Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Psychiatry. Jun 19, 2023; 13(6): 340-350
Published online Jun 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i6.340
Published online Jun 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i6.340
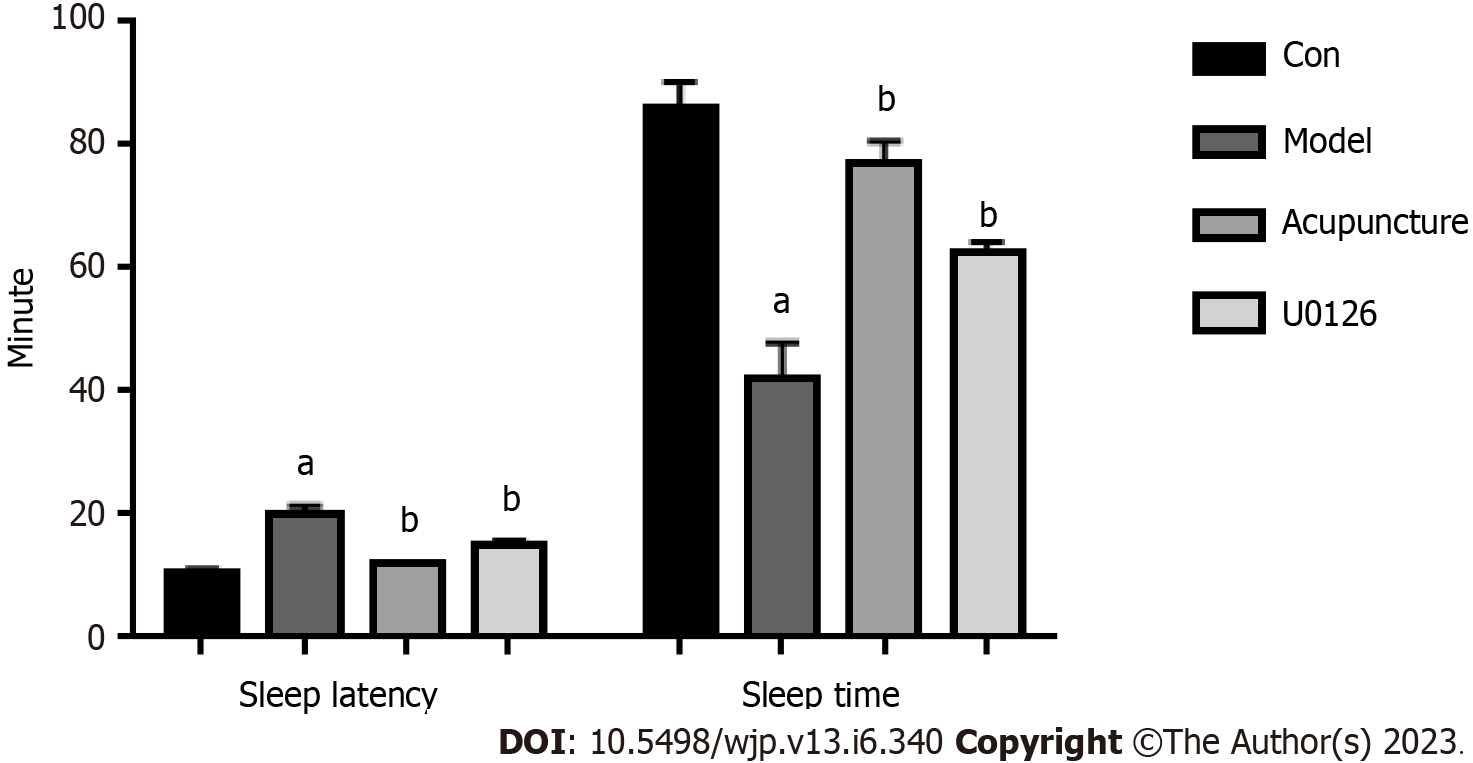
Figure 1 Effects of acupuncture at Back-Shu point on sleep latency and sleep duration in rats.
aP < 0.05, compared to the Con group; bP < 0.05, compared to the Model group.
