Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Psychiatry. Oct 19, 2023; 13(10): 753-762
Published online Oct 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i10.753
Published online Oct 19, 2023. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v13.i10.753
Figure 1 Research ideas.
ACT: Acceptance and commitment therapy; ECBE: Enabling cognitive-behavioral education; AAQ-II: Action Questionnaire-2nd Edition; SAS: Self-Rating Anxiety Scale; SDS: Self-Rating Depression Scale; PSQI: Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index; ESCA: Exercise of Self-Care Agency Scale.
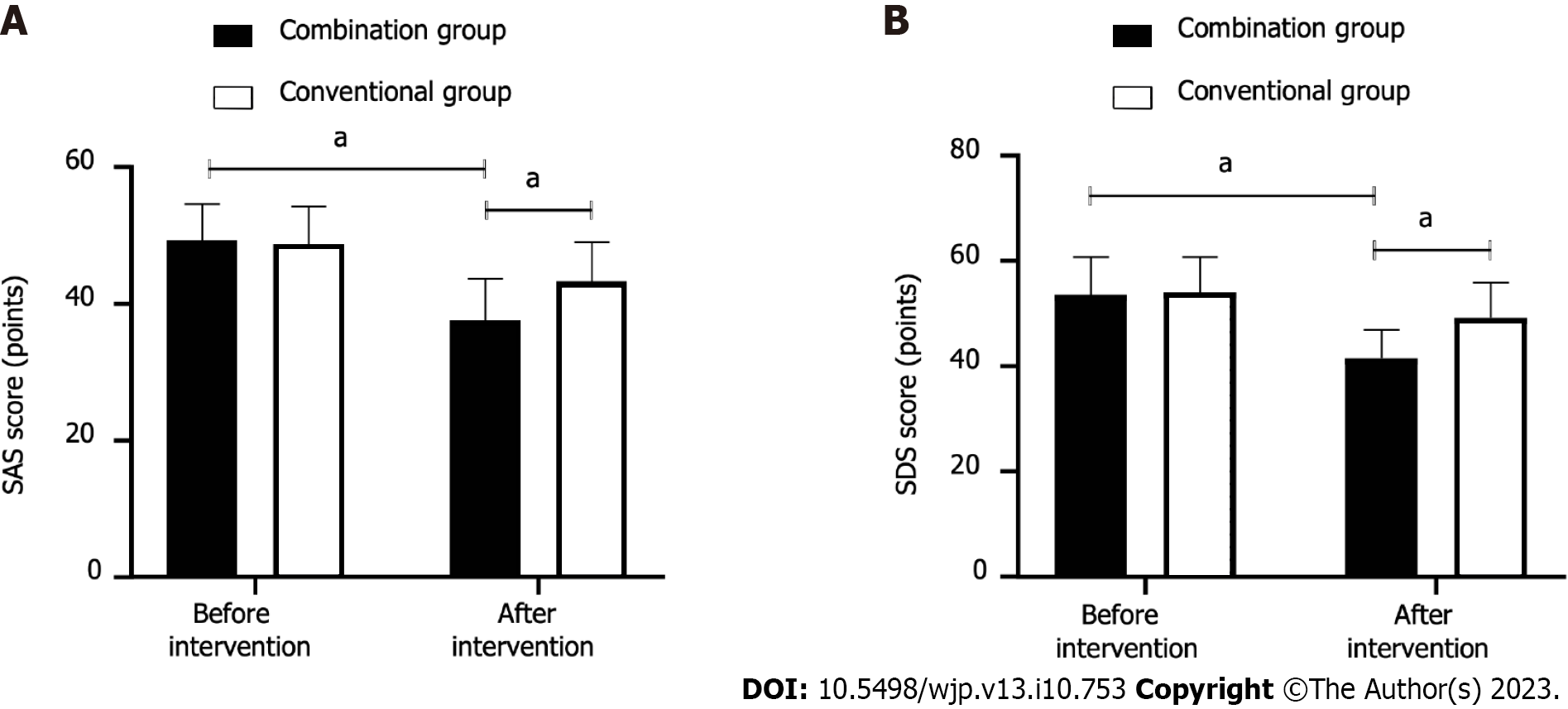
Figure 2 Self-Rating Anxiety Scale score and Self-Rating Depression Scale score.
A: The post-intervention Self-Rating Anxiety Scale score (t = 5.445); B: Self-Rating Depression Scale score (t = 7.076) in the combination group were lower than those in the conventional group (both P < 0.001). aP < 0.05. SAS: Self-Rating Anxiety Scale; SDS: Self-Rating Depression Scale.
