Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Psychiatr. Nov 19, 2021; 11(11): 981-996
Published online Nov 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.981
Published online Nov 19, 2021. doi: 10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.981
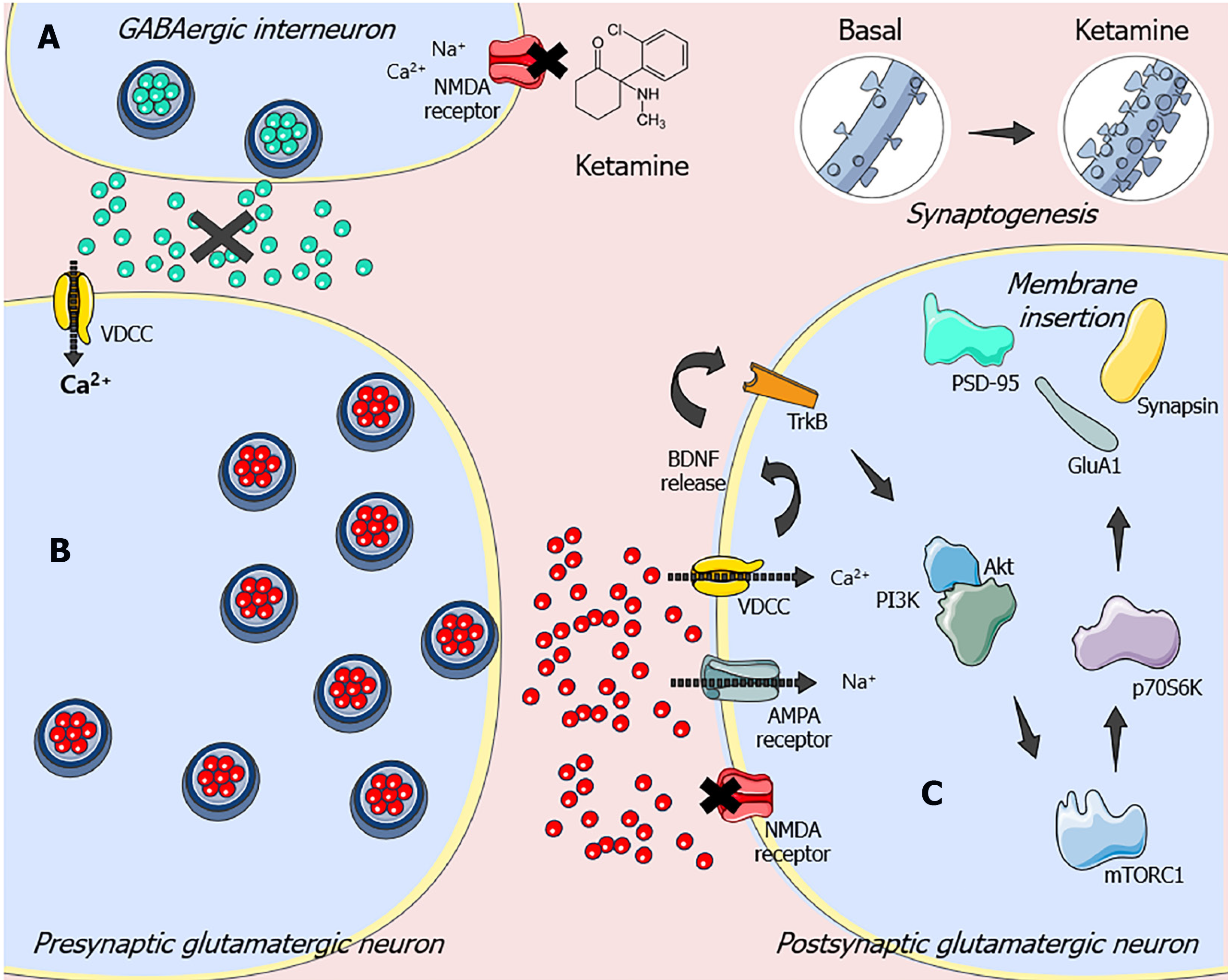
Figure 1 Supposed intracellular signaling pathway implicated in ketamine’s antidepressant-like effects.
