Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Psychiatry. Jan 19, 2024; 14(1): 15-25
Published online Jan 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.15
Published online Jan 19, 2024. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.15
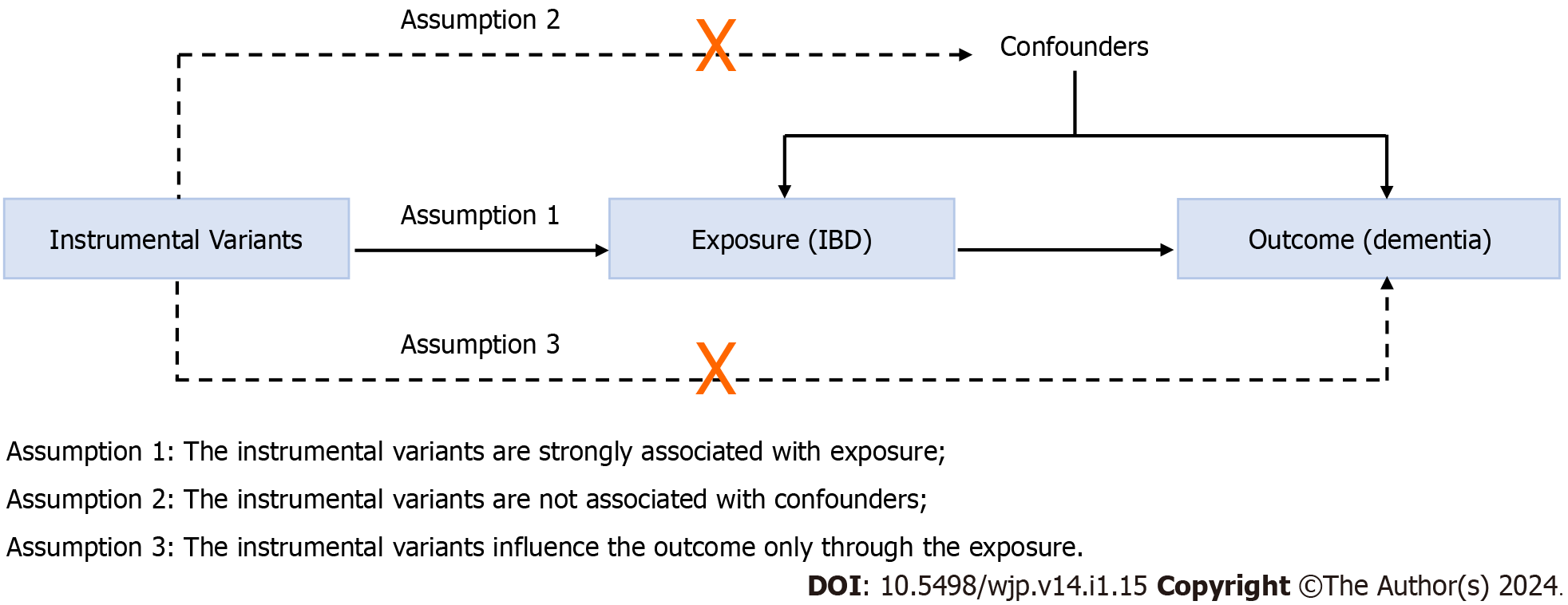
Figure 1 Diagram of the two-sample Mendelian randomization study for the associations of inflammatory bowel disease with dementia.
IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease.
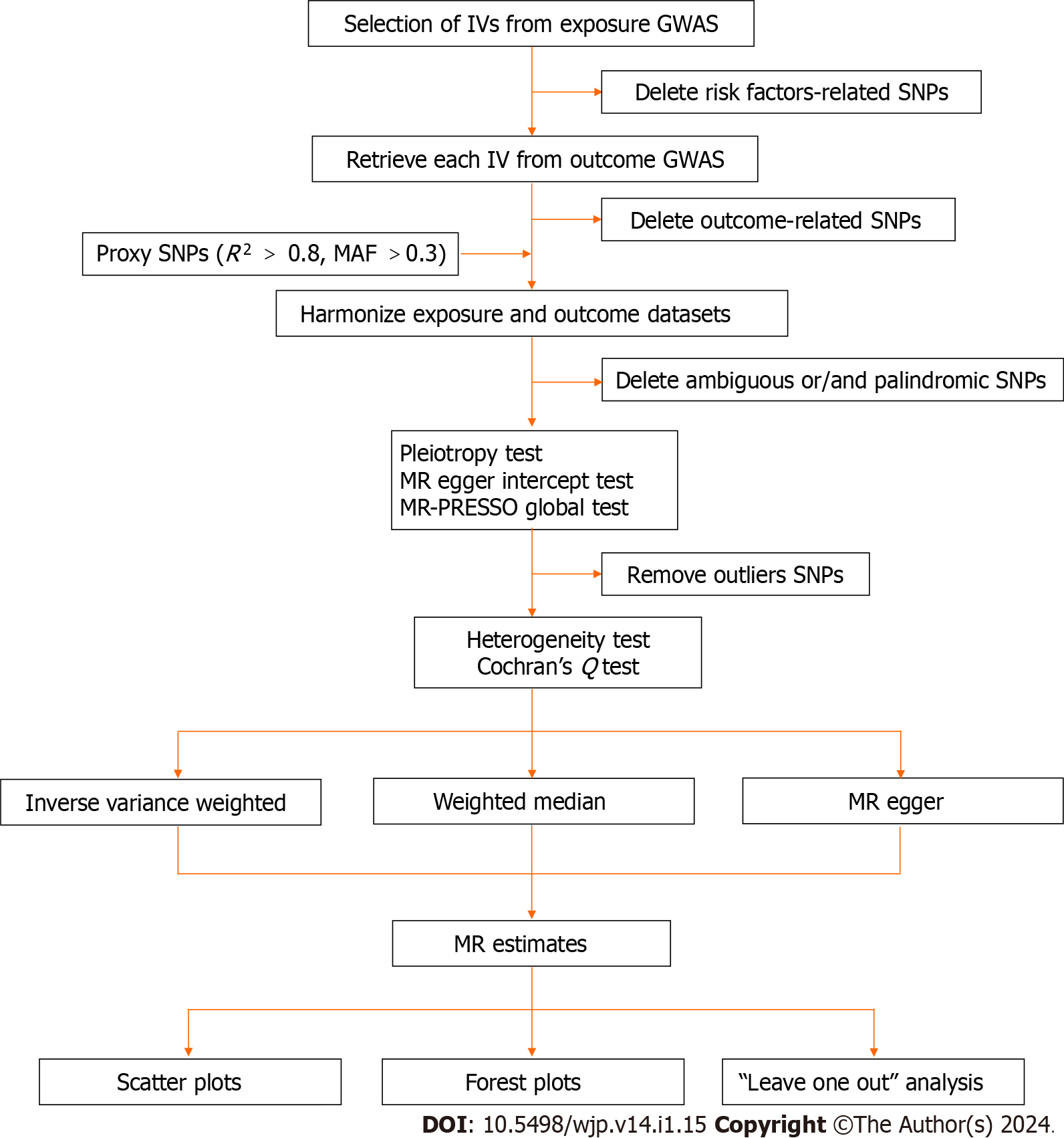
Figure 2 Flow chart of this Mendelian randomization study.
MR: Mendelian randomization; SNPs: Single nucleotide polymorphisms; GWAS: Genome-wide association study; IV: Instrumental variables.
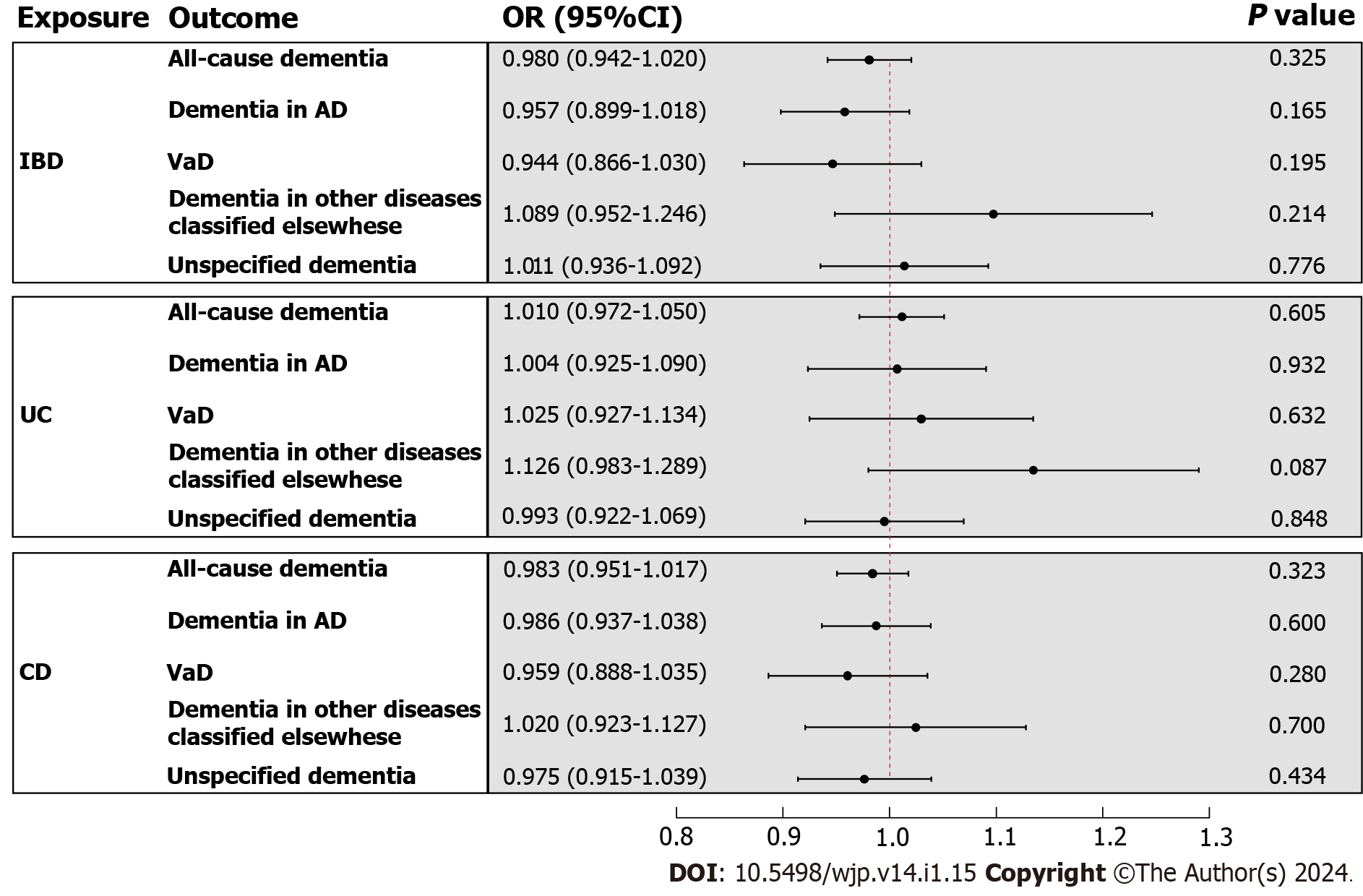