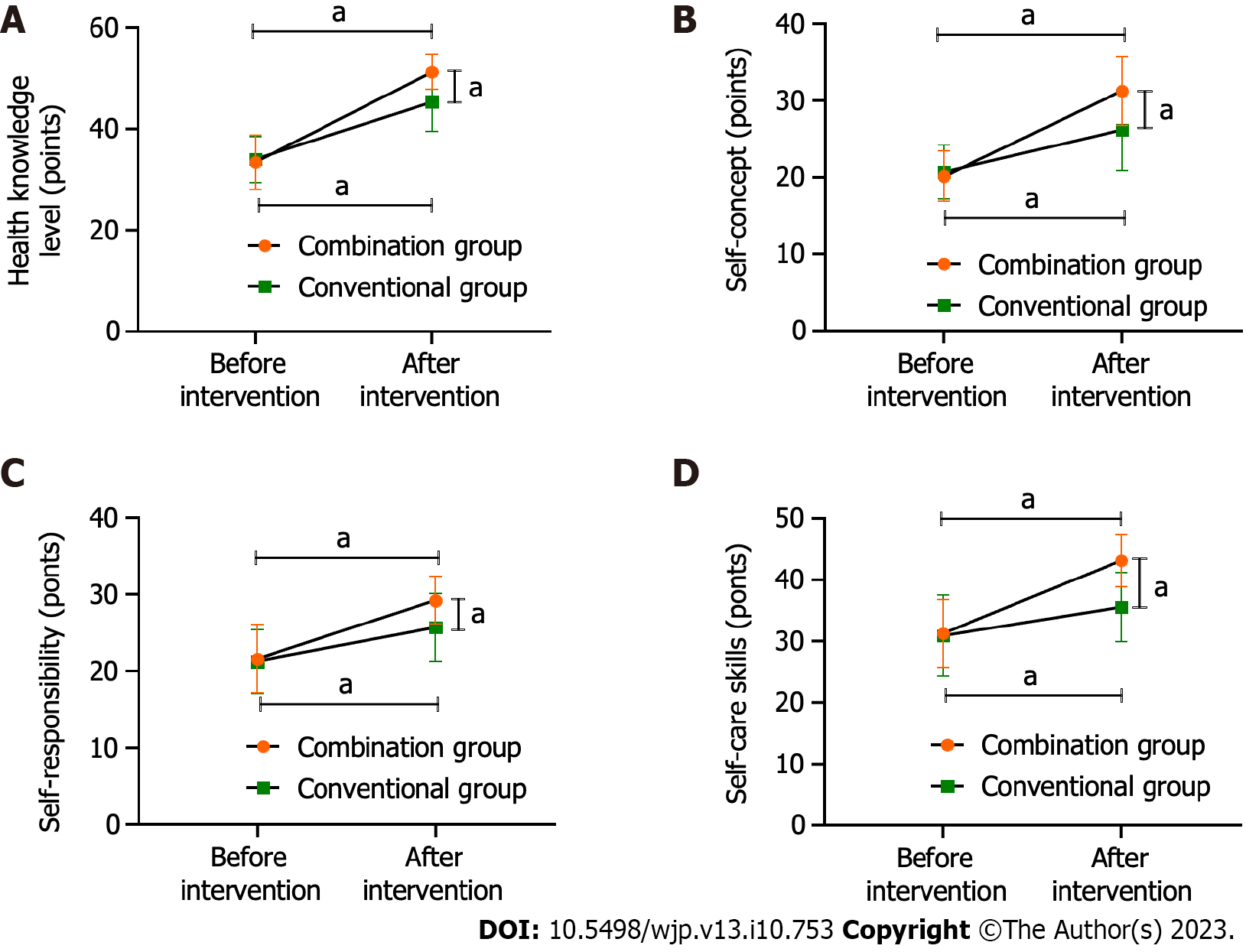
Figure 3 Exercise of Self-Care Agency Scale score.
A: Health knowledge level; B: Self-concept; C: Self-responsibility; D: Self-care skills. The post-interventions scores of each dimension in the combined group were lower than those in the combination group. aP < 0.05.
- Citation: Zheng Y, Wang XW, Xia CX. Effects of different intervention methods on psychological flexibility, negative emotions and sleep quality in chronic hepatitis B. World J Psychiatry 2023; 13(10): 753-762
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v13/i10/753.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v13.i10.753