Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Psychiatry. Mar 19, 2025; 15(3): 99152
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.99152
Published online Mar 19, 2025. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.99152
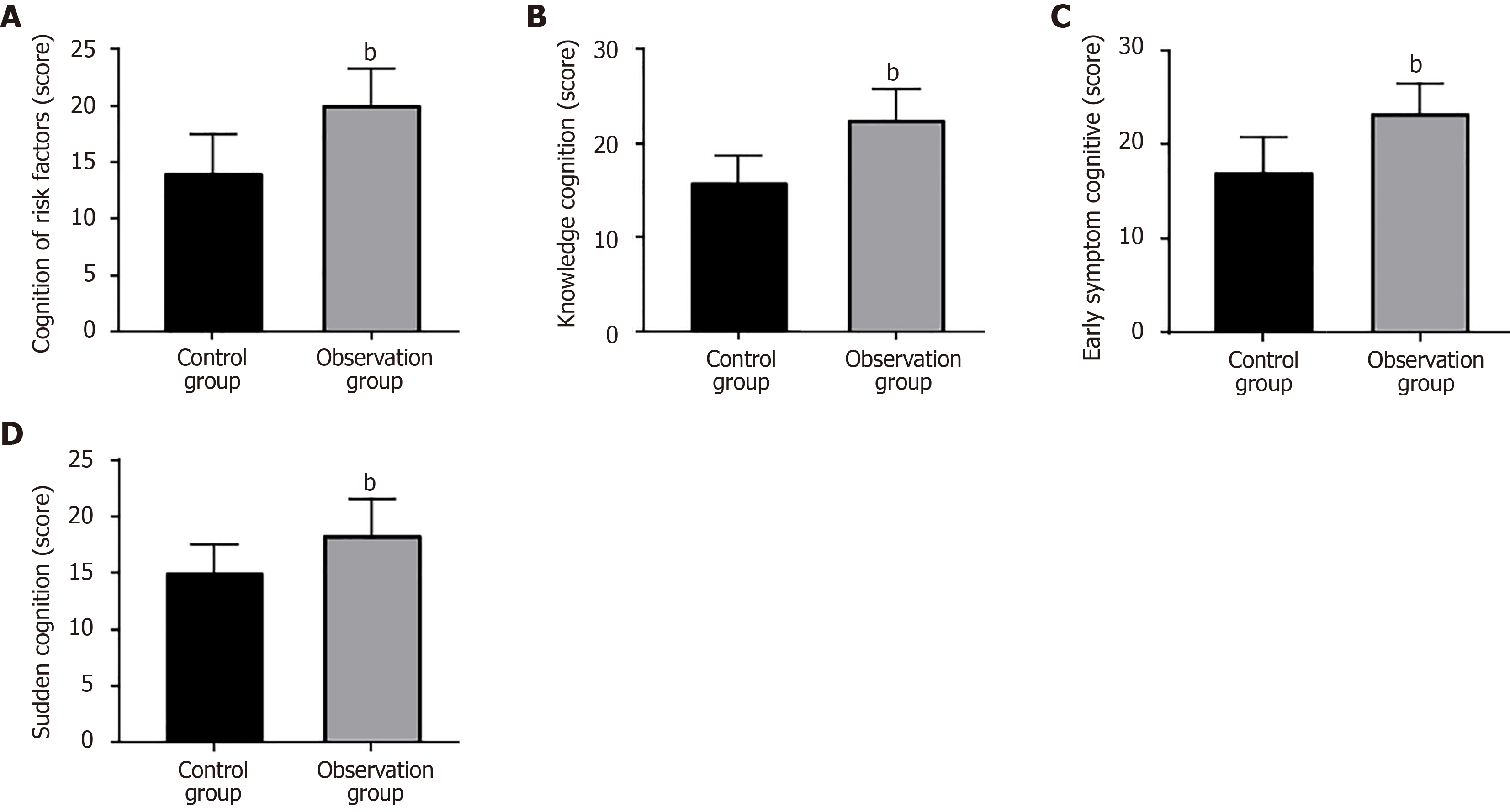
Figure 1 Stroke awareness scores of two high-risk groups for stroke.
