Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Pharmacol. Dec 9, 2013; 2(4): 107-114
Published online Dec 9, 2013. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v2.i4.107
Published online Dec 9, 2013. doi: 10.5497/wjp.v2.i4.107
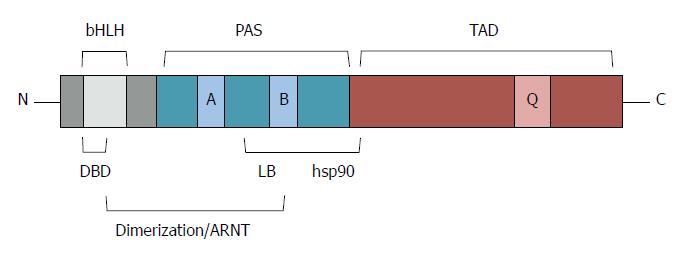
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the functional domains of aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
bHLH: Basic helix loop helix; PAS: Per-Arnt-Sim; TAD: Transcription activation domain; Q: Glutamine-rich region; DBD: DNA binding domain; LB: Ligand binding domain; ARNT: AhR nuclear translocator.
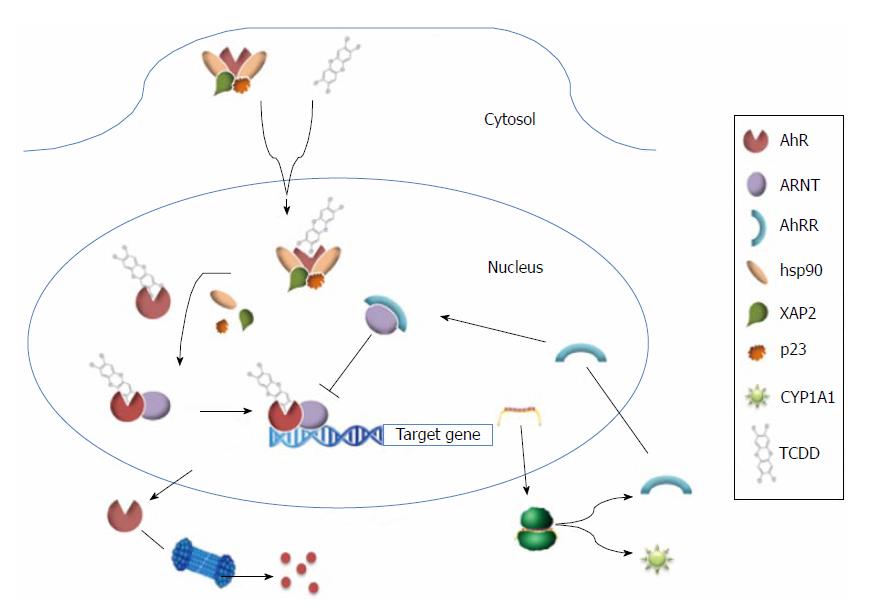
Figure 2 Model of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling pathway.
Upon binding of a ligand to aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) [such as 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin(TCDD)], the nuclear localization signal of AhR is then exposed, and AhR is translocated to the nucleus where dimerizes with AhR nuclear-translocator (ARNT) protein and dissociates from a chaperone complex composed of X-associated protein (XAP2), hsp90, and p23. Then it binds xenobiotic-responsive elements, and up regulates expression of its target genes. AhR subsequently dissociates from ARNT and translocates to the cytosol where it undergoes proteosome-mediated degradation. AhRR: AhR repressor.
- Citation: Vega L, Elizondo G. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a new therapeutic target for cancer and immune disorders. World J Pharmacol 2013; 2(4): 107-114
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2220-3192/full/v2/i4/107.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5497/wjp.v2.i4.107