Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Oct 19, 2024; 14(10): 1547-1557
Published online Oct 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i10.1547
Published online Oct 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i10.1547
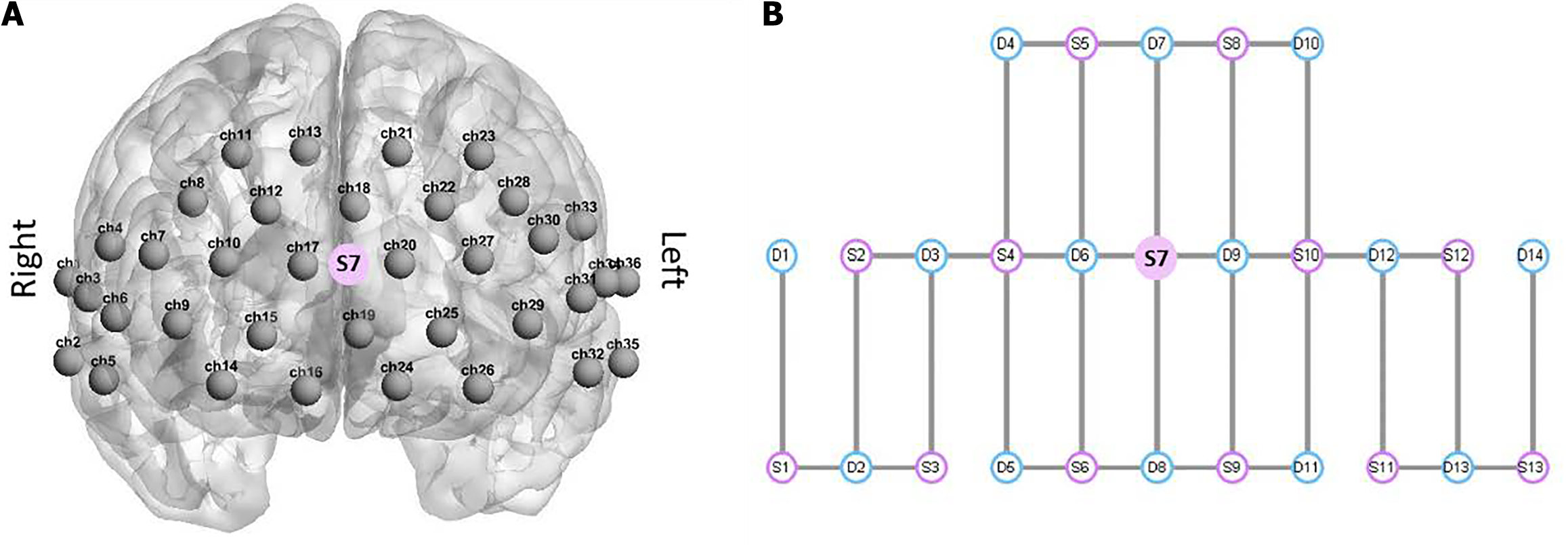
Figure 1 Overview of functional near-infrared spectroscopy channel positions and optode placement.
A: Spatial arrangement of 63 channels on a head template with channel numbers ranging from 1 to 36; B: Layout of the functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) sources and detectors, with the fNIRS source depicted in red and the detector shown in blue. Source 7 is positioned at the center of the layout design and corresponds to the frontal region of the brain, as indicated in A.
