Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
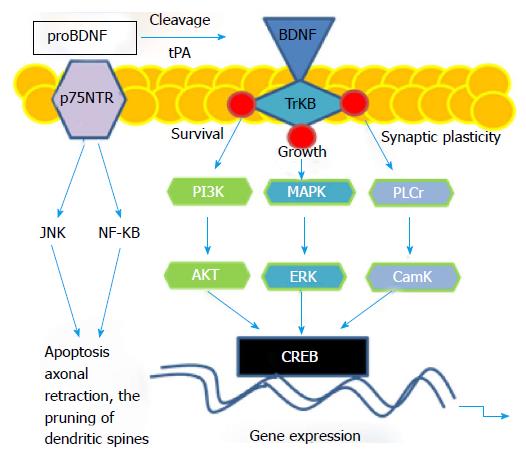
Figure 1 Brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling pathway.
The binding of proBDNF to the p75NTR up-regulates c-Jun N-terminal kinase and nuclear factor κB, triggering apoptosis, axonal retraction, or the pruning of dendritic spines. The proBDNF is cleaved to generate mature BDNF via tPA/plasminogen. When BDNF binding to its receptors, the receptor tyrosine kinase TrkB becomes phosphorylated, leading to phosphorylation at various sites or activation of downstream pathways. Such activation shows at PI3K sites, which activates AKT, regulating cell survival. The activation of MAPK/ERK leads to cell growth and differentiation. The activation of PLC-γ pathway regulates IP3 receptor to release intracellular calcium stores, in turn to enhance CamK activity, regulating synaptic plasticity. All three pathways converge on transcription factor CREB, binging to certain DNA sequences called CRE, playing a key role in BDNF-induced gene expression. BDNF: Brain derived neurotrophic factor; PTSD: Post-traumatic stress disorder; tPA: Tissue-type plasminogen activator; CamK: Calmodulin kinase; CAMP: Cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CREB: CAMP response elements; CRE: CAMP response elements; AKT: Protein kinase B; IP3: Inositol trisphosphate.
- Citation: Zhang L, Li XX, Hu XZ. Post-traumatic stress disorder risk and brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met. World J Psychiatr 2016; 6(1): 1-6
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v6/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v6.i1.1