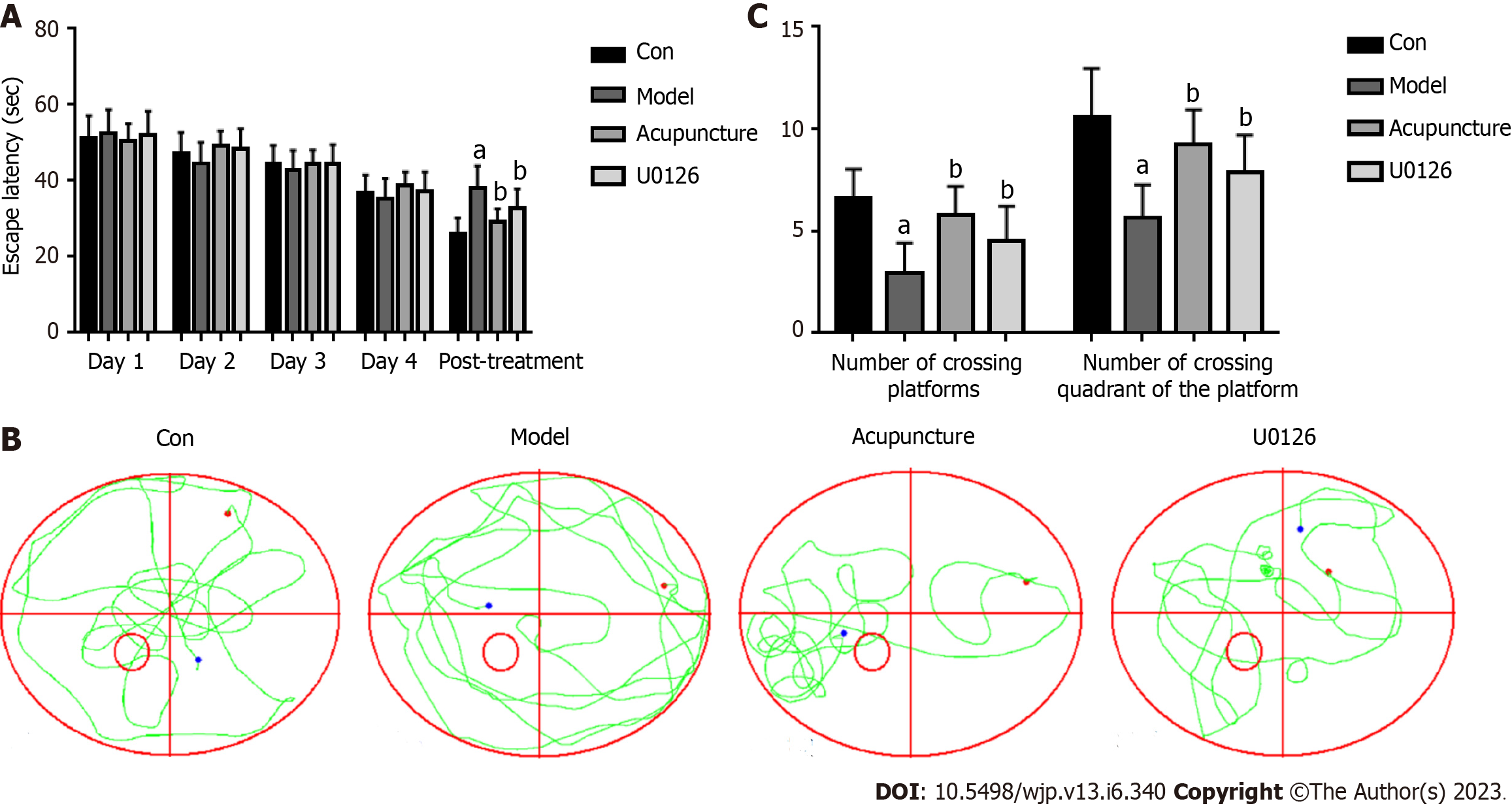
Figure 2 Effects of acupuncture at back-shu point on the behavior of rats.
A: Average escape latency of rats; B: Spatial exploration movement trajectories of rats; C: Spatial exploration results of rats. aP < 0.05, compared to the Con group; bP < 0.05, compared to the Model group.
