Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Psychiatr. Mar 19, 2021; 11(3): 73-86
Published online Mar 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i3.73
Published online Mar 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i3.73
Figure 1 Experimental setup for capturing eye-movement data.
Figure 2 Disease–neutral picture, disease–positive picture, and disease–threat picture presentation examples.
A: Disease–neutral (e.g., oral surgery vs rail); B: Disease–positive (e.g., infusion vs scenery); and C: Disease–threat (e.g., operating room vs traffic).
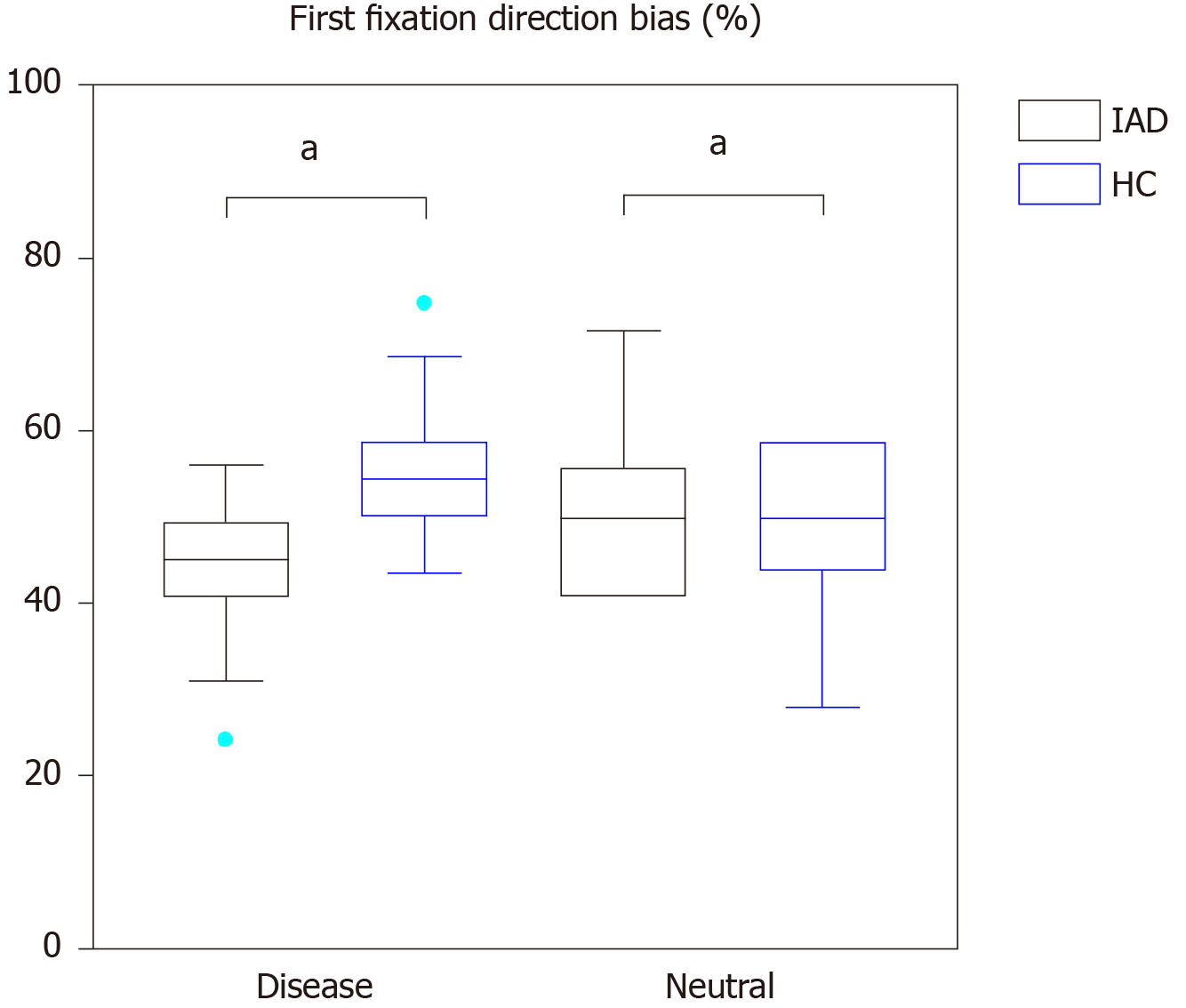
Figure 3 First-fixation direction bias of illness anxiety disorder and healthy subjects when presented with disease-related and neutral image pairs.
