and aggressive affect, arousal, and cognition. These internal processes are highly likely to contain anger rumination and revenge planning and presumably linger for a longer period of time[5]. This in turn increases the likelihood of engaging in aggressive acts. Therefore, trait displaced aggression is of great importance in understanding and explaining aggression, such as in the context of domestic violence and road-rage. More insight in distinct developmental patterns could determine which dimension of trait displaced aggression will be most prominent in a specific individual. In particular, this is important for clinical practice as this would foster the development of targeted interventions that fit the needs of individual patients.
One potential limitation of the present study is that the sample consisted primarily of female participants. The results might therefore not be generalizable to men. This gender disbalance is in line with previous studies[5,10]. Moreover, these studies found no or only small gender differences on DAQ scores. This may suggest that males and females are relatively similar in trait displaced aggression. Future research has to elucidate possible gender differences in further detail in samples consisting of an equal quantity of males/females. Second, the current sample consisted of undergraduate students not typified by clinical levels of aggression. Even though everyone ex
Notwithstanding the limitations, the results encourage the use of the Dutch version of the DAQ to measure individual differences in trait displaced aggression. This study adds to the growing cross-cultural literature showing the robustness of trait displaced aggression in several different cultures. The measurement of individual differences in trait displaced aggression might be a starting point for reducing for instance domestic violence, workplace aggression, and road rage[5]. Once the current findings are confirmed in aggressive samples, an important next step would be to investigate whether currently used general aggression interventions (e.g., Aggression Replacement Training)[49] also reduce anger rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression. If these interventions do not suffice, specific interventions need to be developed to treat the different dimensions of trait displaced aggression. The DAQ is likely to be a valuable instrument to assess trait displaced aggression in clinical settings.
Displaced aggression occurs when a person encounters a provoking situation, is unable or unwilling to retaliate against the original provocateur, and subsequently aggresses against a target that is not the source of the initial provocation. Trait displaced aggression consists of three dimensions: Angry rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression. The displaced aggression questionnaire (DAQ) was developed to measure individual differences in the tendency to displace aggression. Previous studies, however, did not explore any associations with other clinically relevant characteristics.
Elucidating the association between trait displaced aggression, social anxiety, and cognitive distortions will further increase our understanding of the mechanism of trait displaced aggression.
The current study developed a Dutch version of the DAQ and examined relationships between the DAQ and novel individual differences.
A sample of undergraduate students (n = 413) participated in the current study. The DAQ was translated using a back-translation procedure. Subsequently, the Dutch DAQ, aggression questionnaire, How I think questionnaire, State-Trait Anger Scale, Novaco Anger Scale-Provocation Inventory, Barratt Impulsivity Scale, Ten-Item Personality Inventory, and the Liebowitz Social Anxiety Scale were administered in an online survey.
The results confirmed the original three-factor structure and showed good reliability and validity. We also found differential relationships between trait displaced aggression, social anxiety and cognitive distortions.
The results encourage the use of the Dutch version of the DAQ to measure individual differences in trait displaced aggression. The results might indicate that distinct patterns exist in the development of the different dimensions of trait displaced aggression. This study adds to the growing cross-cultural literature showing the robustness of trait displaced aggression in several different cultures.