A: The observation group had a statistically higher score of cognition of risk factors than the control group; B: The observation group had a statistically higher score of knowledge cognition than the control group; C: The observation group scored markedly higher in the early symptom cognitive dimension than the control group; D: The emergency cognitive score was significantly higher in the observation group than in the control group. bP < 0.01.
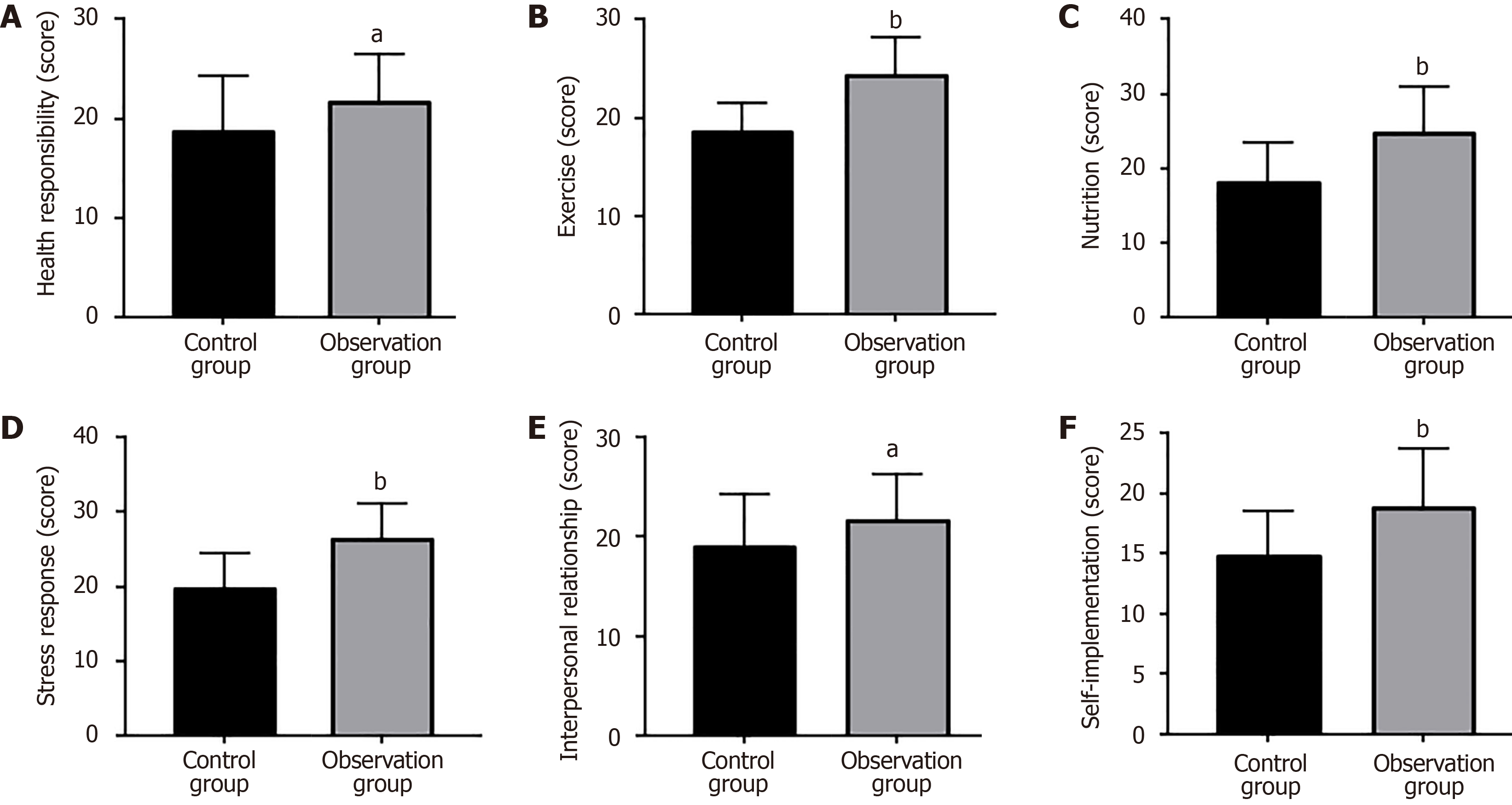
Figure 2 Health behavior levels of two high-risk groups for stroke.