A: Ketamine antagonizes N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors in GABAergic interneurons, which in turn attenuate the inhibitory action of this system on glutamatergic tonus. Subsequently, the disinhibition of pyramidal cells results in a burst of glutamatergic transmission; B: The glutamate released in the synaptic cleft preferentially stimulates alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-methyl-5-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptors, which promotes a transient sodium influx that depolarizes the neurons and activates voltage-dependent calcium channels. C: This event causes the exocytosis of synaptic vesicles containing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the synaptic cleft[16,122]. BDNF culminates in protein kinase B activation that can phosphorylate and activate mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1). In turn, mTORC1 phosphorylates the 70-kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase at Thr389, which regulates synaptic protein synthesis such as AMPA receptor subunit 1 and postsynaptic density-95, which contribute to dendritic spine formation and synaptogenesis[17,13]. NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartic acid; AMPA: Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-methyl-5-4-isoxazole propionic acid; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; VDCC: Voltage-dependent calcium channels; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; TrkB: Tropomyosin receptor kinase B; GluA1: Glutamate AMPA receptor subunit 1; mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; PSD-95: postsynaptic density protein-95 kDa.
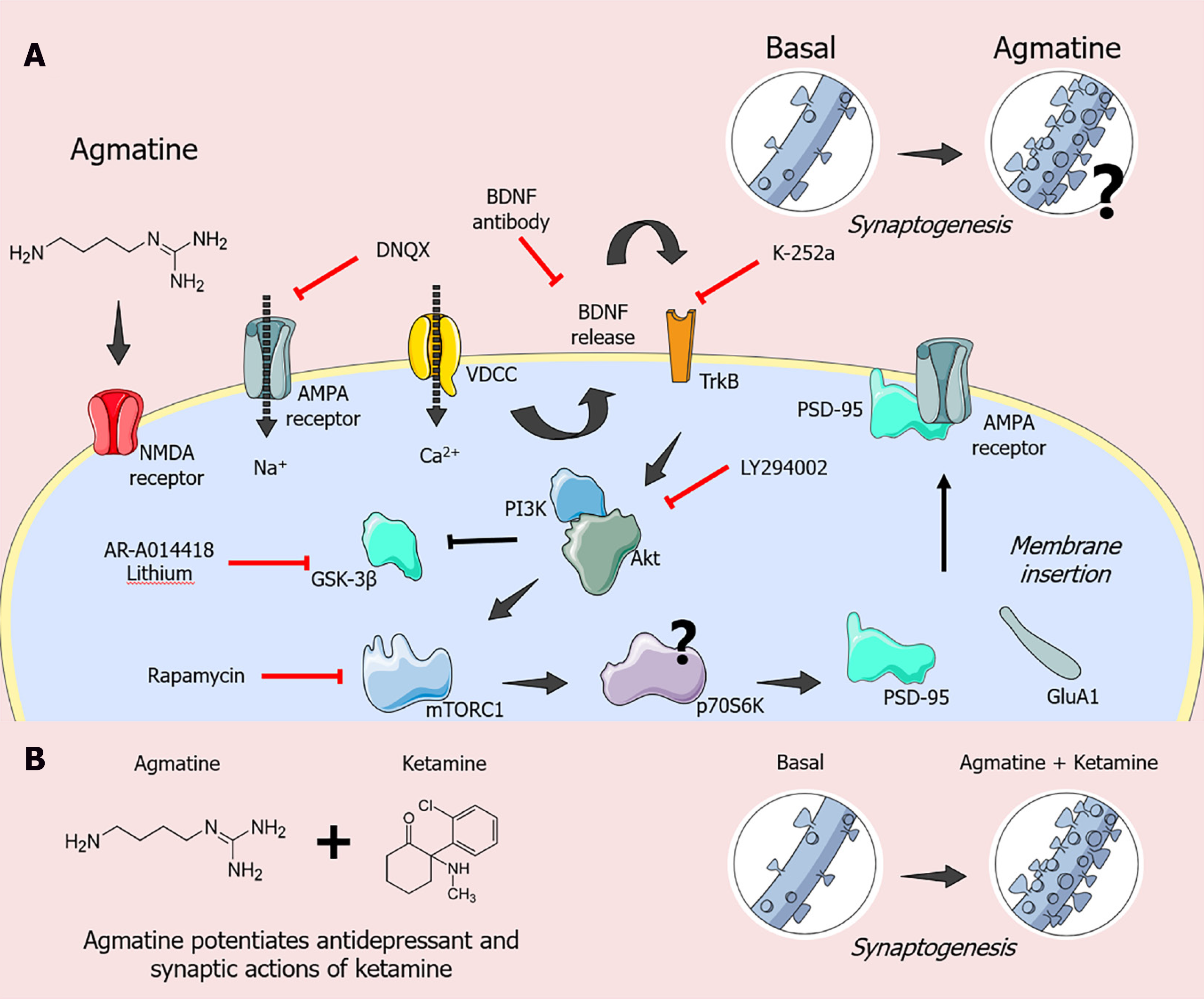
Figure 2 Putative signaling pathways implicated in the rapid-acting antidepressant-like effects of agmatine.
A: The antidepressant-like effect elicited by the acute administration of agmatine in the tail suspension test appears to involve inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptors since it enhanced the antidepressant potency of MK-801 (an NMDA receptor antagonist) by up to 100-fold[60]. Moreover, agmatine's antidepressant-like effect in the tail suspension test is dependent on the activation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-methyl-5-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) and tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) receptors since the administration of 6,7-dinitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (DNQX; an AMPA receptor antagonist) or K-252a (a TrkB receptor antagonist) completely abolished its antidepressant-like response. The antibody anti-brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) also