Once the current findings are confirmed in aggressive samples, an important next step would be to investigate whether currently used general aggression interventions also reduce anger rumination, revenge planning, and behavioral displaced aggression.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Psychology
Country/Territory of origin: Netherlands
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Ünver B S-Editor: Wu YXJ L-Editor: Webster JR P-Editor: Wu YXJ
| 1. | Marcus-Newhall A, Pedersen WC, Carlson M, Miller N. Displaced aggression is alive and well: a meta-analytic review. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2000;78:670-689. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Miller NE. The frustration-aggression hypothesis. Psychological review. 1941;48:337-342. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 246] [Cited by in RCA: 246] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Dollard J, Miller NE, Doob LW, Mowrer OH, Sears RR. Frustration and aggression. 1939, Yale University Press. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 4. | Hovland CI, Sears RR, Minor studies of aggression: VI. Correlation of lynchings with economic indices. J Psychol. 1940;9:301-310. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 206] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Denson TF, Pedersen WC, Miller N. The displaced aggression questionnaire. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2006;90:1032-1051. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 120] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Ruddle A, Pina A, Vasquez E. Domestic violence offending behaviors: A review of the literature examining childhood exposure, implicit theories, trait aggression and anger rumination as predictive factors. Aggression Violent Behavior. 2017;154-165. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 7. | Miller N, Pedersen WC, Earleywine M, Pollock VE. Artificial a theoretical model of triggered displaced aggression. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2003;7:57-97. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 130] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 3.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Denson TF. The multiple systems model of angry rumination. Pers Soc Psychol Rev. 2013;17:103-123. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 96] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Sukhodolsky DG, Golub A, Cromwell EN. Development and validation of the anger rumination scale. Persona Individual Differ. 2001;687-700. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 356] [Cited by in RCA: 335] [Article Influence: 14.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | García-Sancho E, Martín Salguero J, Vasquez EA, Fernández-Berrocal P. Validity and reliability of the Spanish version of the Displaced Aggression Questionnaire. Psicothema. 2016;28:96-101. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Sârbescu, P. Displaced aggression in Romania: Data from a college student sample. Int J Traffic Tran Psych. 2013;1:28-34 Available from: http://www.ijttp.ro/files/vol1no1/ijttp%20vol1%20no%201.pdf#page=28. |
| 12. | Norton AR, Abbott MJ. Self-focused cognition in social anxiety: A review of the theoretical and empirical literature. Behaviour Change. 2016;33:44-64. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 47] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Barriga AQ, Gibbs JC. Measuring cognitive distortion in antisocial youth: Development and preliminary validation of the “How I Think” questionnaire. Aggressive Behavior. 1996;22:333-343. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 14. | Barriga AQ, Hawkins MA, Camelia CR. Specificity of cognitive distortions to antisocial behaviours. Crim Behav Ment Health. 2008;18:104-116. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | de Vries SL, Hoeve M, Stams GJ, Asscher JJ. Adolescent-Parent Attachment and Externalizing Behavior: The Mediating Role of Individual and Social Factors. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2016;44:283-294. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 28] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Smeijers D, Brazil IA, Bulten EBH, Verkes RJ. Retrospective Parental Rejection Is Associated With Aggressive Behavior as Well as Cognitive Distortions in Forensic Psychiatric Outpatients. Psychol Violence. 2018;8:495-504. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 17. | Smeijers D, Bulten E, Buitelaar J, Verkes RJ. Treatment Responsivity of Aggressive Forensic Psychiatric Outpatients. Int J Offender Ther Comp Criminol. 2018;62:3834-3852. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Buss AH, Perry M. The aggression questionnaire. J Pers Soc Psychol. 1992;63:452-459. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3238] [Cited by in RCA: 2948] [Article Influence: 89.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Morren M, Meesters C. Validation of the Dutch version of the Aggression Questionnaire in adolescent male offenders. Aggressive Behavior. 2002;28:87-96. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Nas CN, Brugman D, Koops W. Measuring self-serving cognitive distortions with the “How I Think” Questionnaire. Eur J Psych Asse. 2008;24:181-189. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 62] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Spielberger CD. Preliminary manual for the state-trait anger scale (STAS). Tampa: University of South Florida Human Resources Institute, 1980. |
| 22. | Spielberger CD. Assessment of anger: The state-trait anger scale, in Advances in personality assessment, J.N. Butcher and C. Spielberger, Editors. Lawrence Erlbaum: Hillsdael, NJ 1983: 59-187. |