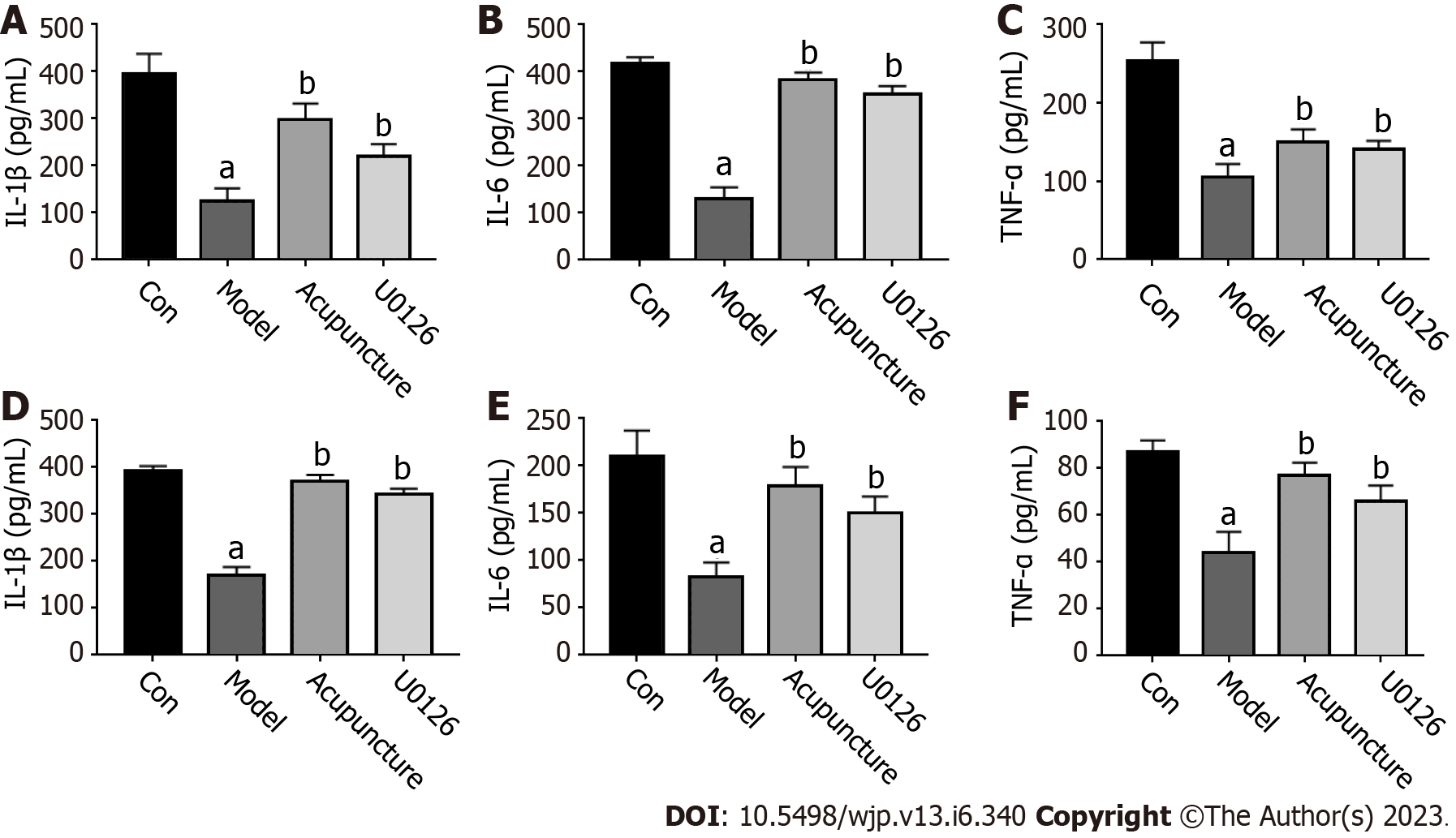
Figure 3 Acupuncture at Back-Shu point increased secretion of inflammatory cytokines in rats.
A-C: Secretion of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in serum; D-F: Secretion of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in rat hippocampus. aP < 0.05, compared to the Con group; bP < 0.05, compared to the Model group.
