Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Apr 19, 2025; 15(4): 104450
Published online Apr 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.104450
Published online Apr 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.104450
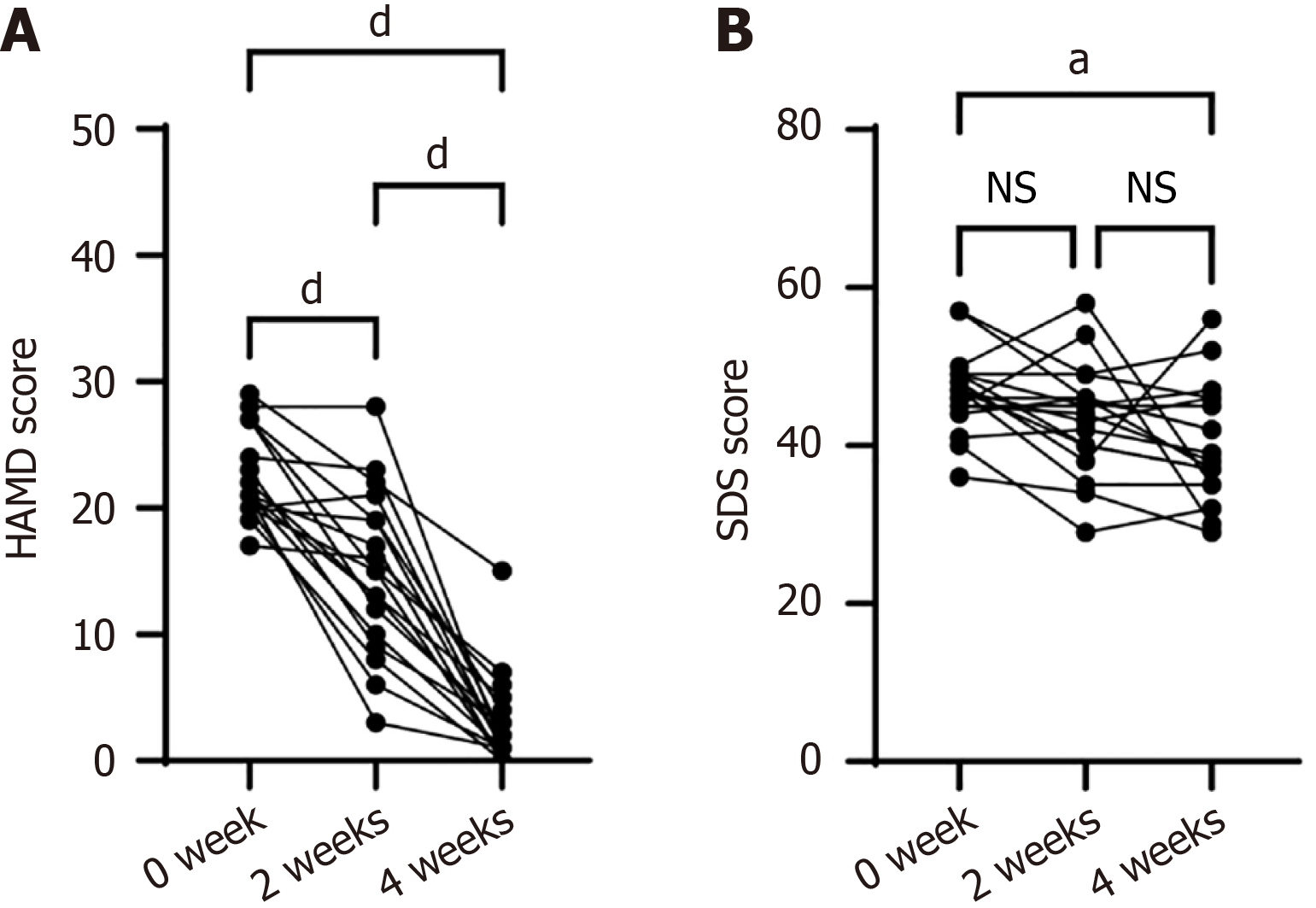
Figure 1 Qi-based mindfulness therapy treatment demonstrated significant improvements in depression severity, as measured by the 17 Hamilton Depression Rating Scale and the Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale, compared to pretest baseline scores.
A: The 17 Hamilton Depression Rating Scale score was significant decreased after two- or four-weeks Qi-based mindfulness therapy than at baseline; B. The Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale score was decreased after four weeks Qi-based mindfulness therapy. aP < 0.05, dP < 0.001. HAMD: 17 Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; SDS: Zung Self-Rating Depression Scale; NS: No significance.