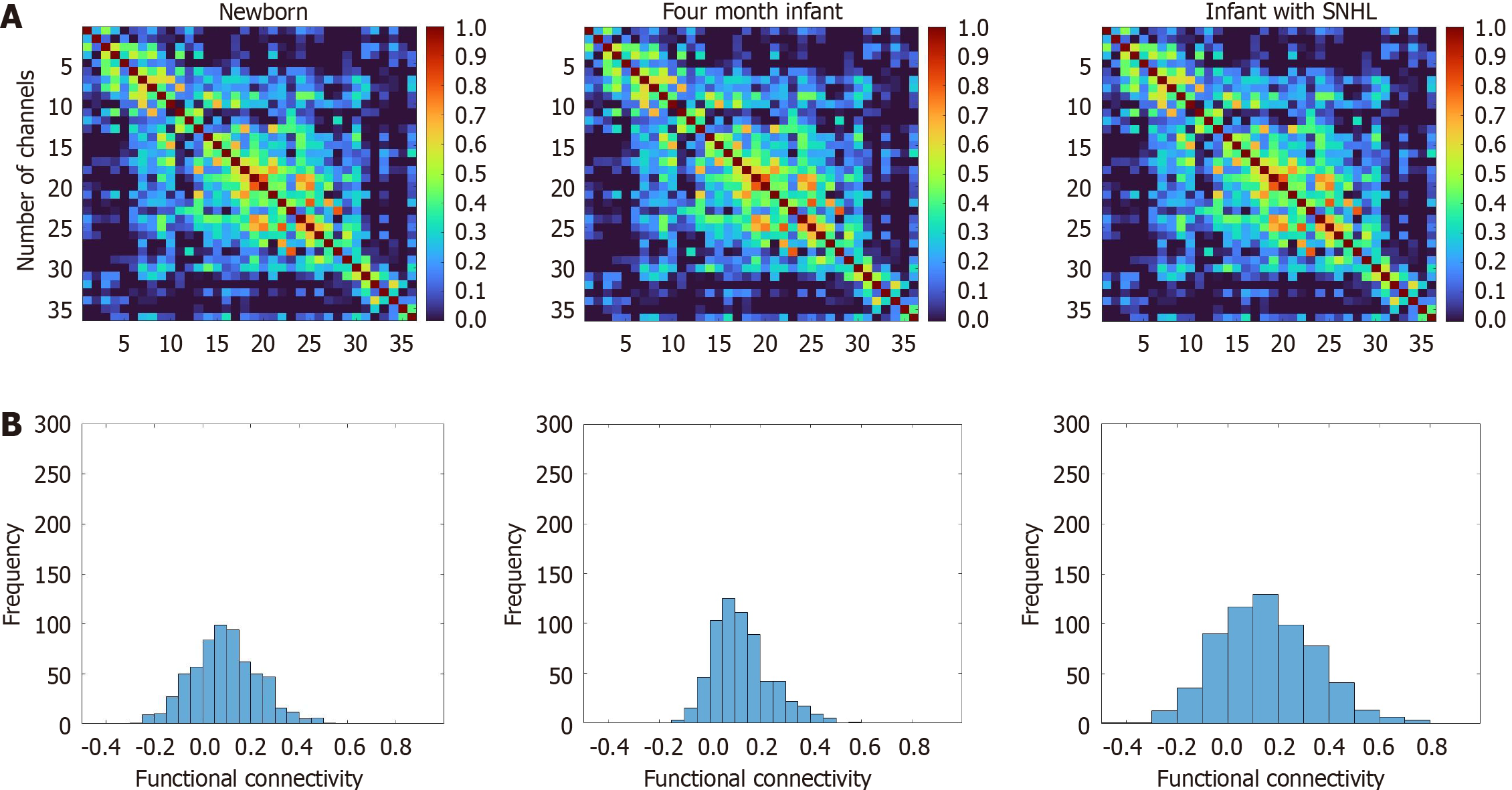
Figure 2 Tests for the newborn, 4-month sensorineural hearing loss, and 4-month healthy groups.
A: Average resting-state functional connectivity at the group level, as represented by correlation matrices with r value indices, for the newborn, 4-month sensorineural hearing loss, and 4-month healthy groups. The numerical values within these matrices denote the correlation strength between pairs of measurement channels; B: Z values of the correlations observed across the three distinct groups. SNHL: Sensorineural hearing loss.
