Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Psychiatr. Jun 22, 2016; 6(2): 215-220
Published online Jun 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i2.215
Published online Jun 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i2.215
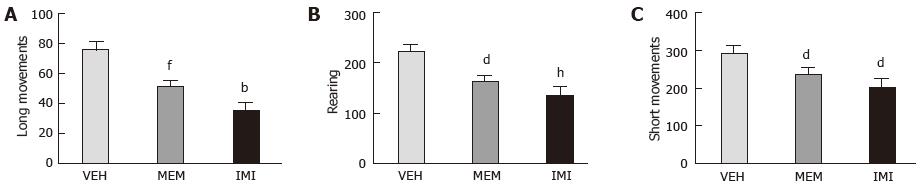
Figure 1 Spontaneous motor activity after 24 h discontinuation of chronic treatments (60 min habituation to the motility cage).
Each value represents the mean ± SEM from 20 rats: Vehicle (VEH), memantine (MEM), imipramine (IMI). Number of long movements (A), rearing (B) and short movements (C) measured as indicated in the materials and methods: Motor activity. A: fP < 0.001, memantine vs vehicle [F (1.51) = 12.21; P = 0.0009]; bP < 10-6, imipramine vs vehicle [F (1.51) = 31.71; P = 0.000001]; B: dP < 0.01, memantine vs vehicle [F (1.51) = 10.58; P = 0.0020]; hP < 10-4, imipramine vs vehicle [F (1.51) = 19.90; P = 0.000045]; C: dP < 0.01, memantine vs vehicle [F (1.51) = 11.57; P = 0.0013]; dP < 0.01, imipramine vs vehicle [F (1.51) = 10.13; P = 0.0024]; ANOVA followed by Newman-Keuls-test.
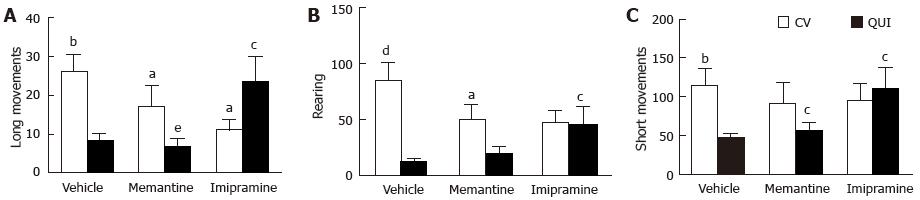
Figure 2 Motor response to quinpirole after 24 h chronic imipramine and memantine withdrawal.
Number of long movements (A), rearing (B) and short movements (C) measured as indicated in the materials and methods: Motor activity. Each value represents the mean ± SEM from 10 rats (ANOVA followed by F test for contrast). Control vehicle (CV), quinpirole (QUI). A: bP < 0.01, Vehicle-CV vs vehicle-QUI [F (1.48) = 11.20; P = 0.0015]; aP≤ 0.05, memantine-CV vs memantine-QUI [F (1.48) = 3.74; P = 0.05]; aP≤ 0.05, imipramine-CV vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 3.74; P = 0.05]. cP≤ 0.05, vehicle-QUI vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 6.39; P = 0.014]; eP < 0.01, memantine-QUI vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 7.74; P = 0.007]; vehicle-QUI vs memantine-QUI [F (1.48) = 0.07; n.s]; B: dP < 10-4, vehicle-CV vs vehicle-QUI [F (1.48) = 22.73; P = 0.000018]; aP≤ 0.05, memantine-CV vs memantine-QUI [F (1.48) = 4.10; P = 0.048]; imipramine-CV vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 0.006; n.s.]. cP≤ 0.05, vehicle-QUI vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 3.80; P = 0.05]; vehicle-QUI vs memantine -QUI [F (1.48) = 22.48; n.s]; C: bP≤ 0.01, vehicle-CV vs vehicle-QUI [F (1.48) = 6.83; P = 0.01]; imipramine-CV vs imipramine -QUI [F (1.48) = 0.24; n.s.]. cP≤ 0.05, vehicle-QUI vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 4.83; P = 0.032]; cP≤ 0.05 memantine-QUI vs imipramine-QUI [F (1.48) = 3.75; P = 0.05].
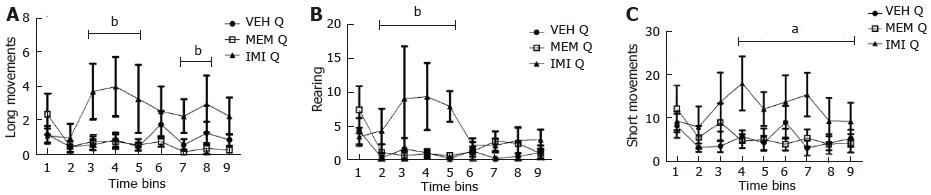
Figure 3 Time course of quinpirole effect on motor activity after 24 h chronic imipramine and memantine withdrawal.
Long movements (A), rearing (B) and short movements (C) measured as indicated in the materials and methods: Motor activity. Each value represents the mean ± SEM from 10 rats: vehicle + quinpirole (VEH Q), memantine + quinpirole (MEM Q), imipramine + quinpirole (IMI Q). A, B: bP < 0.01 imipramine-quinpirole vs vehicle-quinpirole and memantine-quinpirole; C: aP < 0.05 imipramine-quinpirole vs memantine-quinpirole (ANOVA followed by F test for contrast; horizontal lines represent contrast involving consecutive times).
- Citation: Demontis F, Serra G. Failure of memantine to “reverse” quinpirole-induced hypomotility. World J Psychiatr 2016; 6(2): 215-220
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v6/i2/215.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v6.i2.215