A: The observation group showed a notably higher health responsibility score than the control group; B: The exercise score was markedly higher in the observation group than in the other; C: The nutrition score was statistically higher in the observation group vs the control group; D: The observation group had an obviously higher stress management score than the control group; E: The interpersonal relationships score was significantly higher in the observation group vs the control group; F: The self-actualization score of the observation group elevated markedly compared with the control group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
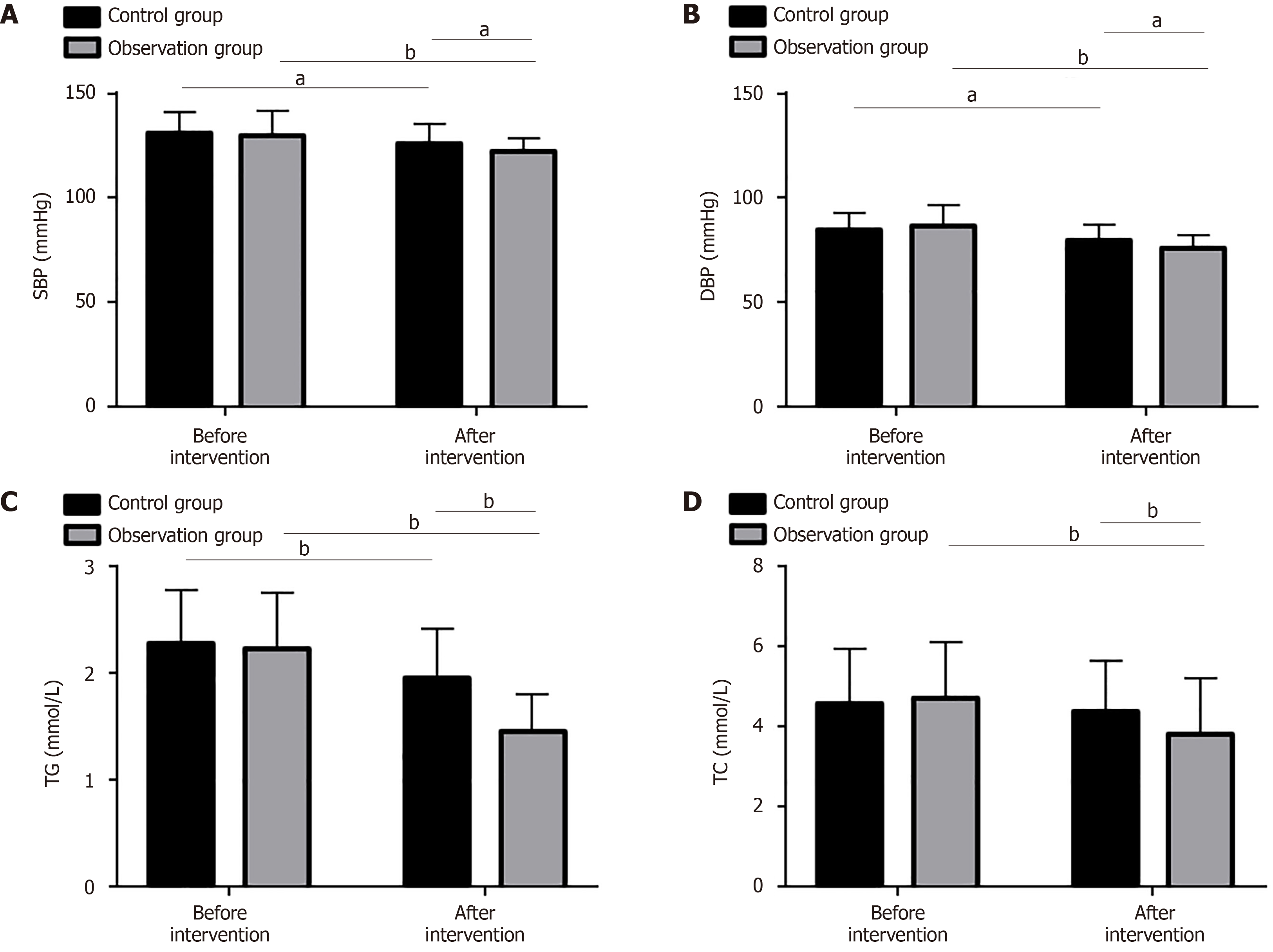
Figure 3 Blood pressure and serum biochemical indices of two high-risk groups for stroke.