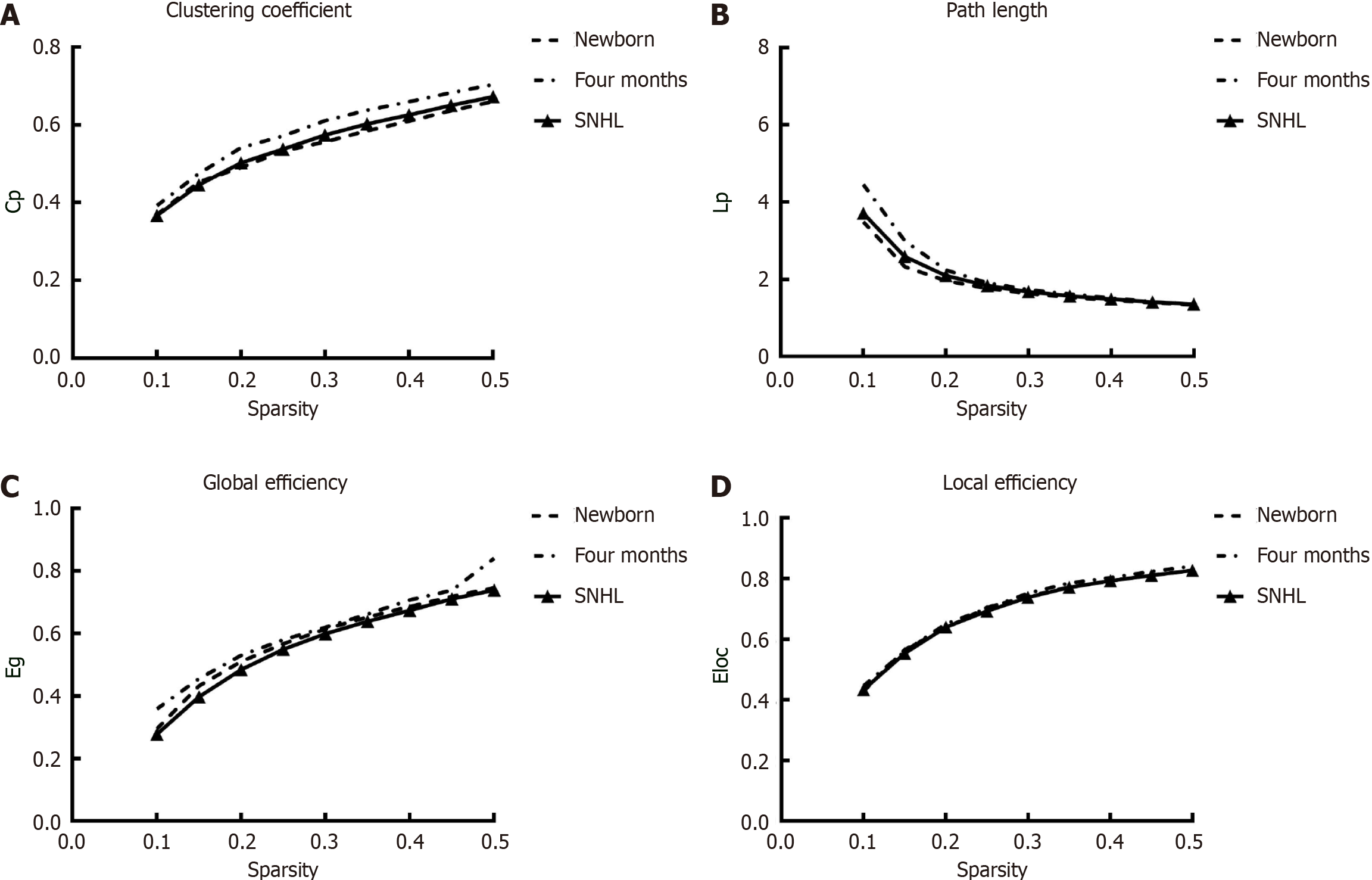
Figure 3 Global network metrics across a range of sparsity thresholds (1%-50%) for newborn and 4-month-old participants and the corresponding random networks.
A: Clustering coefficient; B: Path length; C: Global efficiency; D: Local efficiency. Cp: Clustering coefficient; Lp: Path length; Eg: Global efficiency; Eloc: Local efficiency; SNHL: Sensorineural hearing loss.
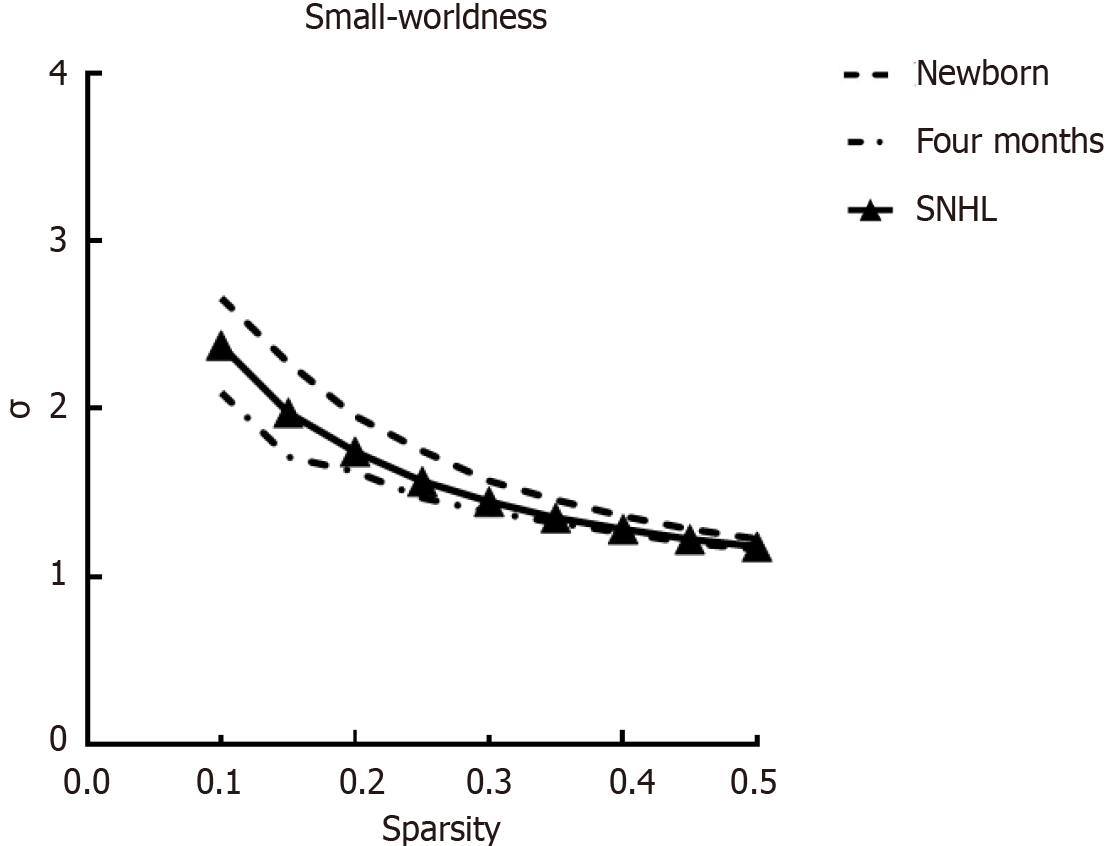
Figure 4 Global network index sigma across a range of sparsity thresholds (1%-50%) for newborns.
SNHL: Sensorineural hearing loss.
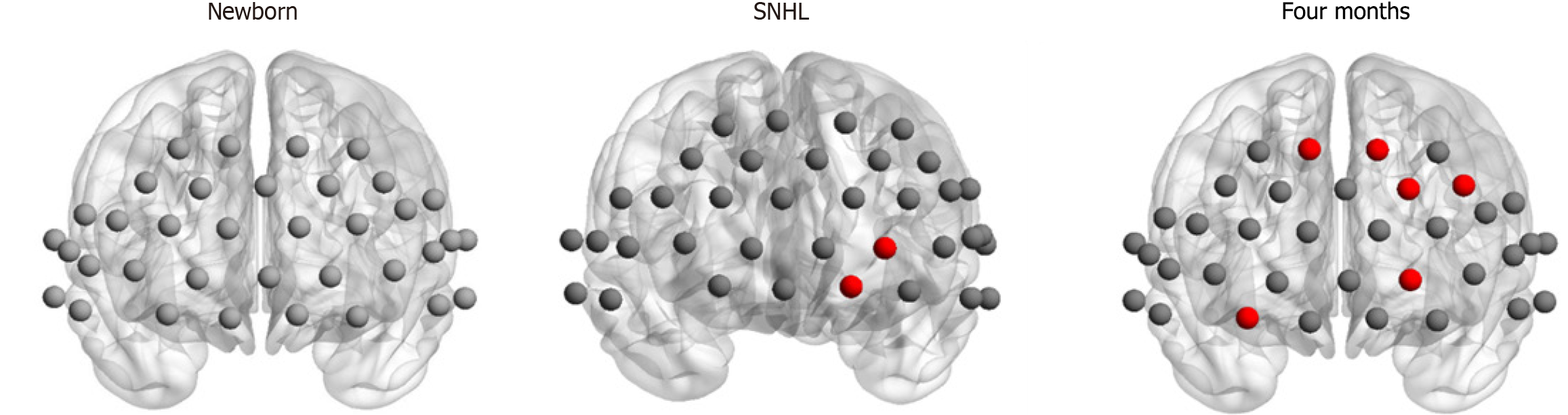
Figure 5 Network regional properties of newborn and 4-month-old participants with and without sensorineural hearing loss.
The red circles represent hubs identified in 4-month-old participants with and without sensorineural hearing loss (P < 0.05, corrected by false discovery rate). No hubs were identified in the newborns. SNHL: Sensorineural hearing loss.
- Citation: Tan J, Hou QM, Zhang F, Duan X, Zhang YL, Lee YJ, Yan H. Brain networks in newborns and infants with and without sensorineural hearing loss: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(10): 1547-1557
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i10/1547.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i10.1547