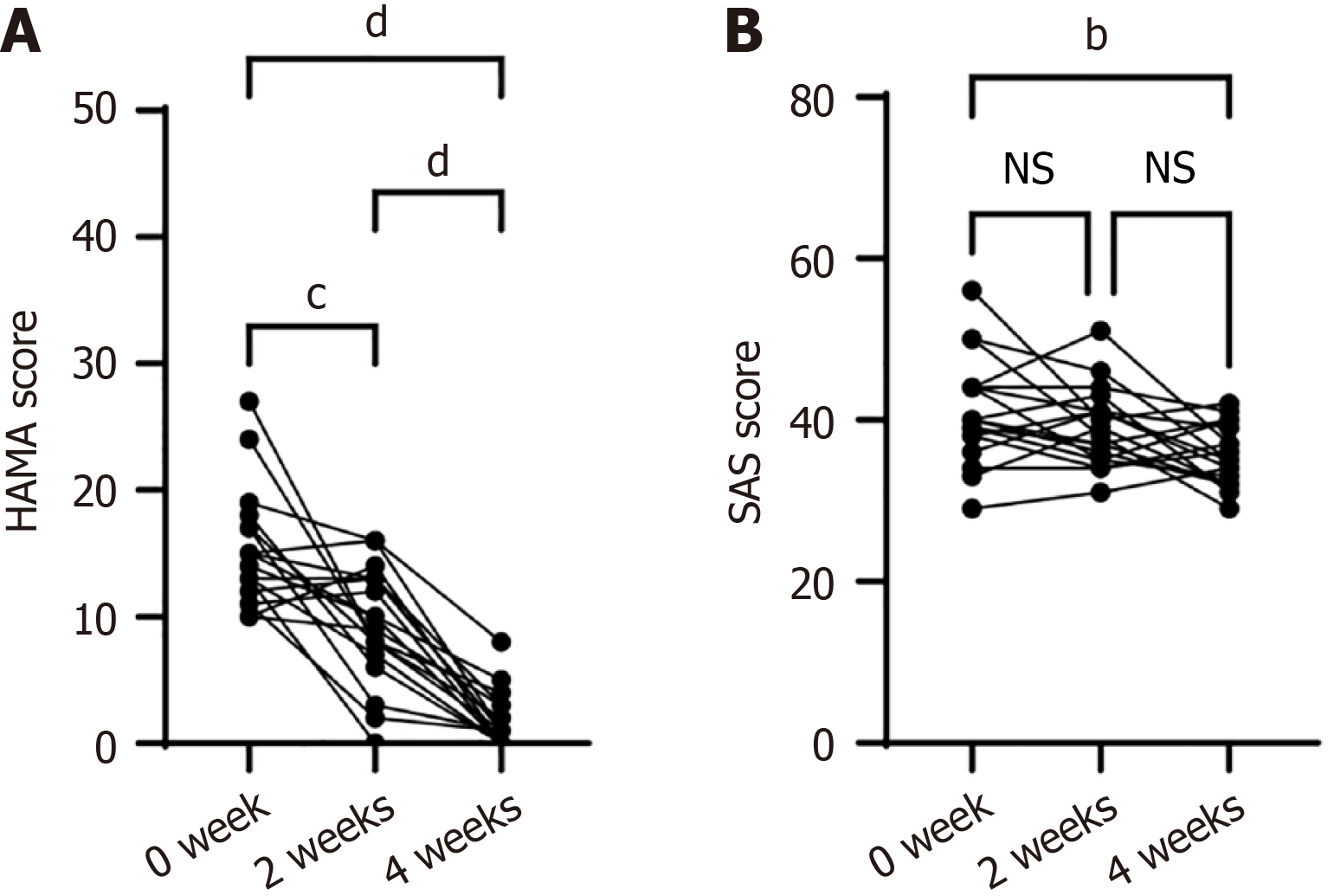
Figure 2 Anxiety questionnaires indicated a significant reduction in emotional regulation related to anxiety between the pretest and posttest phases.
A: Hamilton Anxiety Scale score was decreased after two- or four-weeks Qi-based mindfulness therapy; B: The Self-Rating Anxiety Scale score was decreased after four weeks Qi-based mindfulness therapy. bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001, dP < 0.001. HAMA: Hamilton Anxiety Scale; SAS: Self-Rating Anxiety Scale; NS: No significance.
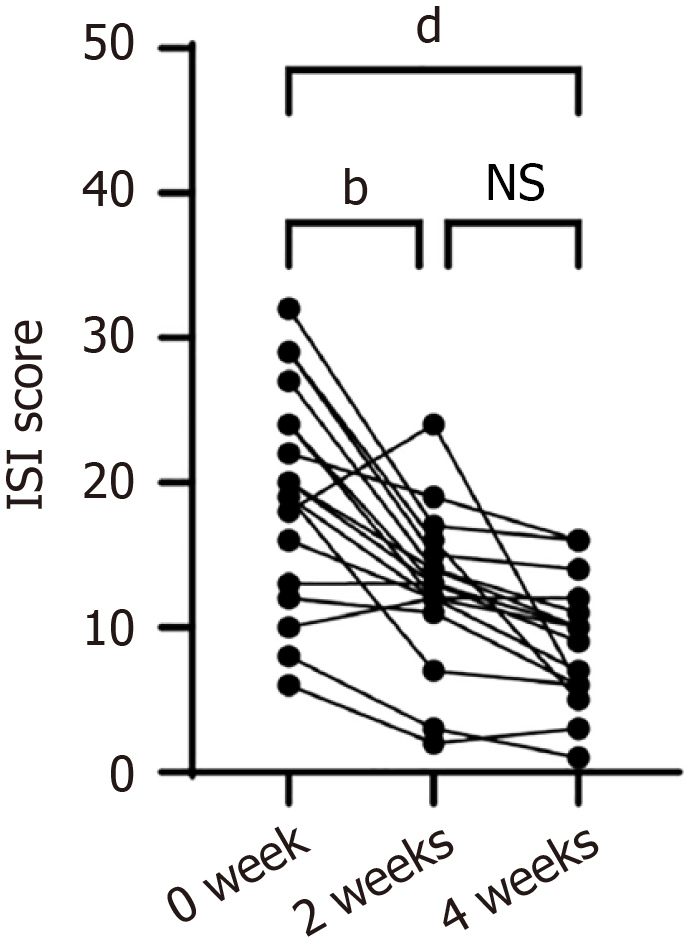
Figure 3 The Insomnia Severity Index score was decreased after four weeks Qi-based mindfulness therapy.
bP < 0.01, dP < 0.0001. ISI: Insomnia Severity Index; NS: No significance.
- Citation: Li QW, Yang Y, Gao XJ, Ma A, Sun W. Effect of Qi-based mindfulness therapy for mild-to-moderate depression. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(4): 104450
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i4/104450.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i4.104450