A: The observation group showed notably reduced systolic blood pressure after intervention, lower than the pre-interventional level and that in the control group; B: After intervention, the diastolic blood pressure level in the observation group was significantly lower compared to the pre-interventional level and the control group; C: After intervention, the triglyceride level in the observation group was significantly lower compared to before intervention and the control group; D: The observation group showed notably reduced total cholesterol after intervention, lower than the pre-interventional level and that in the control group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. SBP: Systolic blood pressure; DBP: Diastolic blood pressure; TG: Triglyceride; TC: Total cholesterol.
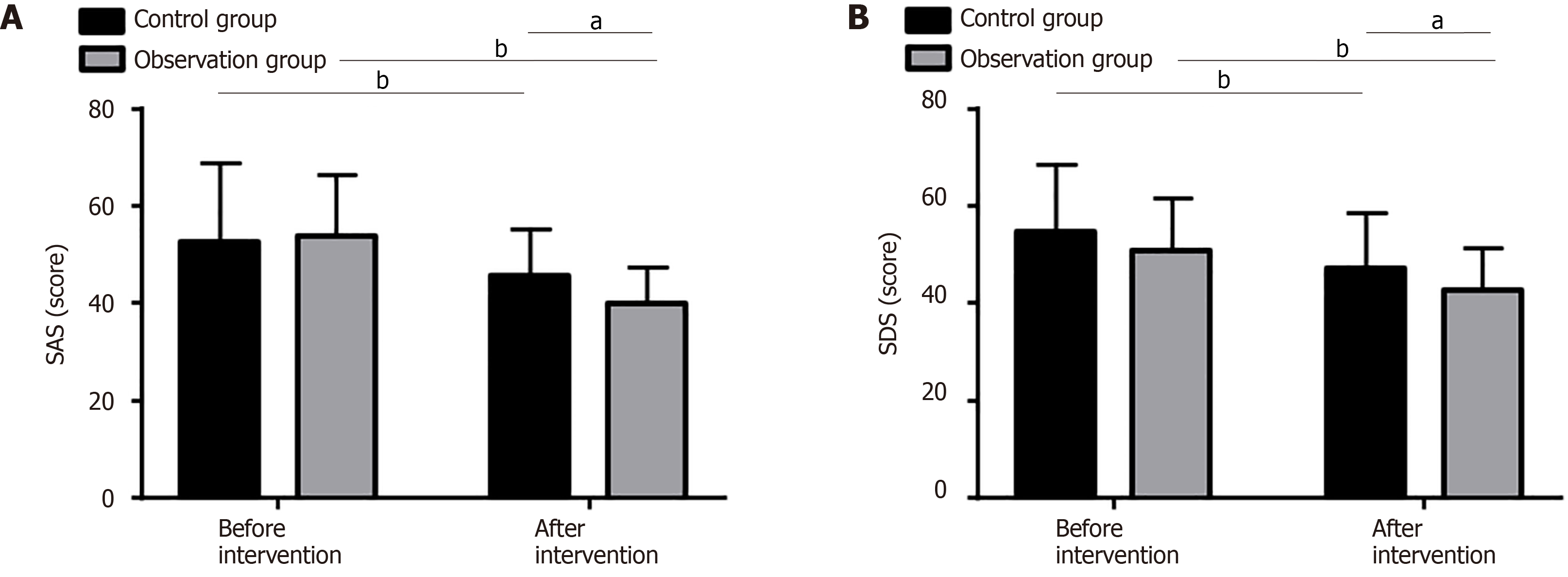
Figure 4 Psychological and emotional changes in two high-risk groups for stroke.
A: In the observation group, the self-rating anxiety scale score after intervention was significantly reduced compared to the pre-interventional level and the control group; B: The post-interventional self-rating depression scale score of the observation group was significantly reduced compared to the pre-interventional level and the control group. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. SAS: Self-rating anxiety scale; SDS: Self-rating depression scale.
- Citation: Wang J, Zhao CX, Tian J, Li YR, Ma KF, Du R, Li MK, Hu R. Effect of hospital-community-home collaborative health management on symptoms, cognition, anxiety, and depression in high-risk individuals for stroke. World J Psychiatry 2025; 15(3): 99152
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v15/i3/99152.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v15.i3.99152