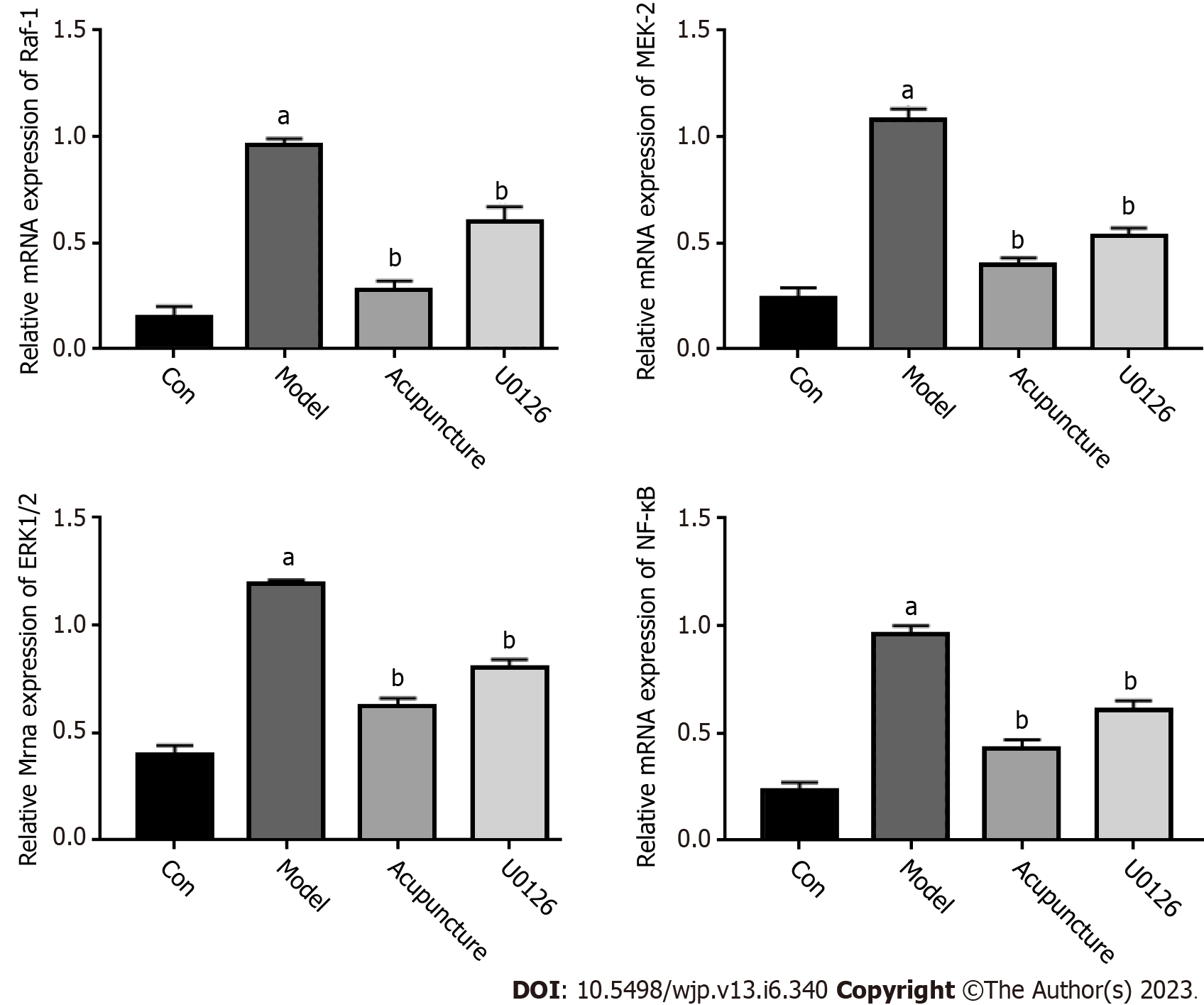
Figure 4 Relative mRNA expression levels of RAF-1, MEK-2, ERK1/2 and NF-κB in rat hippocampus.
aP < 0.05, compared to the Con group; bP < 0.05, compared to the Model group.
