Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Pharmacol. Jan 30, 2019; 8(2): 14-25
Published online Jan 30, 2019. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v8.i2.14
Published online Jan 30, 2019. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v8.i2.14
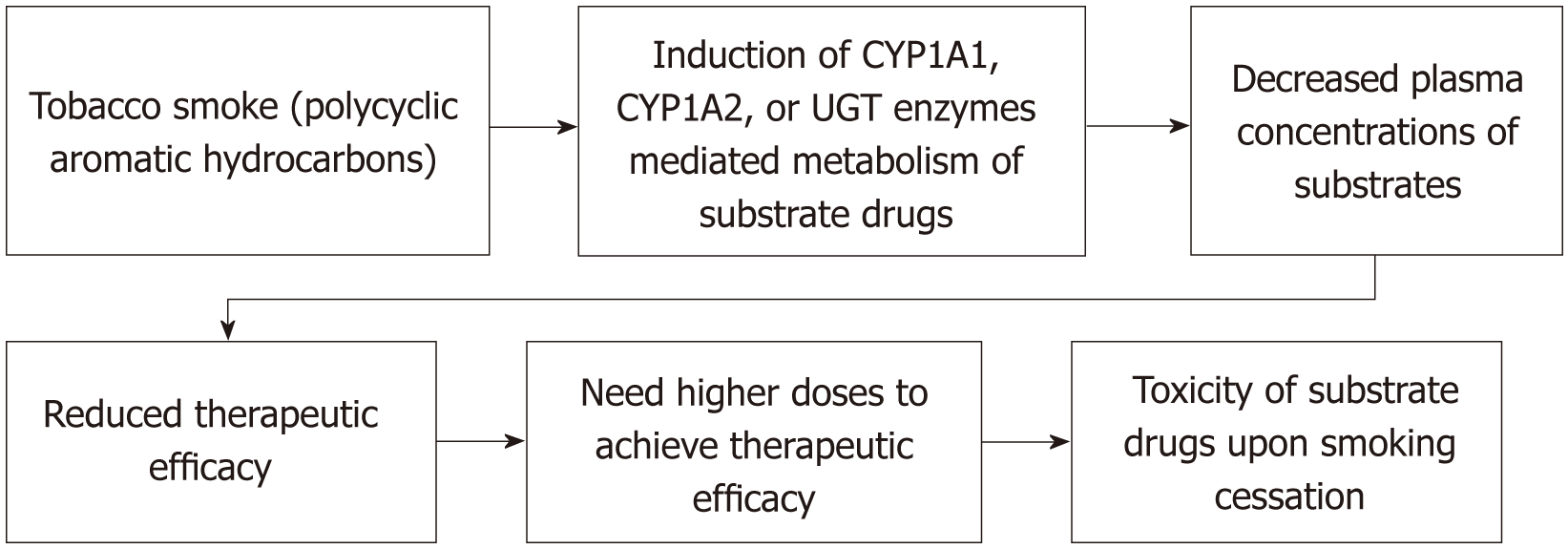
Figure 1 Pharmacokinetic drug interactions of smoking.
Main mechanisms contributing to hyperkalemia with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEi)/angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) include decreased aldosterone concentrations, decreased delivery of sodium to the distal nephron, abnormal collecting tubule function, and excessive potassium intake Main mechanisms contributing to hyperkalemia with ACEi/ARB include decreased aldosterone concentrations, decreased delivery of sodium to the distal nephron, abnormal collecting tubule function, and excessive potassium intake Main mechanisms contributing to hyperkalemia with ACEi/ARB include decreased aldosterone concentrations, decreased delivery of sodium to the distal nephron, abnormal collecting tubule function, and excessive potassium intake.
- Citation: Maideen NMP. Tobacco smoking and its drug interactions with comedications involving CYP and UGT enzymes and nicotine. World J Pharmacol 2019; 8(2): 14-25
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v8/i2/14.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v8.i2.14