HC: Healthy control; IAD: Illness anxiety disorder. aP < 0.05.
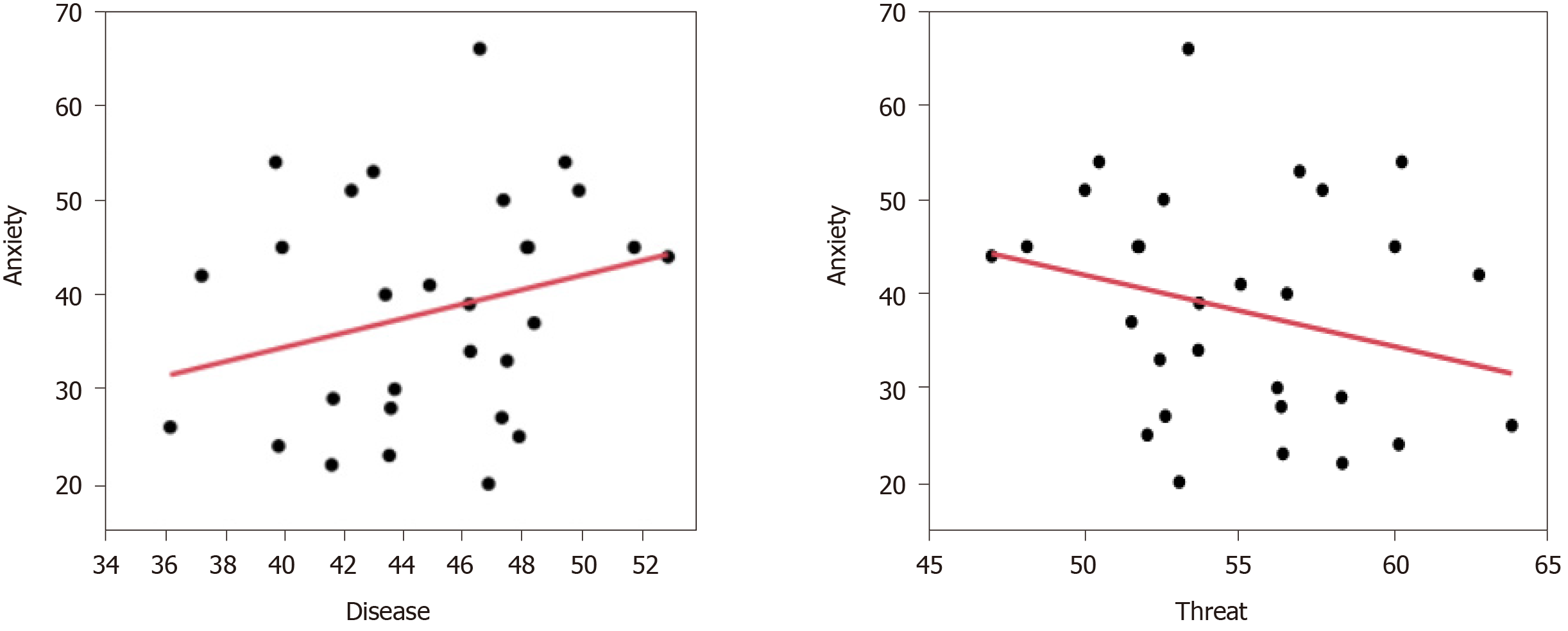
Figure 4 Total gaze duration to disease and threat in disease–threat image pairs.
- Citation: Zhang YB, Wang PC, Ma Y, Yang XY, Meng FQ, Broadley SA, Sun J, Li ZJ. Using eye movements in the dot-probe paradigm to investigate attention bias in illness anxiety disorder. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(3): 73-86
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i3/73.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i3.73