abolished the antidepressant-like effect elicited by agmatine in the tail suspension test[46]. Of note, the antidepressant-like effect of agmatine is also dependent on phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/ glycogen synthase kinase-3β/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling. In particular, the administration of LY294002 (a PI3K inhibitor) or rapamycin (a selective mTOR inhibitor) completely abrogated the behavioral responses of agmatine in the tail suspension test. The combined treatment with a sub-effective dose of agmatine and lithium chloride (10 mg/kg, po; a non-selective GSK-3β inhibitor) or AR-A014418 (a selective GSK-3β inhibitor) produced an antidepressant-like effect in the tail suspension test[46]. Importantly, these behavioral responses were accompanied by an increase in the BDNF, glutamate AMPA receptor subunit 1 and postsynaptic density protein-95 kDa immunocontent in the prefrontal cortex of the mice[46]; B: Reinforcing the notion that ketamine and agmatine share common behavioral responses and molecular targets, the ability of agmatine to potentiate the antidepressant and synaptic actions of ketamine was also demonstrated[47]. In particular, the combined administration of subthreshold doses of agmatine and ketamine produced a fast (starting in 1 h) and sustained (lasting up to 7 d) antidepressant-like effect in the tail suspension test. These behavioral responses were associated with stimulation of the Akt/70-kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase signaling pathway and increased synaptic protein synthesis in the prefrontal cortex in a time-dependent manner. More importantly, the combined administration of sub-effective doses of agmatine and ketamine raised the dendritic arbor and spine densities and effectively remodeled the dendritic spinal architecture in the prefrontal cortex[47]. NMDA: N-methyl-D-aspartic acid; AMPA: Alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-methyl-5-4-isoxazole propionic acid; BDNF: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor; VDCC: Voltage-dependent calcium channels; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; TrkB: Tropomyosin receptor kinase B; GluA1: Glutamate AMPA receptor subunit 1; mTORC1: mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; PSD-95: postsynaptic density protein-95 kDa; GSK-3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β.
- Citation: Valverde AP, Camargo A, Rodrigues ALS. Agmatine as a novel candidate for rapid-onset antidepressant response. World J Psychiatr 2021; 11(11): 981-996
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3206/full/v11/i11/981.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v11.i11.981