Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Psychiatr. Mar 22, 2016; 6(1): 31-42
Published online Mar 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.31
Published online Mar 22, 2016. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.31
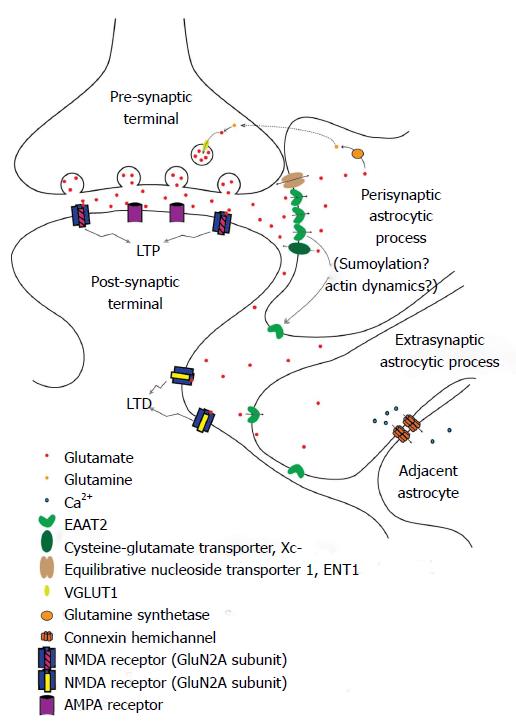
Figure 1 Fine regulation of glutamate levels and excitatory amino acid transporter 2 localization in neuron-glial interaction.
The perisynaptic astrocytic process contains a higher concentration of EAAT2 immediately adjacent to the synapse. The EAP also contains EAAT2, but in lower concentrations. Glutamate spillover results in activation of GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors (increasing LTD response in the post-synaptic neuron), increased EAAT2 surface expression on and migration of EAPs, and activation of adjacent astrocytes via calcium waves propagated through connexin channels. LTP: Long term potentiation; LTD: Long term depression; EAAT2: Excitatory amino acid transporter 2; Xc-: Cysteine-glutamate transporter; ENT1: Equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1; VGLUT1: Vesicular glutamate transporter 1; NMDA: N-Nitrosodimethylamine; AMPA: α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid; EAP: Extrasynaptic astrocytic process.
- Citation: Ayers-Ringler JR, Jia YF, Qiu YY, Choi DS. Role of astrocytic glutamate transporter in alcohol use disorder. World J Psychiatr 2016; 6(1): 31-42
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v6/i1/31.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.31