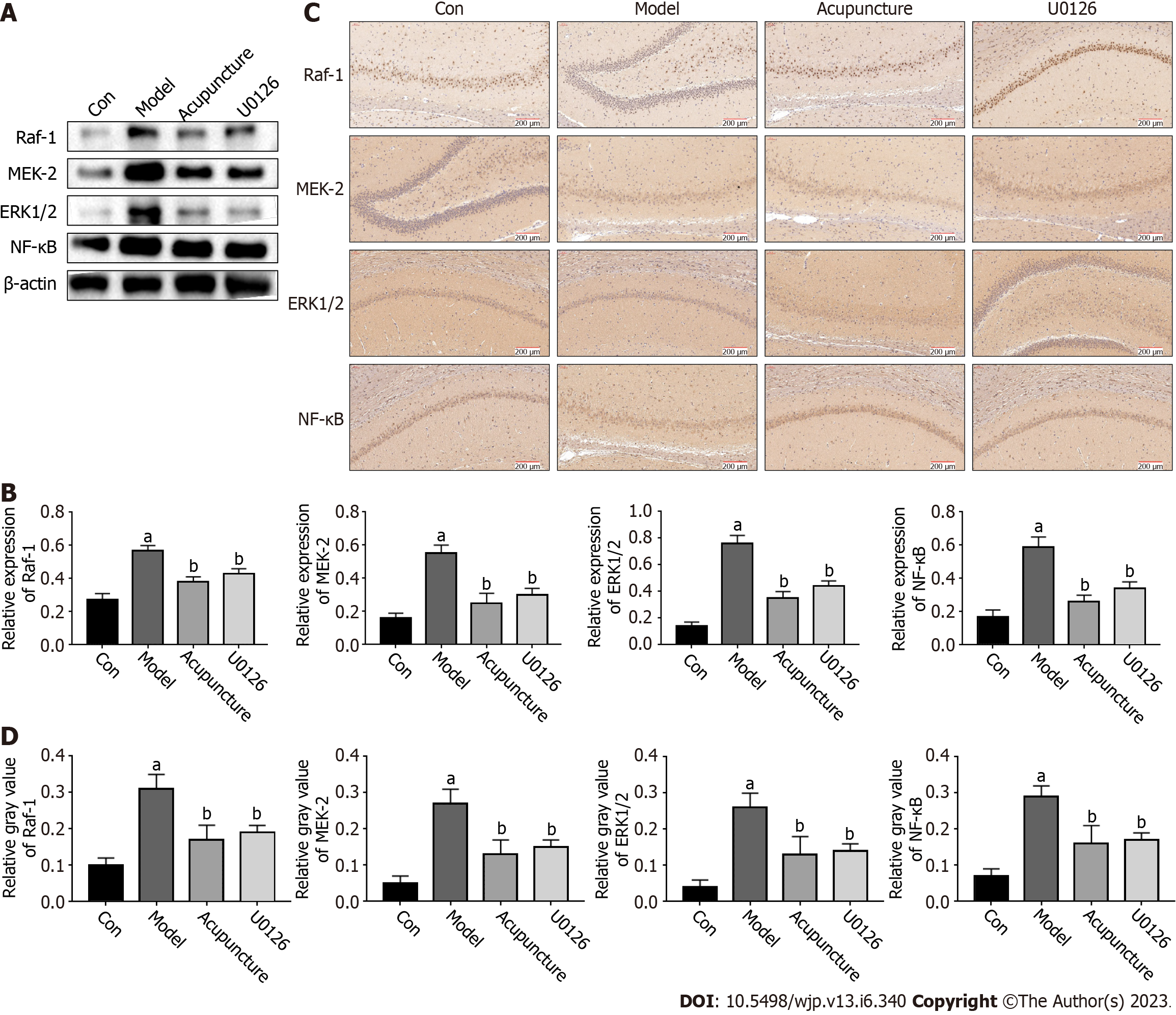
Figure 5 Acupuncture at Back-Shu point inhibited the ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway in rats.
A: The expression of ERK/NF-κB pathway-related proteins in rat hippocampus was detected by western blot; B: The relative protein expression level of RAF-1, MEK-2, ERK1/2 and NF-κB in rat hippocampus; C: The expression levels of ERK/NF-κB pathway-related proteins in the hippocampus in rats were detected by immunohistochemistry, scale bars = 100 μm (× 200); D: The gray values of RAF-1, MEK-2, ERK1/2 and NF-κB. aP < 0.05, compared to the Con group; bP < 0.05, compared to the Model group.
- Citation: Zhang MM, Zhao JW, Li ZQ, Shao J, Gao XY. Acupuncture at Back-Shu point improves insomnia by reducing inflammation and inhibiting the ERK/NF-κB signaling pathway. World J Psychiatry 2023; 13(6): 340-350
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v13/i6/340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v13.i6.340