| 23. | Van der Ploeg H, Defares P, and Spielberger C, Handleiding bij de Zelf-Analyse Vragenlijst, ZAV [Manual for the self-analysis questionnaire, ZAV]. Lisse, NL: Swets & Zeitlinger, 1982. |
| 24. | Hornsveld RH, Muris P, Kraaimaat FW. The Novaco Anger Scale-Provocation Inventory (1994 version) in Dutch forensic psychiatric patients. Psychol Assess. 2011;23:937-944. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 28] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Novaco RW. The Novaco anger scale and provocation inventory. Los Angeles, CA: Western Psychological Services, 2003. |
| 26. | Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES. Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J Clin Psychol. 1995;51:768-774. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 98] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Goudriaan AE, Oosterlaan J, De Beurs E, Van Den Brink W. The role of self-reported impulsivity and reward sensitivity vs neurocognitive measures of disinhibition and decision-making in the prediction of relapse in pathological gamblers. Psychol Med. 2008;38:41-50. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 142] [Cited by in RCA: 131] [Article Influence: 7.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Gosling SD, Rentfrow PJ, Swann Jr WB. A very brief measure of the Big-Five personality domains. J Research Personality. 2003;504-528. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 3957] [Cited by in RCA: 2830] [Article Influence: 128.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Hofmans J, Kuppens P, Allik J. Is short in length short in content? Personality Individual Differences. 2008;45:750-755. |
| 30. | Liebowitz MR. Social phobia. Mod Probl Pharm. 1987;22:141-173. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1507] [Cited by in RCA: 1633] [Article Influence: 163.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Van Balkom A, Debeurs E, Hovens J, van Vliet I. Meetinstrumenten bij angststoornissen. Tijdschrift voor psychiatrie. 2004;46:687-692 Available from: https://www.tijdschriftvoorpsychiatrie.nl/assets/articles/articles_1291pdf.pdf. |
| 32. | Muthén LK, Muthén BO. Mplus User’s Guide, 7th edition. 1998, Los Angeles: CA: Muthén & Muthén. |
| 33. | Li CH. Confirmatory factor analysis with ordinal data: Comparing robust maximum likelihood and diagonally weighted least squares. Behav Res Methods. 2016;48:936-949. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 915] [Cited by in RCA: 1149] [Article Influence: 143.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Hooper D, Coughlan J, Mullen M. Structural equation modelling: Guidelines for determining model fit. Electronic J Business Research Methods. 2008;6:53-60. |
| 35. | Hu LT, Bentler PM. Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria vs new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal. 2009;6:1-55. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 36. | Hoyle RH. Structural equation modeling: Concepts, issues, and applications. Thousand Oaks: California: Sage. 1995. |
| 37. | Lai K, Green SB. The Problem with Having Two Watches: Assessment of Fit When RMSEA and CFI Disagree. Multivariate Behav Res. 2016;51:220-239. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 201] [Cited by in RCA: 204] [Article Influence: 22.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Field A. Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics. London: Sage publications Ltd. 2013. |
| 39. | Sideridis GD, Simos P. What is the actual correlation between expressive and receptive measures of vocabulary? International J. 2010;5. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 1.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Hesterberg T. Bootstrap methods and permutation tests: Companion chapter 18., In The practice of business statistics. W.H. Freemand and Co: New York. 2003. |
| 41. | van de Schoot R, Kaplan D, Denissen J, Asendorpf JB, Neyer FJ, van Aken MAG. A gentle introduction to bayesian analysis: applications to developmental research. Child Dev. 2014;85:842-860. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 357] [Cited by in RCA: 327] [Article Influence: 27.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Muthén B. Bayesian analysis in Mplus: A brief introduction. 2010; 203. [cited 25 April 2021]. Available from: http:// www. statmodel. com/download/IntroBayesVersion. |
| 43. | Gelman A. Two simple examples for understanding posterior p-values whose distributions are far from unform. Electronic Journal of Statistics. 2013;7:2595-2602. |
| 44. | Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association. 2013. |
| 45. | Darcy K, Davila J, Beck JG. Is social anxiety associated with both interpersonal avoidance and interpersonal dependence? Cognitive Therapy Research. 2005;29:171-186. [RCA] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 53] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Helmond P, Overbeek G, Brugman D, Gibbs JC. A Meta-Analysis on Cognitive Distortions and Externalizing Problem Behavior: Associations, Moderators, and Treatment Effectiveness. Criminal Justice Behavior. 2015;42:245-262. |
| 47. | Barriga AQ, Landau JR, Stinson BL, Liau AK, Gibbs JC. Cognitive distortion and problem behaviors in adolescents. Criminal Justice Behavior. 2000;27:36-56. [DOI] [Full Text] |
| 48. | Smeijers D, Bulten EBH, Brazil IA. The Computations of hostile biases (CHB) model: Grounding hostility biases in a unified cognitive framework. Clin Psychol Rev. 2019;73:101775. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Glick B, Goldstein AP. Aggression replacement training. J Counseling Development. 1987;65:356-362. |