Figure 3 The inverse variance weighted estimates of inflammatory bowel disease on dementia.
The exposure is inflammatory bowel disease and subentities including ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, and the outcome is all-cause dementia and its subtypes including dementia in Alzheimer’s disease, vascular dementia, dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere, and unspecified dementia. The inverse variance weighted estimates, presented as odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals, are the summed ORs calculated from the individual instrumental variables. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; VaD: Vascular dementia; UC: Comprising ulcerative colitis; CD: Crohn's disease.
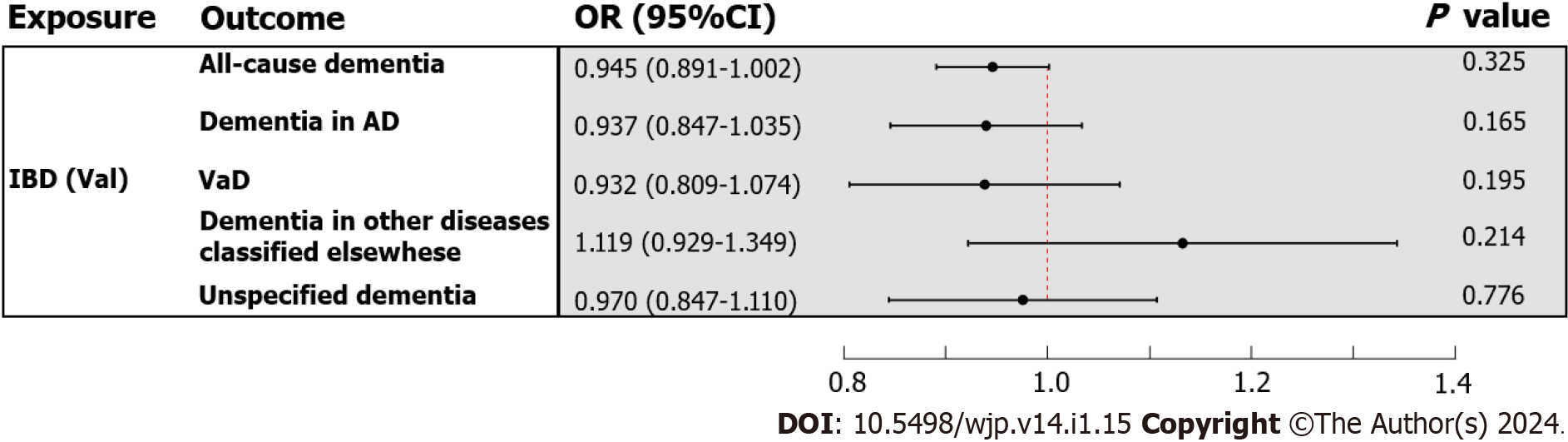
Figure 4 The inverse variance weighted estimates of inflammatory bowel disease (validation) on dementia.
The exposure is inflammatory bowel disease (validation), and the outcome is all-cause dementia and its four subtypes. The inverse variance weighted estimates, presented as odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence intervals, are the summed ORs calculated from the individual instrumental variables. IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; VaD: Vascular dementia.
- Citation: Liao OL, Xie SY, Ye J, Du Q, Lou GC. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and all-cause dementia: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. World J Psychiatry 2024; 14(1): 15-25
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v14/i1/15.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v14.i1.15